UVA297:Quadtrees(四分树)
Posted alphawa
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了UVA297:Quadtrees(四分树)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题目描述
四象树是每个内结点均有4个子结点的特殊四叉树,它可用于描述平面上黑白图像。平面上的黑白图像是32行×32列的正方形,每个格子称为1个象素,是最小的图像单位。正方形图像可分成四个相等的小正方形,可按直角坐标系四个象限的顺序分别编号1,2,3,4,分别对应于四象树的四个子结点。这样,32行×32列的图像就对应于一棵深度为6的完全四叉树,最底层的每个叶结点正好对应于一个象素。但我们可以压缩四象树的结点数量。
当图像上某个区域为全白或者全黑时,可把该区域在四象树上对应的结点描述为全白(用小写字母e表示)或者全黑(用小写字母f表示),并且对这样的结点不再扩展子结点,因为再扩展出的子树上每个结点都是相同的颜色。
只有当图像上某个区域为“杂色”时,才继续划分成四个子区域(在四象树上对应的结点用小写字母p表示),然后“纯”色的子区域也不再扩展,并继续扩展“杂”色子区域。例如,下图左、中两个图像可分别用它们下边的四象树描述。
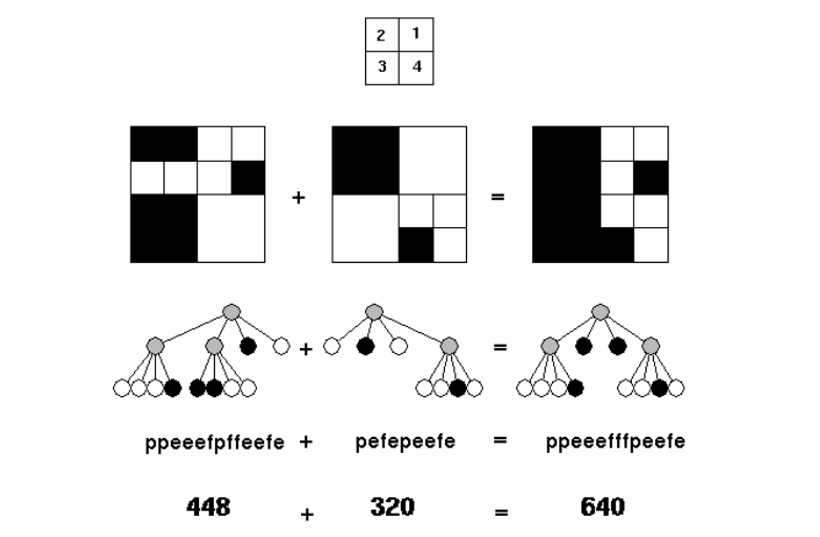
我们感兴趣的问题是:当两个大小均为32*32的黑白图像叠加后,合成的新图像是什么样子。合成的规则是:当一个图像上某个区域为全黑时,新图像的这个区域即为全黑;当一个图像上某个区域为全白时,新图像的这个区域的颜色是另加一个图像上这个区域的颜色。上图准确地示例了本合成的规则。
我们给出两个图像对应四象树的先序遍历顺序,求合成后的图像中,黑色象素点的数量。
输入
多组测试数据,第1行一个整数T,表示测试数据的组数,每组数据的格式为:
第1行:一个字符串,描述第1棵四象树的先序序列
第2行:一个字符串,描述第2棵四旬树的先序序列
输出
对每组数据,在单独一行上输出一个整数,表示合成后的图像上黑色象素的数量,格式如输出样例所示:
样例输入
3
ppeeefpffeefe
pefepeefe
peeef
peefe
peeef
peepefefe
样例输出
There are 640 black pixels.
There are 512 black pixels.
There are 384 black pixels.
我直接把BZOJ的翻译粘过来了(逃
思路1:数据量很小。我第一次写时直接模拟了两棵四叉树的建树与搜索,然后捎带着把最后的黑色个数算出来了。其中黑色结点的值跟它的深度有关,写一写就能找到规律。
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <cmath> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 struct node 8 { 9 char c; 10 node *ptr[4]; 11 node(){for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) ptr[i] = NULL;} 12 }; 13 14 node *root1, *root2; 15 16 int sum, cnt;//sum是最终结果,cnt是记录字符串走到哪个位置了 17 18 void release(node *root)//释放 19 { 20 if (!root) return; 21 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 22 release(root->ptr[i]); 23 delete root; 24 } 25 26 void build(string cur, node *&root)//建树,记得root要加地址符 27 { 28 root = new node(); 29 root->c = cur[cnt++]; 30 if (root->c == ‘p‘) 31 for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) 32 { 33 root->ptr[i] = new node(); 34 build(cur, root->ptr[i]); 35 } 36 } 37 38 void dfs(node *root1, node *root2, int depth) 39 { 40 //大概分了三种情况讨论 41 if (root1->c == ‘f‘ || root2->c == ‘f‘)//有一个是黑 42 { 43 sum += pow(4,6-depth);//数学可推…… 44 return; 45 } 46 else if (root1->c == ‘e‘ && root2->c == ‘e‘)//全是白 47 return; 48 //对于‘p‘的点深搜 49 bool flag1 = root1->c==‘p‘, flag2 = root2->c==‘p‘; 50 node *x = root1, *y = root2; 51 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 52 { 53 if (flag1) x = root1->ptr[i]; 54 if (flag2) y = root2->ptr[i]; 55 dfs(x, y, depth+1); 56 } 57 } 58 59 int main() 60 { 61 int test; 62 scanf("%d", &test); 63 64 while (test--) 65 { 66 sum = 0; 67 string s,t; 68 cin >> s >> t; 69 cnt = 0, build(s, root1); 70 cnt = 0, build(t, root2); 71 72 dfs(root1, root2, 1); 73 74 printf("There are %d black pixels. ", sum); 75 76 release(root1),release(root2); 77 } 78 79 return 0; 80 }
思路2:书上代码思路是在32*32的正方形里面涂色然后查找,貌似跟树也没什么关系了……书中的注释已经很明白了,见代码。(PS:UVA有毒)
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 4 const int len = 32; 5 const int maxn = 1024 + 10; 6 //下面这个char数组和int变量定义顺序变一下UVA居然会WA啊! 7 //我从未见过如此厚颜无耻之OJ 8 char s[maxn]; 9 int buf[len][len], cnt; 10 11 //把字符串s[p..]导出到以(r,c)为左上角,边长为w的缓冲区中 12 //2 1 13 //3 4 14 void draw(const char* s, int& p, int r, int c, int w) 15 { 16 char ch = s[p++]; 17 if (ch == ‘p‘) 18 { 19 draw(s, p, r , c+w/2, w/2);//1 20 draw(s, p, r , c , w/2);//2 21 draw(s, p, r+w/2, c , w/2);//3 22 draw(s, p, r+w/2, c+w/2, w/2);//4 23 } 24 else if (ch == ‘f‘) 25 for (int i = r; i < r+w; i++) 26 for (int j = c; j < c+w; j++) 27 if (buf[i][j] == 0) 28 buf[i][j] = 1,cnt++; 29 } 30 31 int main() 32 { 33 int t; 34 scanf("%d", &t); 35 36 while (t--) 37 { 38 memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); 39 cnt = 0; 40 for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) 41 { 42 scanf("%s",s); 43 int p = 0; 44 draw(s, p, 0, 0, len); 45 } 46 47 printf("There are %d black pixels. ", cnt); 48 49 } 50 51 return 0; 52 }
以上是关于UVA297:Quadtrees(四分树)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章