自动化测试--testNG
Posted clairejing
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了自动化测试--testNG相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
该文章主要介绍 testNG(testing next generation,下一代测试技术)框架的使用。
1.首先安装testNG
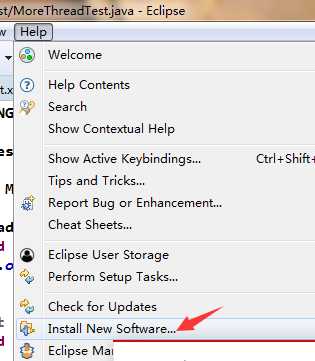
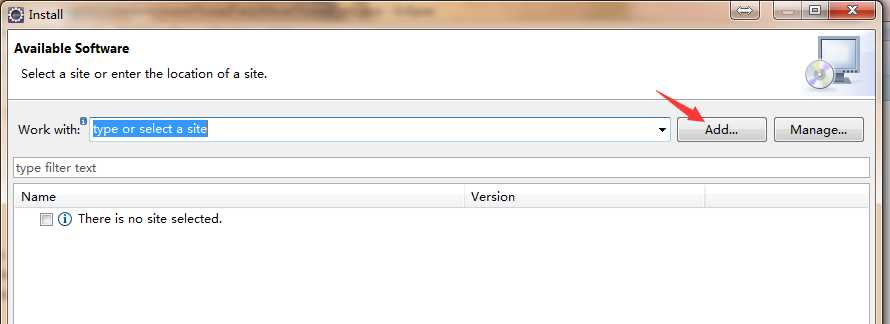
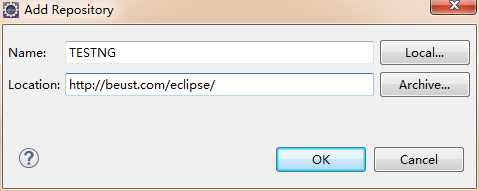
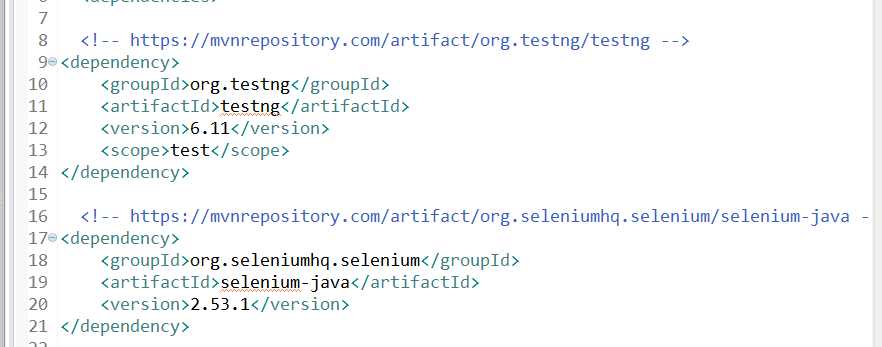
2.安装完成后,创建maven项目,导入TESTNG和selenium依赖。
3.此时就可以直接创建testNG的测试类了
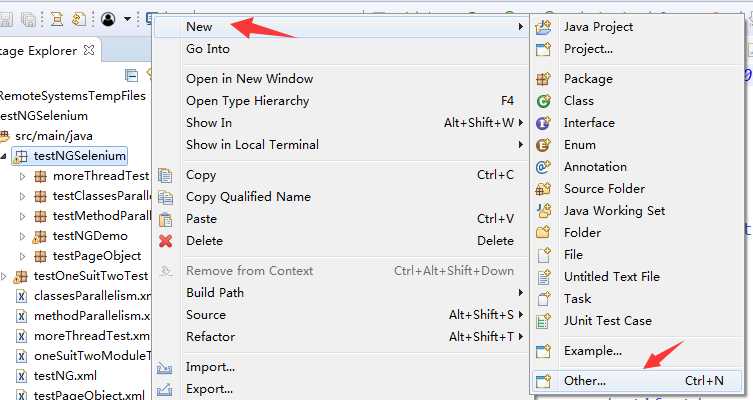
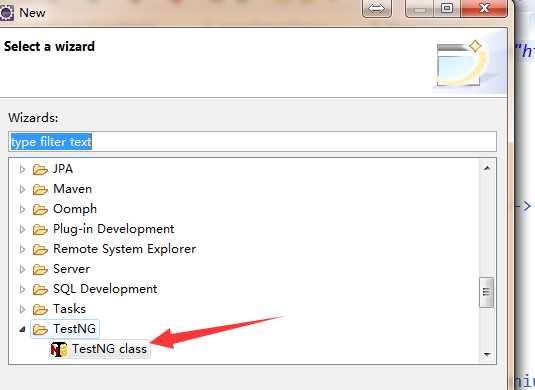
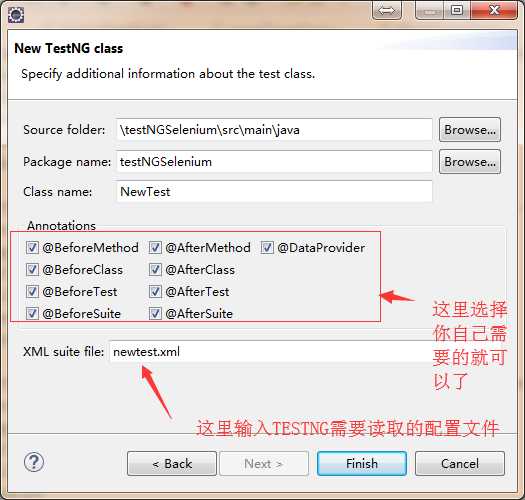
4.下面通过 百度页面打开、输入关键字、进行搜索,来简单演示一下testNG的使用

1 package testNGSelenium.testNGDemo; 2 3 import org.testng.annotations.Test; 4 import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest; 5 import org.testng.annotations.DataProvider; 6 import org.testng.annotations.Parameters; 7 8 import java.util.Date; 9 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 10 11 import org.apache.bcel.generic.NEW; 12 import org.apache.commons.collections.map.StaticBucketMap; 13 import org.openqa.selenium.By; 14 import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver; 15 import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement; 16 import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver; 17 import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedCondition; 18 import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait; 19 import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest; 20 21 public class NewTest { 22 //声明一个全局变量 23 private WebDriver driver; 24 25 26 27 @Test 28 @Parameters({"keyWord"}) 29 public void f(String keywords) { 30 final By input1 = By.id("kw"); 31 final By button1 = By.id("su"); 32 33 //智能等待页面的输入框加载出来 34 try { 35 36 (new WebDriverWait(driver, 3)).until(new ExpectedCondition<Boolean>() { 37 38 public Boolean apply(WebDriver input) { 39 WebElement element = input.findElement(input1); 40 System.out.println(new Date()); 41 return element!= null; 42 } 43 }); 44 45 } catch (Exception e) { 46 System.out.println("输入框3S还没加载出来!!!"); 47 e.printStackTrace(); 48 } 49 50 51 //智能等待页面的搜索按钮加载出来 52 try { 53 (new WebDriverWait(driver, 3)).until(new ExpectedCondition<Boolean>() { 54 55 public Boolean apply(WebDriver input) { 56 WebElement element = input.findElement(button1); 57 System.out.println(new Date()); 58 return element!= null; 59 } 60 }); 61 } catch (Exception e) { 62 System.out.println("搜索按钮等待了3秒还未加载出来"); 63 e.printStackTrace(); 64 } 65 66 67 driver.findElement(input1).sendKeys(keywords); 68 driver.findElement(button1).click(); 69 70 //等待10S,便于观察结果 71 try { 72 Thread.sleep(10000); 73 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 74 75 e.printStackTrace(); 76 } 77 78 79 } 80 @BeforeTest 81 public void beforeTest() { 82 driver = new ChromeDriver(); 83 //窗口最大化 84 driver.manage().window().maximize(); 85 86 //加载页面 87 driver.get("http://www.baidu.com"); 88 89 //设置页面完全加载时间为3秒,第二个参数TimeUnit.SECONDS是指定时间单位 90 driver.manage().timeouts().pageLoadTimeout(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 91 92 } 93 94 @AfterTest 95 public void afterTest() { 96 driver.quit(); 97 } 98 99 }
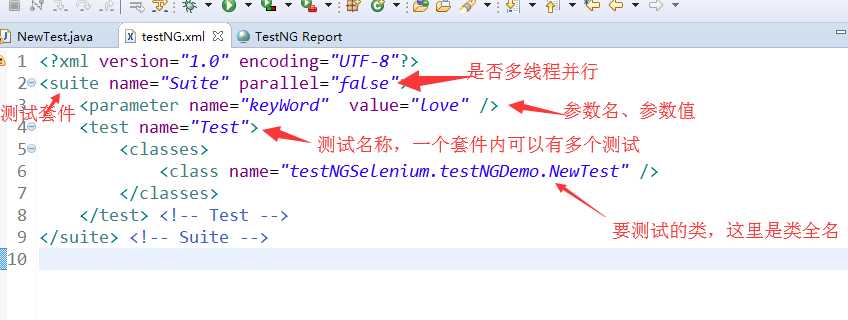
上面代码中用到了参数化,是需要在xml文件中设置的:
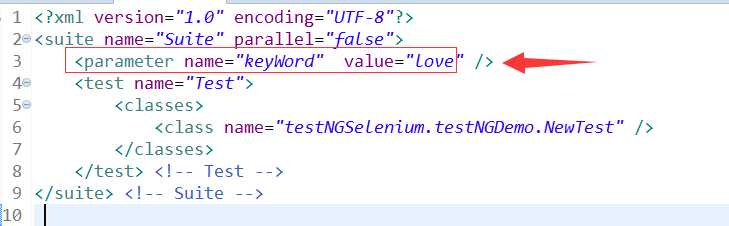
注意:
1.如果使用了参数化,则必须在XML文件上run as TestNG,否则会提示得不到参数的。
2.运行完成后,我们可以在项目目录中看到多了一个test-output
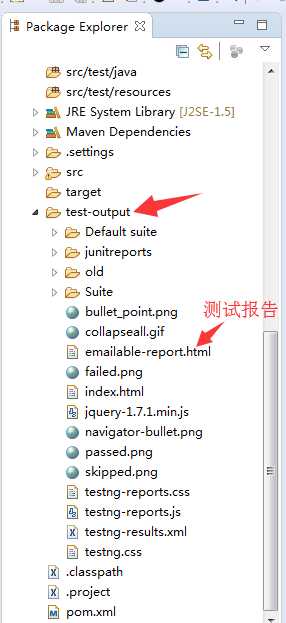
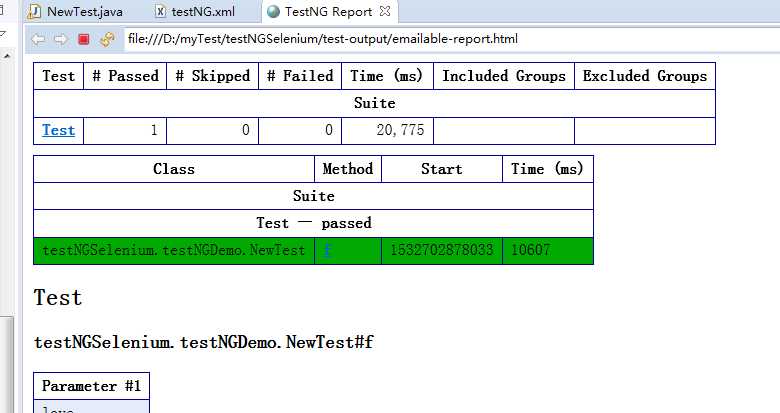
对其中的emailable-report.html右键---open with---web browser,就可以打开如下的测试报告:
关于配置文件的简单介绍:
通过上面的配置文件介绍,你可能会问,如果parallelism设置为true,是不是就可以跑多线程了??
是的!!!激不激动,开不开心!这个多线程可以支持我们做两件事:
1.多个线程来跑同一套件中的不同方法、不同类、不同组件---------------------这样,当我们的测试代码很庞大的时候,会非常节省运行时间
2.用来测试多线程同步问题。举个栗子-----------当有段代码涉及到:不同线程访问同一对象,并且会对该对象作出修改的时候,我们就可以针对这段代码来设计:多个线程同时跑这段代码,来测试下开发的线程同步是不是已经处理好啦。
下面来介绍下TestNG提供的多线程测试的不同使用方法,为了便于理解,这里使用的都是笔者写的最简单的demo:
一:并行的执行某方法
package testNGSelenium.testMethodParallelism; import org.testng.annotations.Test; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeMethod; import org.testng.annotations.AfterMethod; public class MethodParallelismTest { @Test public void f1() { System.out.println("这里是方法1,执行该方法的当前线程ID为"+ Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @Test public void f2() { System.out.println("这里是方法2,执行该方法的当前线程ID为"+ Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @BeforeMethod public void beforeMethod() { System.out.println("这里是before,执行该方法的当前线程ID为"+ Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @AfterMethod public void afterMethod() { System.out.println("这里是after,执行该方法的当前线程ID为"+ Thread.currentThread().getId()); } }
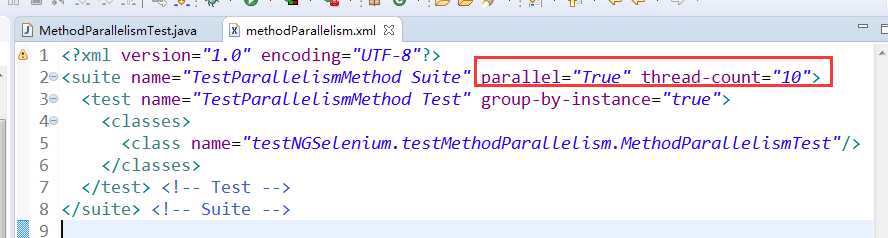
对应修改XML文件为:
该代码的执行结果为:
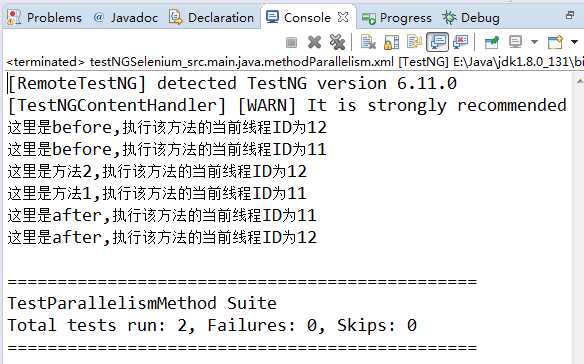
二:并行的执行同一套间下同一组件中的不同class
package testNGSelenium.testClassesParallelism; import org.testng.annotations.Test; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeMethod; import org.testng.annotations.DataProvider; import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass; import org.testng.annotations.AfterMethod; public class ClassesParallelism1 { @Test public void f() { System.out.println("test1" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @BeforeClass public void beforeClass() { System.out.println("beforeClass1" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @AfterClass public void afterClass() { System.out.println("afterClass2" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } }
package testNGSelenium.testClassesParallelism; import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass; import org.testng.annotations.Test; public class ClassesParallelism2 { @Test public void f() { System.out.println("test2" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @BeforeClass public void beforeClass() { System.out.println("beforeClass2" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @AfterClass public void afterClass() { System.out.println("afterClass2" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } }
对应XML的设置:
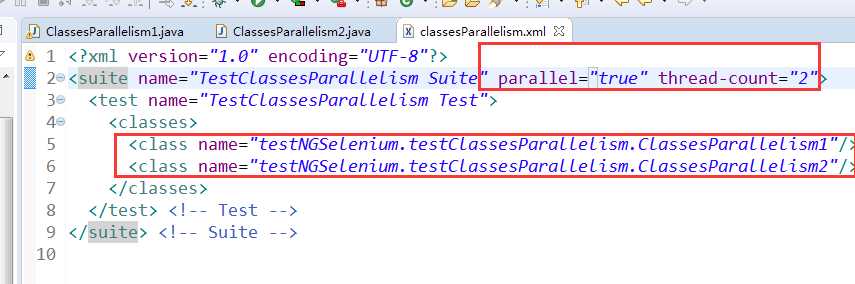
该代码的执行结果为:
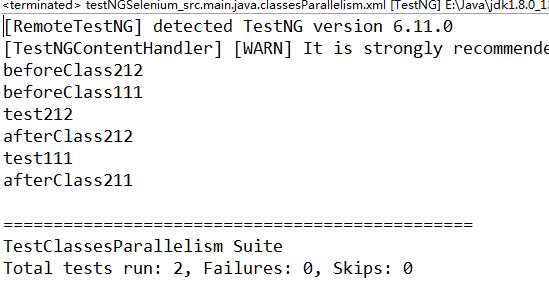
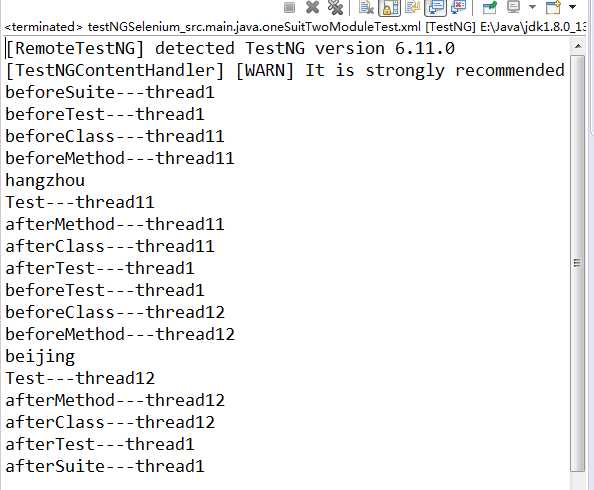
三:同一套间中的不同组件并行
package testOneSuitTwoTest; import org.testng.annotations.Test; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeMethod; import org.testng.annotations.AfterMethod; import org.testng.annotations.DataProvider; import org.testng.annotations.Parameters; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass; import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest; import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeSuite; import org.testng.annotations.AfterSuite; public class OneSuitTwoModuleTest { @Test @Parameters({"location"}) public void f(String p) { System.out.println(p); System.out.println("Test---thread" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @BeforeMethod public void beforeMethod() { System.out.println("beforeMethod---thread" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @AfterMethod public void afterMethod() { System.out.println("afterMethod---thread" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } /* @DataProvider public Object[][] dp() { return new Object[][] { new Object[] { 1, "a" }, new Object[] { 2, "b" }, }; }*/ @BeforeClass public void beforeClass() { System.out.println("beforeClass---thread" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @AfterClass public void afterClass() { System.out.println("afterClass---thread" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @BeforeTest public void beforeTest() { System.out.println("beforeTest---thread" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @AfterTest public void afterTest() { System.out.println("afterTest---thread" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @BeforeSuite public void beforeSuite() { System.out.println("beforeSuite---thread" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @AfterSuite public void afterSuite() { System.out.println("afterSuite---thread" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); } }
对应的XML设置为:
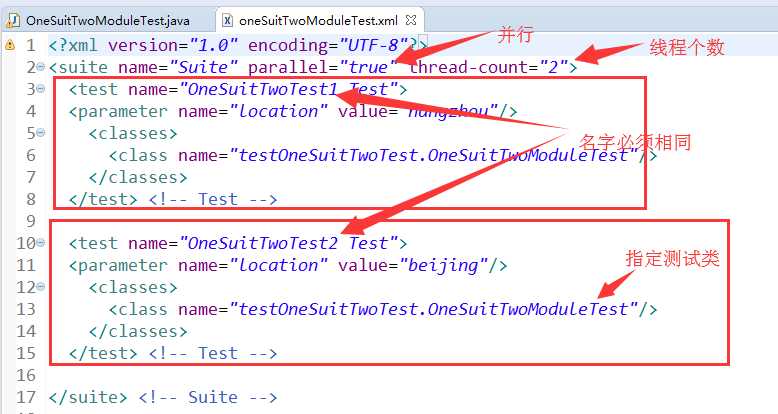
上面代码的执行结果为;
四:多线程执行某方法
package testNGSelenium.moreThreadTest; import org.testng.annotations.Test; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest; import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest; public class MoreThreadTest { //这里代表 启动三个线程,该方法总共执行9遍,设置每个线程的执行时间最大为2S,超过2S之后就算执行失败 @Test(threadPoolSize=3,invocationCount=9,timeOut=2000) public void f() { System.out.println("Test---threadId:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()); } @BeforeTest public void beforeTest() { } @AfterTest public void afterTest() { } }
对应的XML文件并没有特别设置啥参数。
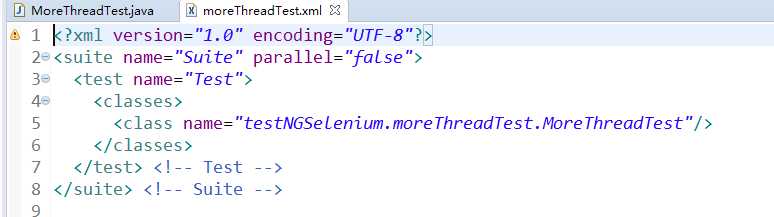
执行结果为: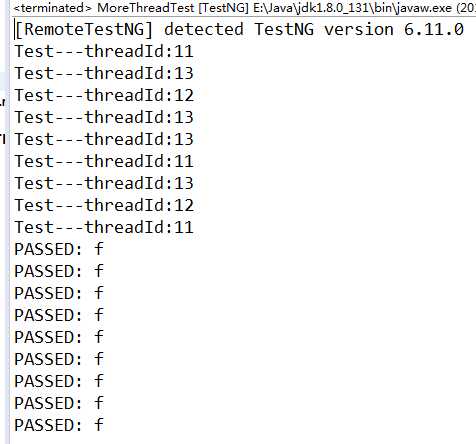
以上是关于自动化测试--testNG的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
