查询总结HQL语法QBC(QueryByCriteria)深入学习
Posted qlqwjy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了查询总结HQL语法QBC(QueryByCriteria)深入学习相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.查询总结
在之前的批量查询练习的时候练习基本五种查询方法的使用:
1.OID查询---根据对象ID进行查询
2.对象属性导航查询: obj.getXXX
3.HQL查询:Query对象查询
4.QBC(QueryByCriteria):Criteria对象查询
5.原生SQL查询:SQLQuery查询
测试代码如下:
package cn.qlq.query; import java.util.Set; import org.hibernate.Criteria; import org.hibernate.Query; import org.hibernate.SQLQuery; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.criterion.Restrictions; import org.junit.Test; import cn.qlq.domain.Customer; import cn.qlq.domain.LinkMan; import cn.qlq.util.HibernateUtil; /** * 之前的查询总结 * @author liqiang * */ public class HibernateQuery { @Test /** * OID查询(get方法) */ public void fun1(){ Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 7l); System.out.println(customer); tx.commit(); session.close(); } @Test /** * 属性导航语言(对象.getXXX) */ public void fun2(){ Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 7l); Set<LinkMan> linkMens = customer.getLinkMens(); System.out.println(linkMens); tx.commit(); session.close(); } @Test /** * HQL查询(Query对象进行查询) */ public void fun3(){ Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); String hql = "from cn.qlq.domain.Customer";//如果整个项目只有一个类名,可以省去包名 Query query = session.createQuery(hql); System.out.println(query.list()); tx.commit(); session.close(); } @Test /** * Criteria查询(也被叫做QBC---query by criteria) */ public void fun4(){ Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Customer.class); // criteria.add(Restrictions.ilike("name", "xxx"));//添加过滤条件 System.out.println(criteria.list()); tx.commit(); session.close(); } @Test /** * 原生SQL查询(SQLQuery对象进行查询) */ public void fun5(){ Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); String sql = "select * from cst_customer"; SQLQuery sqlQuery = session.createSQLQuery(sql); sqlQuery.addEntity(Customer.class); System.out.println(sqlQuery.list()); tx.commit(); session.close(); } }
2.HQL深入学习(Hibernate query language)
1.HQL介绍
HQL是面向对象的查询语言,它和SQL查询有些类似,但它使用的是类、对象、属性的概念,而没有表和字段的概念,也就是在HQL中如果出现DB中的表和字段名是错误的。在Hibernate的各种检索方式中,官方推荐的是HQL检索,也是使用最广泛的一种查询方式。它具有如下功能:
- 在查询中设定各种查询条件
- 支持投影查询,即检索对象的部分属性
- 支持分页查询
- 支持分组查询,允许使用group by关键字和having关键字
- 提供内置聚集函数。如sum、avg、min、max、count等函数
- 能够调用用户定义的SQL函数
- 支持子查询,即嵌套查询
- 支持动态参数绑定
Hibernate提供的Query接口是专门的HQL查询接口,它能够执行各种复杂的HQL查询语句。完整的SQL语句结构如下:
Select ... from... where ... group by ... having...order by ...desc/asc
HQL非常类似于SQL。通常情况下如果查询表中的所有记录的时候,查询语句中可省略select关键字,如下:
from Customer
如果执行该语句,则会返回应用程序中的所有的Customer对象,需要注意的是Customer是类名而不是对象名,类名区分大小写,from不区分大小写,如果项目中有多个相同的类名需要加包名。
2.HQL学习
1.基本检索-检索所有
@Test // HQL查询所有数据 public void fun1() { // 1 获得session Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); // 2.书写HQL语句 // String hql = "from cn.qlq.domain.Customer";// from 类名全路径 String hql1 = "from Customer";//整个项目只有一个类名可以省略包名 // String hql2 = "from java.lang.Object";//写Object的时候会查询项目中的所有类,切勿使用,浪费内存 // 3.根据hql创建查询对象 // Query query = session.createQuery(hql); Query query = session.createQuery(hql1); // Query query = session.createQuery(hql2); // 4.根据查询对象获取查询结果 List<Customer> objs = query.list(); System.out.println(objs); }
结果:
Hibernate: select customer0_.cust_id as cust_id1_0_, customer0_.cust_name as cust_nam2_0_, customer0_.cust_source as cust_sou3_0_, customer0_.cust_industry as cust_ind4_0_, customer0_.cust_level as cust_lev5_0_, customer0_.cust_linkman as cust_lin6_0_, customer0_.cust_phone as cust_pho7_0_, customer0_.cust_mobile as cust_mob8_0_ from cst_customer customer0_ [Customer [cust_id=7, cust_name=测试名称1], Customer [cust_id=8, cust_name=测试名称2], Customer [cust_id=9, cust_name=测试名称3], Customer [cust_id=10, cust_name=测试名称4], Customer [cust_id=11, cust_name=测试名称5], Customer [cust_id=12, cust_name=测试名称6], Customer [cust_id=13, cust_name=测试名称7]]
2.排序
@Test //排序查询 public void fun2() { // 1 获得session Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); // 2.书写HQL语句 String hql1 = "from Customer order by cust_id asc,cust_name desc";//整个项目只有一个类名可以省略包名 // 3.根据hql创建查询对象 Query query = session.createQuery(hql1); // 4.根据查询对象获取查询结果 List<Customer> objs = query.list(); System.out.println(objs); }
结果:
Hibernate: select customer0_.cust_id as cust_id1_0_, customer0_.cust_name as cust_nam2_0_, customer0_.cust_source as cust_sou3_0_, customer0_.cust_industry as cust_ind4_0_, customer0_.cust_level as cust_lev5_0_, customer0_.cust_linkman as cust_lin6_0_, customer0_.cust_phone as cust_pho7_0_, customer0_.cust_mobile as cust_mob8_0_ from cst_customer customer0_ order by customer0_.cust_id asc, customer0_.cust_name desc [Customer [cust_id=7, cust_name=测试名称1], Customer [cust_id=8, cust_name=测试名称2], Customer [cust_id=9, cust_name=测试名称3], Customer [cust_id=10, cust_name=测试名称4], Customer [cust_id=11, cust_name=测试名称5], Customer [cust_id=12, cust_name=测试名称6], Customer [cust_id=13, cust_name=测试名称7]]
3.条件检索
(1)?占位符查询
类似于JDBC的占位符,只是hibernate的?下标从0开始,而JDBC的下标从1开始,基本上所有的编程索引都从0开始,唯独JDBC从1开始。。。。
@Test // HQL的?占位符查询 public void fun3() { // 1 获得session Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); // 2.书写HQL语句 // String hql = "from cn.qlq.domain.Customer";// from 类名全路径 String hql = "from Customer where cust_id = ?";// 如果整个项目中只有这一个类名可以直接写名字 // 3.根据hql创建查询对象 Query query = session.createQuery(hql); // query.setLong(0, 1l);//类似于JDBC的占位符,只是JDBC的占位符下标从0开始,hibernate从1开始 query.setParameter(0, 1l);//这种写法不用管类型 // 4.根据查询对象获取查询结果 Customer customer = (Customer) query.uniqueResult(); System.out.println(customer); }
(2)命令占位符 :name格式的查询,固定格式,name随便起,习惯性的起做和条件名字一样
@Test // HQL的命令占位符查询 public void fun4() { // 1 获得session Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); // 2.书写HQL语句 // String hql = "from cn.qlq.domain.Customer";// from 类名全路径 String hql = "from Customer where cust_id = :cust_id";// :cust_id的名字随便起,只不过习惯性的起做一样 // 3.根据hql创建查询对象 Query query = session.createQuery(hql); // query.setLong(0, 1l);//类似于JDBC的占位符,只是JDBC的占位符下标从0开始,hibernate从1开始 query.setParameter("cust_id",1l); // 4.根据查询对象获取查询结果 Customer customer = (Customer) query.uniqueResult(); System.out.println(customer); }
4.排序查询
@Test // HQL分页查询 public void fun5() { // 1 获得session Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); // 2.书写HQL语句 // String hql = "from cn.qlq.domain.Customer";// from 类名全路径 String hql = "from Customer order by cust_id desc";// 3.根据hql创建查询对象 Query query = session.createQuery(hql); /** * 类似于 limit start,pageSize; * 假设页大小是2 * 页号 起始值 页大小 * 1 0 2 * 2 2 2 */ //例如取第二页数据 query.setFirstResult(2); query.setMaxResults(2); // 4.根据查询对象获取查询结果 List<Customer> customers = query.list(); System.out.println(customers); }
5.聚合函数的使用:
@Test //聚集函数的使用 public void fun3() { // 1 获得session Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); // 2.书写HQL语句 String hql1 = "select count(*) from Customer";//统计总数 String hql2 = "select avg(cust_id) from Customer";//平均 String hql3 = "select sum(cust_id) from Customer";//和 String hql4 = "select max(cust_id) from Customer";//最大 String hql5 = "select min(cust_id) from Customer";//最小 // 3.根据hql创建查询对象 Query query = session.createQuery(hql4); // 4.根据查询对象获取查询结果 Number number = (Number) query.uniqueResult();//Number是所有数字类型的父类 System.out.println(number); }
6.投影检索---查询指定的属性,不查全部
(1)投影单个属性
@Test //投影单个 public void fun7() { // 1 获得session Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); // 2.书写HQL语句 String hql1 = "select cust_name from Customer";//整个项目只有一个类名可以省略包名 // 3.根据hql创建查询对象 Query query = session.createQuery(hql1); // 4.根据查询对象获取查询结果 List<String> objs = query.list();//那一列是什么类型用什么类型,也可以省去不写 System.out.println(objs); }
结果:
Hibernate: select customer0_.cust_name as col_0_0_ from cst_customer customer0_ [测试名称1, 测试名称2, 测试名称3, 测试名称4, 测试名称5, 测试名称6, 测试名称7]
(2)投影多列---映射为数组
@Test //投影多列 public void fun7() { // 1 获得session Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); // 2.书写HQL语句 String hql1 = "select cust_id,cust_name from Customer";//整个项目只有一个类名可以省略包名 // 3.根据hql创建查询对象 Query query = session.createQuery(hql1); // 4.根据查询对象获取查询结果 List<Object[]> objs = query.list();//那一列是什么类型用什么类型,也可以省去不写 System.out.println(objs); }
结果:
Hibernate: select customer0_.cust_id as col_0_0_, customer0_.cust_name as col_1_0_ from cst_customer customer0_ [[Ljava.lang.Object;@29bd3793, [Ljava.lang.Object;@458ba94d, [Ljava.lang.Object;@541821e6, [Ljava.lang.Object;@7c59ae2b, [Ljava.lang.Object;@63b9c8d4, [Ljava.lang.Object;@3a300972, [Ljava.lang.Object;@27bc3936]
(3)将投影映射为对象:(构造方式查询)
在原来的类中创建需要投影的属性的构造方法,同时需要显示的创建无参构造函数:
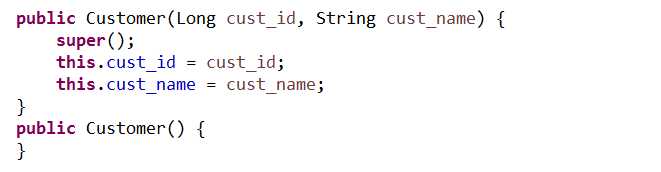
测试代码:
@Test //投影多列---映射为JavaBean public void fun7() { // 1 获得session Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); // 2.书写HQL语句 String hql1 = "select new Customer(cust_id,cust_name) from Customer";//整个项目只有一个类名可以省略包名 // 3.根据hql创建查询对象 Query query = session.createQuery(hql1); // 4.根据查询对象获取查询结果 List<Customer> objs = query.list();//那一列是什么类型用什么类型,也可以省去不写 System.out.println(objs); }
结果
Hibernate: select customer0_.cust_id as col_0_0_, customer0_.cust_name as col_1_0_ from cst_customer customer0_ [Customer [cust_id=7, cust_name=测试名称1], Customer [cust_id=8, cust_name=测试名称2], Customer [cust_id=9, cust_name=测试名称3], Customer [cust_id=10, cust_name=测试名称4], Customer [cust_id=11, cust_name=测试名称5], Customer [cust_id=12, cust_name=测试名称6], Customer [cust_id=13, cust_name=测试名称7]]
以上是关于查询总结HQL语法QBC(QueryByCriteria)深入学习的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章