数据结构:链表(单链表)
Posted zengguowang
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构:链表(单链表)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、链表
概念:链表[Linked List]是由一组不必相连(可连续可不连续)的内存结构(节点),按照特定的顺序链接在一起的抽象数据类型;
分类:链表常用的大概有三类:单链表、双向链表、循环链表(这篇文章主要讲单链表)
操作:链表的核心操作主要有三个(查找遍历、插入、删除)
二、单链表
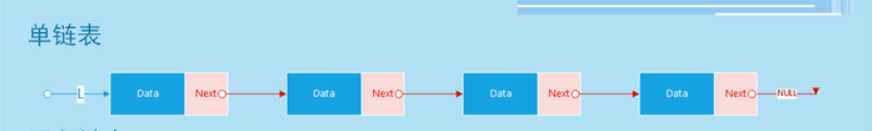
上图就是一个单链表的数据结构了,从上图可以看出,每个节点包含两个重要的元素(data、next),那么什么是单链表呢?
概念:各个内存结构通过一个Next指针链接在一起,每个内存结构都存在后续的内存结构(链尾除外);内存域由两部分组成(Data数据域和Next指针域)
三、操作
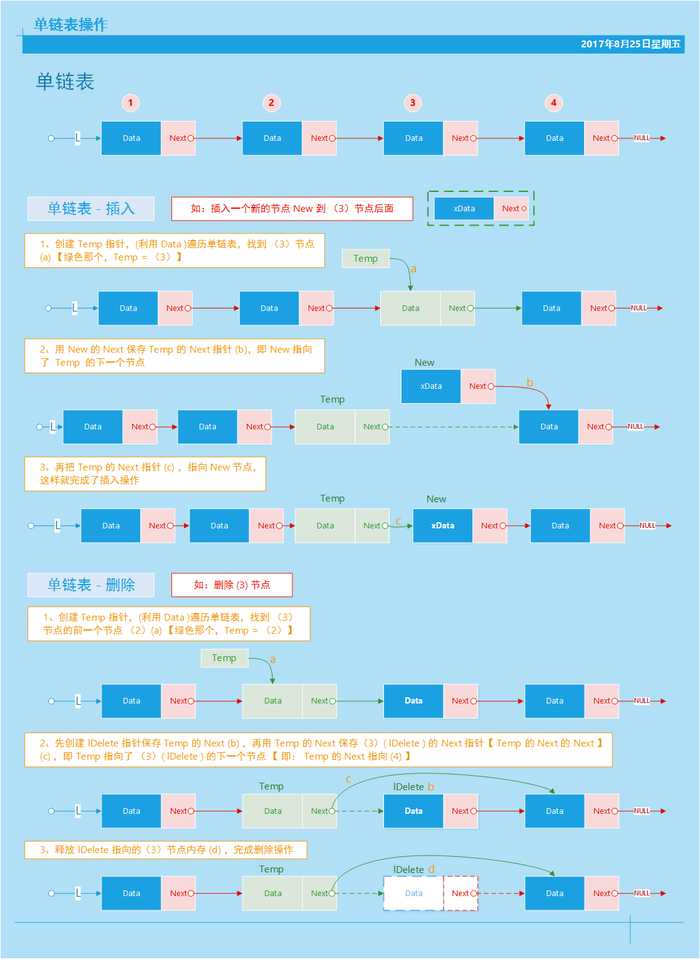
上图展示了单链表的插入和删除的过程,很清楚的能够知道是怎么一回事,针对我这样的小白来说,至少我看懂了;
下面是本人结合上面的图写的代码(随便写的,将就着看,代码只是验证你是否真的了解 该数据结构,所以理解了即可,没有必要在意代码的好坏,谢谢!):
<?php /*** * 单链表数据结构 * 链表是一种递归的数据结构,它或为空(Null),或指向一个结点的引用,该结点还有一个元素和指向下一个链表的引用 * 单链表的每个节点由两个元素组成:data、next */ class Node{ public $data; public $next=null; public $linkedSize = 0; // 记录链表的大小(每个节点都保存了这个值为0,其实也可以保持个id,看个人习惯) public function __construct($data){ $this->data = $data; } } class LinkedList{ /*** * 创建链表 * @param array $data * @return Node|string */ public static function createLinked($data=array()) { if(empty($data)) return ‘参数为空‘; $header = new Node(‘‘); $headerObj = $header; foreach ($data as $key=>$val) { $nextHeader = new Node($val); $headerObj->next = $nextHeader; $headerObj = $nextHeader; $header->linkedSize++; } return $header; } /*** * 遍历链表数据 * @param Node $header * @return bool */ public static function selectLinkedList(Node $header) { $linkedObj = $header; $i = 0; while($linkedObj->next != null) { echo $i.‘ Node data:‘.$linkedObj->next->data." "; $linkedObj = $linkedObj->next; $i++; } return true; } /*** * @param Node $header * @param $key * @param $data * @param string $lmr l 指定key的前边插入 m 指定位置插入 r 指定位置的后边插入 * @return bool|string */ public static function insertKeyLinkedList(Node $header, $key, $data, $lmr=‘r‘) { // 链表可能为空(添加一个节点) if($header->linkedSize < 1) { $newHeader = new Node($data); $header->next = $newHeader; $header->linkedSize++; return true; } # 配置插入方向和位置 $lmrKey = array(‘l‘, ‘m‘, ‘r‘); $lmrConfig = array( ‘l‘ => $key - 1,// 往指定位置的前边插入数据 ‘m‘ => $key, // 往指定位置插入数据 ‘r‘ => $key + 1 // 往指定位置的后边插入数据 ); // 验证key的合法性 if(!preg_match(‘/^[0-9]{1,}$/si‘, $key) || !in_array(trim($lmr), $lmrKey)) return ‘请输入正确的key和lmr方向‘; # 获取真实的位置 if(!isset($lmrConfig[trim($lmr)])) return ‘计算位置错误(可能参数有误)‘; $positionKey = $lmrConfig[trim($lmr)]; $maxSize = $header->linkedSize-1; if(trim($lmr) == ‘r‘) $maxSize = $header->linkedSize; if($positionKey > $maxSize) return ‘未知的位置‘; $i = 0; $headerObj = $header; while($headerObj->next != null) { // 这里有点类似咱们经常用的冒泡排序,交换位置 if($positionKey == $i || $positionKey < 0) { $newHeader = new Node($data); $temp = $headerObj->next; $headerObj->next = $newHeader; $newHeader->next = $temp; $header->linkedSize++; return true; } if(trim($lmr) == ‘r‘ && ($i+1) == $maxSize) // 插入到末尾 { $newHeader = new Node($data); $headerObj->next->next = $newHeader; $header->linkedSize++; return true; } $headerObj = $headerObj->next; $i++; } return true; } /*** * @param Node $header * @param int $key * @return bool|string */ public static function deleteKeyLinkedList(Node $header, $key=0) { if(!preg_match(‘/^[0-9]{1,}$/si‘, $key) || $key > ($header->linkedSize-1) || $key < 0) return ‘输入的key不合法/当前位置没有数据‘; if($header->next == null || $header->linkedSize < 1) return ‘链表中暂无数据‘; $i = 0; $position = $key; $headerObj = $header; while($headerObj->next != null) { if($i == $position) { $tmp = $headerObj->next->next; unset($headerObj->next); $headerObj->next = $tmp; $header->linkedSize--; return true; } $headerObj = $headerObj->next; $i++; } return true; } } # 创建链表 $data = array(22, 2, 90, 6, 43, 76, 89); $header = LinkedList::createLinked($data); # 遍历单向链表 LinkedList::selectLinkedList($header); echo " "; # 插入一个元素 $header = new Node(‘‘); LinkedList::insertKeyLinkedList($header,6, 250, ‘l‘); # 插入后遍历单向链表 LinkedList::selectLinkedList($header); //var_dump($header); // 删除指定的节点 LinkedList::deleteKeyLinkedList($header, 1); # 删除后遍历单向链表 LinkedList::selectLinkedList($header);
博客内容出自:https://www.jianshu.com/p/73d56c3d228c
以上是关于数据结构:链表(单链表)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章