spring boot 1.5.4 配置文件详解
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring boot 1.5.4 配置文件详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
上一篇:spring boot 1.5.4 集成spring-Data-JPA(七)
1 Spring Boot配置文件详解
相信很多人选择Spring Boot主要是考虑到它既能兼顾Spring的强大功能,还能实现快速开发的便捷。我们在Spring Boot使用过程中,最直观的感受就是没有了原来自己整合Spring应用时繁多的XML配置内容,替代它的是在pom.xml中引入模块化的Starter POMs,其中各个模块都有自己的默认配置,所以如果不是特殊应用场景,就只需要在application.properties中完成一些属性配置就能开启各模块的应用。
关于application.properties的使用,主要用来配置数据库连接、日志相关配置等。除了这些配置内容之外,还有一些在application.properties配置中的其他特性和使用方法。
spring boot配置详解spring-boot-jsp项目源码:
https://git.oschina.net/wyait/springboot1.5.4.git
1.1 自定义属性与加载
1,在application.properties中添加
# 自定义属性和加载
wyait.name=wyait
wyait.title=Spring boot之web开发
2,新增properties包,新建ParamPropertis类加载配置属性
@Component
public class ParamProperties {
@Value("${wyait.name}")
privateString wyaitName;
@Value("${wyait.title}")
privateString wyaitTitle;
//TODOgetter和setter方法
}
3,在CatController新增方法调用ParamProperties
@Autowired
privateParamProperties paramProperties;
@ApiIgnore
@RequestMapping("/wyait")
@ResponseBody
publicString getMsg(HttpServletResponse response) {
LOGGER.debug("===========>>>>"+ paramProperties);
//会有中文乱码问题 TODO
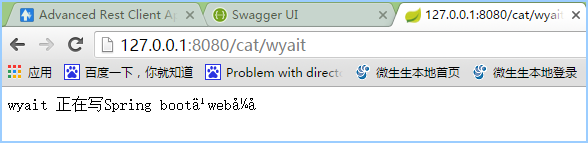
returnparamProperties.getWyaitName() + " 正在写"
+paramProperties.getWyaitTitle();
}
4,启动,访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/cat/wyait
1.2 properties参数间引用
1,properties参数间引用
# 自定义属性和加载
wyait.name=wyait
wyait.title=Spring boot web
# 参数间引用
wyait.message=${wyait.name} do${wyait.title}.docx
参数:wyait.message引用了上文中的name和title属性的值,通过${}
2,ParamPropertis类加载配置属性
@Value("${wyait.message}")
privateString wyaitMessage;
3,CatController
@ApiIgnore
@RequestMapping("/wyait")
@ResponseBody
publicString getMsg(HttpServletResponse response) {
LOGGER.debug("===========>>>>"+ paramProperties);
//会有中文乱码问题 TODO
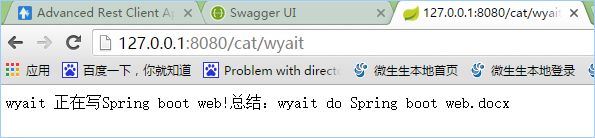
returnparamProperties.getWyaitName() + " 正在写"
+paramProperties.getWyaitTitle() + "!总结:"
+paramProperties.getWyaitMessage();
}
4,启动,访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/cat/wyait
1.3 使用随机数
在一些情况下,有些参数我们需要希望它不是一个固定的值,比如密钥、服务端口等。Spring Boot的属性配置文件中可以通过${random}来产生int值、long值或者string字符串,来支持属性的随机值。
# 随机字符串
com.wyait.value=${random.value}
# 随机int
com.wyait.number=${random.int}
# 随机long
com.wyait.bignumber=${random.long}
# 10以内的随机数
com.wyait.test1=${random.int(10)}
# 10-20的随机数
com.wyait.test2=${random.int[10,20]}
1.4 通过命令行设置属性值
相信使用过一段时间Spring Boot的用户,一定知道这条命令:java-jar xxx.jar --server.port=8888,通过使用–server.port属性来设置xxx.jar应用的端口为8888。
在命令行运行时,连续的两个减号--就是对application.properties中的属性值进行赋值的标识。所以,java -jar xxx.jar --server.port=8888命令,等价于我们在application.properties中添加属性server.port=8888,该设置在样例工程中可见,读者可通过删除该值或使用命令行来设置该值来验证。
通过命令行来修改属性值固然提供了不错的便利性,但是通过命令行就能更改应用运行的参数,那岂不是很不安全?是的,所以Spring Boot也贴心的提供了屏蔽命令行访问属性的设置,只需要这句设置就能屏蔽:SpringApplication.setAddCommandLineProperties(false)。
如:
// 这是一个配置Spring的配置类
@Configuration
// @SpringBootApplication:Spring Boot项目的核心注解,主要目的是开启自动配置。
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
publicstatic void main(String[] args) {
//启动spring boot应用
SpringApplicationsa = new SpringApplication(DemoApplication.class);
//禁用devTools热部署
System.setProperty("spring.devtools.restart.enabled","false");
//禁用命令行更改application.properties属性
sa.setAddCommandLineProperties(false);
sa.run(args);
}
}
1.5 多环境配置
我们在开发Spring Boot应用时,通常同一套程序会被应用和安装到几个不同的环境,比如:开发、测试、生产等。其中每个环境的数据库地址、服务器端口等等配置都会不同,如果在为不同环境打包时都要频繁修改配置文件的话,那必将是个非常繁琐且容易发生错误的事。
对于多环境的配置,各种项目构建工具或是框架的基本思路是一致的,通过配置多份不同环境的配置文件,再通过打包命令指定需要打包的内容之后进行区分打包,Spring Boot也不例外,或者说更加简单。
在Spring Boot中多环境配置文件名需要满足application-{profile}.properties的格式,其中{profile}对应你的环境标识,比如:
application-dev.properties:开发环境
application-test.properties:测试环境
application-prod.properties:生产环境
至于哪个具体的配置文件会被加载,需要在application.properties文件中通过spring.profiles.active属性来设置,其值对应{profile}值。
如:spring.profiles.active=test就会加载application-test.properties配置文件内容
下面,以不同环境配置不同的服务端口为例,进行样例实验。
针对各环境新建不同的配置文件application-dev.properties、application-test.properties、application-prod.properties
在这三个文件均都设置不同的server.port属性,如:dev环境设置为1111,test环境设置为2222,prod环境设置为3333
application.properties中设置spring.profiles.active=dev,就是说默认以dev环境设置
测试不同配置的加载
执行java -jar xxx.jar,可以观察到服务端口被设置为8080,也就是默认的开发环境(dev)
执行java -jar xxx.jar --spring.profiles.active=test,可以观察到服务端口被设置为2222,也就是测试环境的配置(test)
执行java -jar xxx.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod,可以观察到服务端口被设置为3333,也就是生产环境的配置(prod)
按照上面的实验,可以如下总结多环境的配置思路:
application.properties中配置通用内容,并设置spring.profiles.active=dev,以开发环境为默认配置
application-{profile}.properties中配置各个环境不同的内容(数据源、日志级别、参数等)
通过命令行方式去激活不同环境的配置
spring boot系列文章:
spring boot 1.5.4 集成devTools(五)
spring boot 1.5.4 集成JdbcTemplate(六)
spring boot 1.5.4 集成spring-Data-JPA(七)
spring boot 1.5.4 定时任务和异步调用(十)
本文出自 “架构的路上” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://wyait.blog.51cto.com/12674066/1969160
以上是关于spring boot 1.5.4 配置文件详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章