自动化运维Ansible之Playbook剧本
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了自动化运维Ansible之Playbook剧本相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Playbook介绍
Playbook是由一个或多个play组成的列表,主要功能是将task定义好的角色并为一组进行统一管理,也就是通过task调用Ansible的模板将多个play组织在一个Playbook中运行
Playbook本身由以下各部分组成:
- Tasks:任务,调用模块完成的某操作
- Variables:变量
- Templates:模板
- Handlers:处理器 ,当某条件满足时,触发执行的操作
- Roles:角色
执行一个playbook
ansible-playbook [yaml文件名]
例如:ansible-playbook ping.yaml参数:-k(–ask-pass) 用来交互输入ssh密码
-K(-ask-become-pass) 用来交互输入sudo密码
-u 指定用户补充命令:
ansible-playbook nginx.yaml --syntax-check #检查yaml文件的语法是否正确
ansible-playbook nginx.yaml --list-task #检查tasks任务
ansible-playbook nginx.yaml --list-hosts #检查生效的主机
ansible-playbook nginx.yaml --start-at-task=‘Copy Nginx.conf‘ #指定从某个task开始运行hosts和users介绍
Playbook的设计目的是为了让某个或某些主机以某个用户的身份去执行相应的任务。其中用于指定要执行指定任务的主机用hosts定义,可以是一个主机也可以是由冒号分隔的多个主机组;用于指定被管理主机上执行任务的用户用remote_ser来定义。
- hosts: xxy //指定主机组,可以是一个或多个组。
remote_user: root //指定远程主机执行的用户名还可以为每个任务定义远程执行用户:
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: test connection
ping:
remote_user: zhangsan //指定远程主机执行tasks的运行用户为zhangsan指定远程主机sudo切换用户:
vim sudo.yaml
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
become: yes //2.6版本以后的参数,之前是sudo,意思为切换用户运行
become_user: zhangsan //指定sudo用户为zhangsan
执行:ansible-playbook sudo.yaml -Ktasks列表和action
- Play的主体部分是task列表,task列表中的各任务按次序逐个在hosts中指定的主机上执行,即在所有主机上完成第一个任务后再开始第二个任务。在运行playbook时(从上到下执行),如果一个host执行task失败,整个tasks都会回滚,请修正playbook中的错误,然后重新执行即可。Task的目的是使用指定的参数执行模块,而在模块参数中可以使用变量,模块执行时幂等的,这意味着多次执行是安全的,因为其结果一致。
- 每一个task必须有一个名称name,这样在运行playbook时,从其输出的任务执行信息中可以很好的辨别出是属于哪一个task的。如果没有定义name,‘action’的值将会用作输出信息中标记特定的task。
- 定义一个task,常见的格式:”module: options” 例如:yum: name=httpd
- ansible的自带模块中,command模块和shell模块无需使用key=value格式
小示例:
vim http.yaml
- hosts: 192.168.1.25
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: disable selinux
command: ‘/sbin/setenforce 0‘
- name: make sure apache is running
service: name=httpd state=started
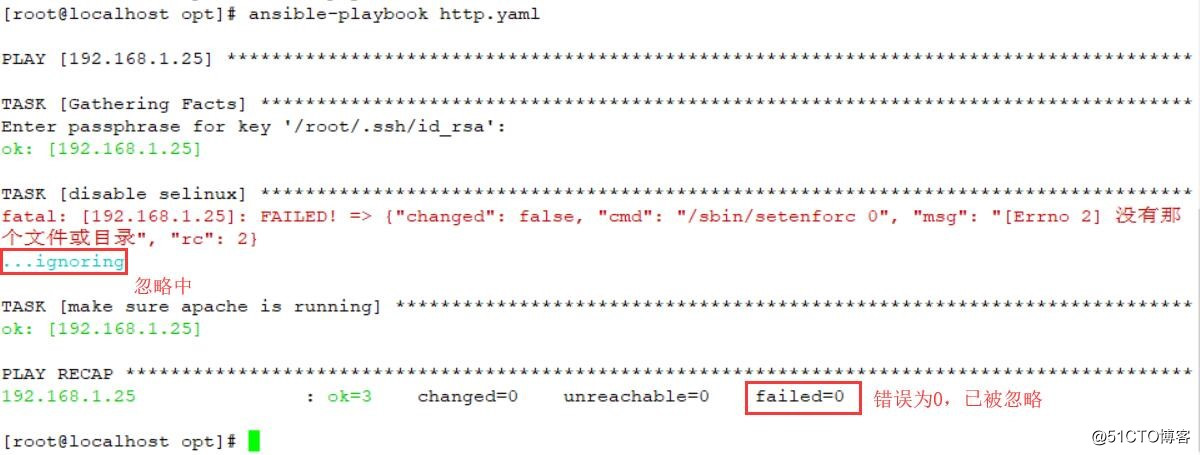
ansible-playbook http.yaml 正常执行
修改如下
- hosts:192.168.1.25
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: disable selinux
command: ‘/sbin/setenforc 0‘ //故意写错setenforc
ignore_errors: True //忽略错误,强制返回成功
- name: make sure apache is running
service: name=httpd state=started执行结束,没有中途停止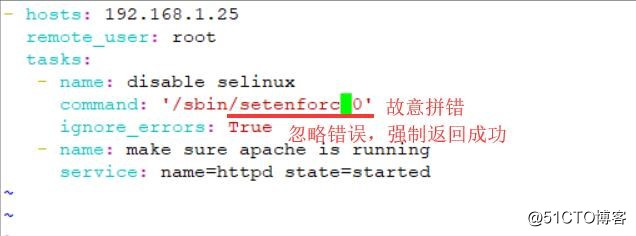
Handlers介绍
Handlers也是一些task的列表,和一般的task并没有什么区别。是由通知者进行的notify,如果没有被notify,则Handlers不会执行,假如被notify了,则Handlers被执行,不管有多少个通知者进行了notify,等到play中的所有task执行完成之后,handlers也只会被执行一次
示例
vim http.yaml
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd package
yum: name=httpd state=latest
- name: install configuration file for httpd
copy: src=/opt/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify:
-restart httpd
- name: start httpd service
service: enabled=true name=httpd state=started
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
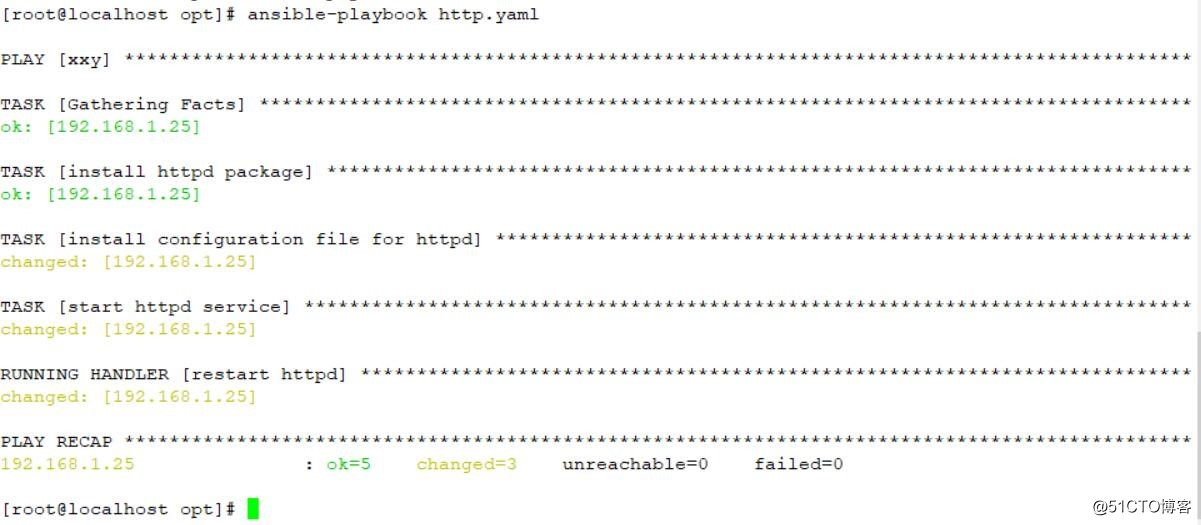
ansible-playbook http.yaml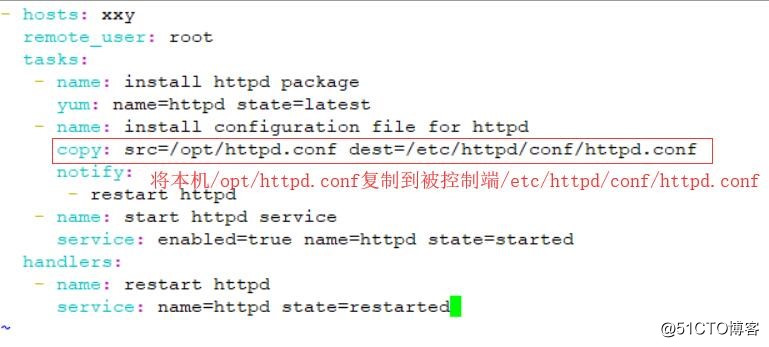
也可以引入变量
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
vars:
- package: httpd //变量
- service: httpd //变量
tasks:
- name: install httpd package
yum: name={{package}} state=latest
- name: install configuration file for httpd
copy: src=/opt/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify:
-restart httpd
- name: start httpd service
service: enabled=true name={{service}} state=started
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name={{service}} state=restarted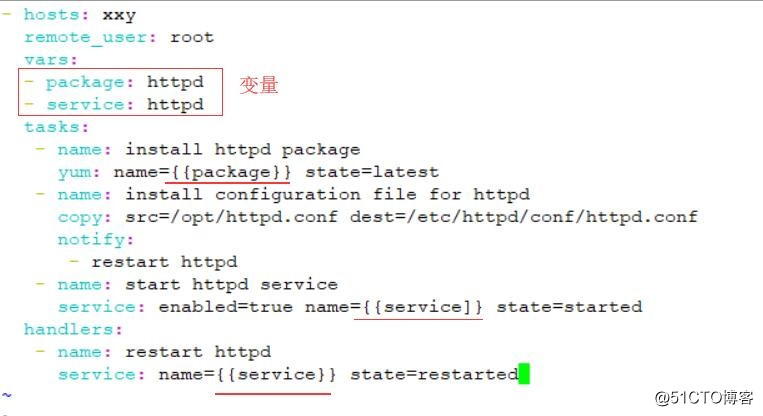
playbook使用变量的方法
1.通过ansible命令传递
vi user.yaml
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
vars:
- user: //此处先不指定
tasks:
- name: add new user
user: name={{user}}
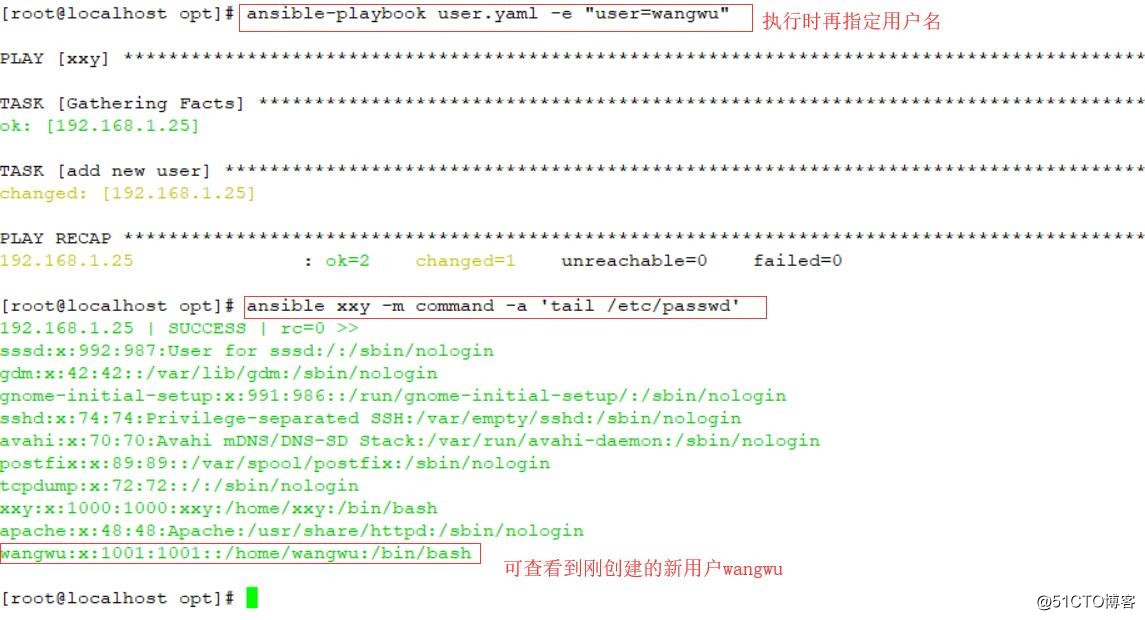
执行:ansible-playbook user.yml -e "user=wangwu"
可以执行命令查看:ansible xxy -m command -a ‘tail /etc/passwd‘
2.直接在yaml中定义变量,如上handlers示例
3.直接引用一些变量
如:引用ansible的固定变量
vi test.yaml
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy file
copy: content="{{ansible_all_ipv4_addresses}}," dest=/opt/vars.txt
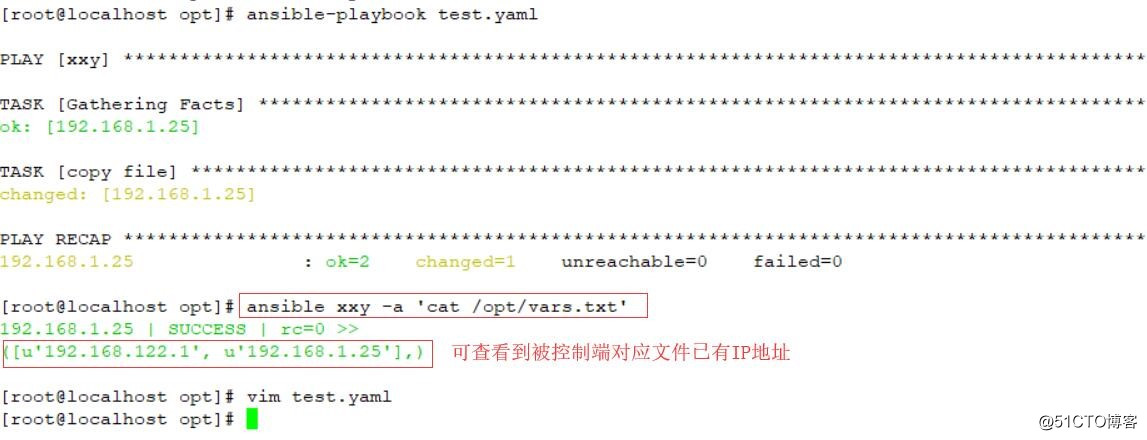
执行:ansible-playbook test.yaml
执行:ansible xxy -a ‘cat /opt/vars.txt‘ //查看文件内容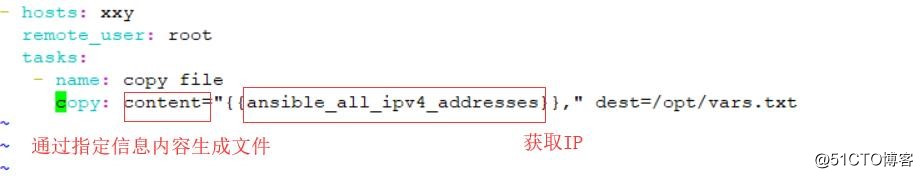
4.引用主机变量
vi /etc/ansible/hosts //在xxy组的主机后面添加如下
[xxy]
192.168.1.25 testvar="haha" //定义testvar变量的值为haha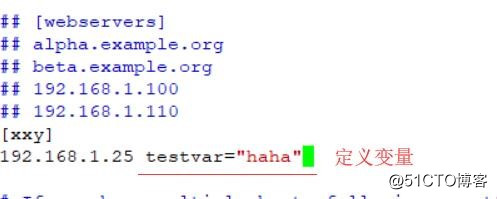
vi test.yml //添加{{testvar}}主机变量
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy file
copy: content="{{ansible_all_ipv4_addresses}},{{testvar}}" dest=/opt/vars.txt
执行:ansible-playbook test.yml
执行:ansible xxy -a ‘cat /opt/vars.txt‘ //查看文件内容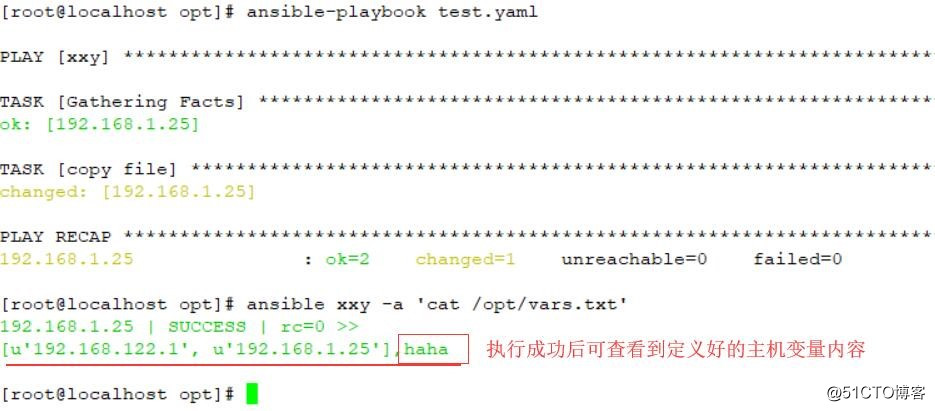
条件测试
如果需要根据变量、facts(setup)或此前任务的执行结果来作为某task执行与否的前提时要用到条件测试,在Playbook中条件测试使用when子句。
在task后添加when子句即可使用条件测试:when子句支持jinjia2表达式或语法,例如:
vi when.yaml
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: "shutdown CentOS"
command: /sbin/shutdown -h now
when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS"
//如果被控制端是CentOS系统,则立即关闭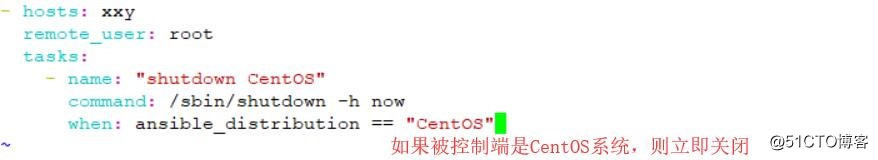
多条件判断
vi when.yaml
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: "shut down CentOS 7 systems"
command: /sbin/shutdown -r now
when:
- ansible_distribution == "CentOS"
- ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"
//如果被控制端是CentOS系统,版本是7,则立即关闭
组条件判断
vi when.yaml
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: "shut down CentOS 6 and Debian 7 systems"
command: /sbin/shutdown -t now
when: (ansible_distribution == "CentOS" and ansible_distribution_major_version == "6") or
(ansible_distribution == "Debian" and ansible_distribution_major_version == "7")
//如果被控制端是CentOS 6 系统,Debian 7 系统,则立即关闭
自定义变量进行条件测试
vi when.yaml
- hosts: all
vars:
exist: "True" //定义变量
tasks:
- name: creaet file
command: touch /tmp/test.txt
when: exist | match("True") //True则创建文件
- name: delete file
command: rm -rf /tmp/test.txt
when: exist | match("False") //False则删除文件
迭代
当有需要重复性执行的任务时,可以使用迭代机制。其使用格式为将需要迭代的内容定义为item变量引用,并通过with_items语句指明迭代的元素列表即可。
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: "Install Packages"
yum: name={{ item }} state=latest
with_items:
- httpd
- mysql-server
- php //依次安装这三个包
Templates介绍
Jinja是基于Python的模板引擎。template类是Jinja的另一个重要组件,可以看作一个编译过的模块文件,用来生产目标文本,传递Python的变量给模板去替换模板中的标记。
编辑好模板
管理端:
mkdir templates
cp conf/httpd.conf templates/httpd.conf
vi templates/httpd.conf
Listen {{http_port}}
ServerName {{server_name}}
MaxClients {{access_num}}编辑主机变量
vi /etc/ansible/hosts
[xxy]
192.168.1.25 http_port=192.168.1.25:80 access_num=100 server_name="www.xxy.com:80"编辑yaml文件
vi apache.yaml
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
vars:
- package: httpd
- service: httpd
tasks:
- name: install httpd package
yum: name={{package}} state=latest
- name: install configure file
template: src=/templates/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify:
- restart httpd
- name: start httpd server
service: name={{service}} enabled=true state=started
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name={{service}} state=restarted
执行:ansible-playbook apache.yaml 可以去被控制端主机上查看是否已修改好配置文件
grep -i listen /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
grep -i MaxClients /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
grep -i ServerName /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conftags模块
在一个playbook中,我们一般会定义很多个task,如果我们只想执行其中的某一个task或多个task时就可以使用tags标签功能了,格式如下:
vi hosts.yaml
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Copy hosts file
copy: src=/etc/hosts dest=/etc/hosts
tags:
- only //定义标签
- name: touch file
file: path=/opt/hosts state=touch
执行:ansible-playbook hosts.yml --tags="only"
#只执行标签部分内容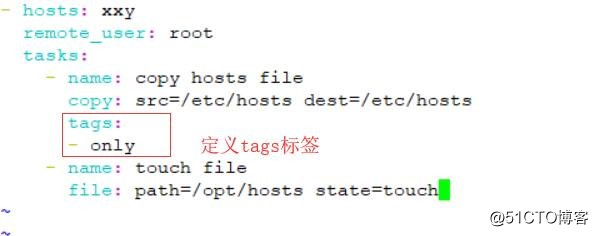
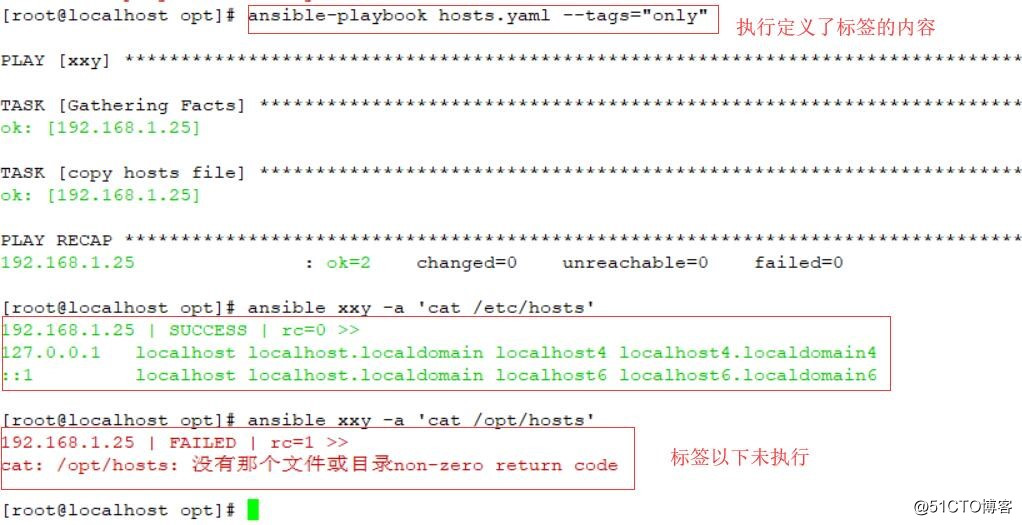
事实上,不光可以为单个或多个task指定同一个tags。playbook还提供了一个特殊的tags为always。作用就是当使用always当tags的task时,无论执行哪一个tags时,定义有always的tags都会执行。
vi hosts.yaml
---
- hosts: xxy
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Copy hosts file
copy: src=/etc/hosts dest=/etc/hosts
tags:
- only
- name: touch file
file: path=/opt/hosts state=touch
tags:
- always
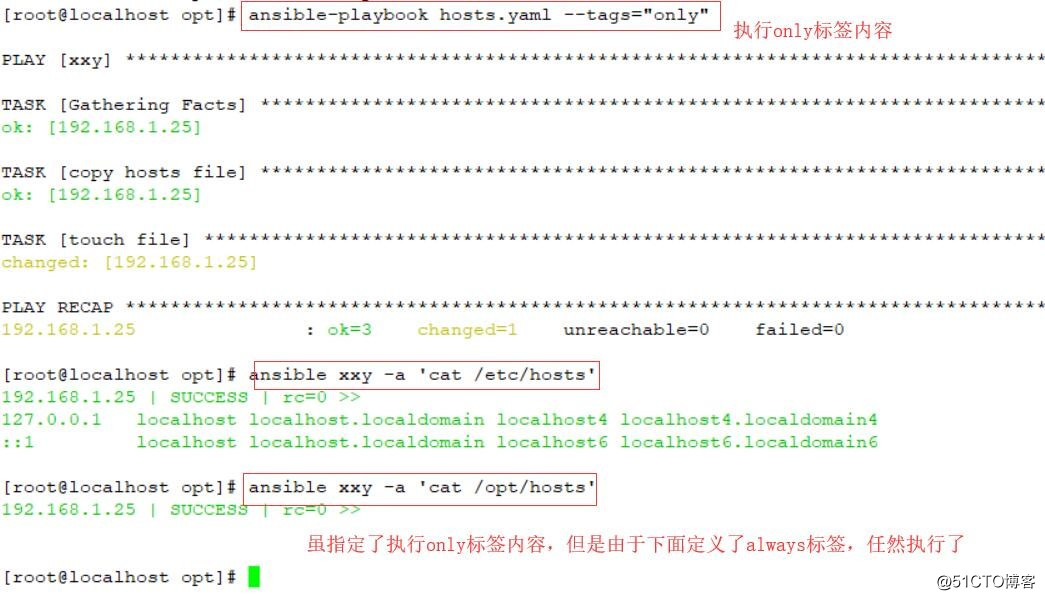
执行:ansible-playbook hosts.yml --tags="only"
#虽然指定执行only标签内容,但是由于下面定义了always标签,所以任然执行了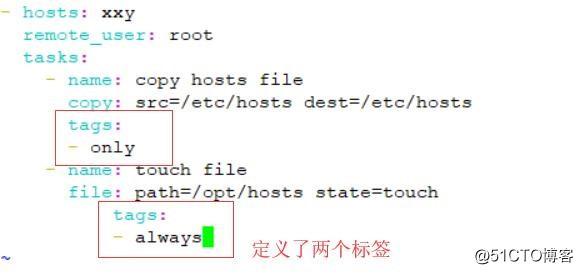
以上是关于自动化运维Ansible之Playbook剧本的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章