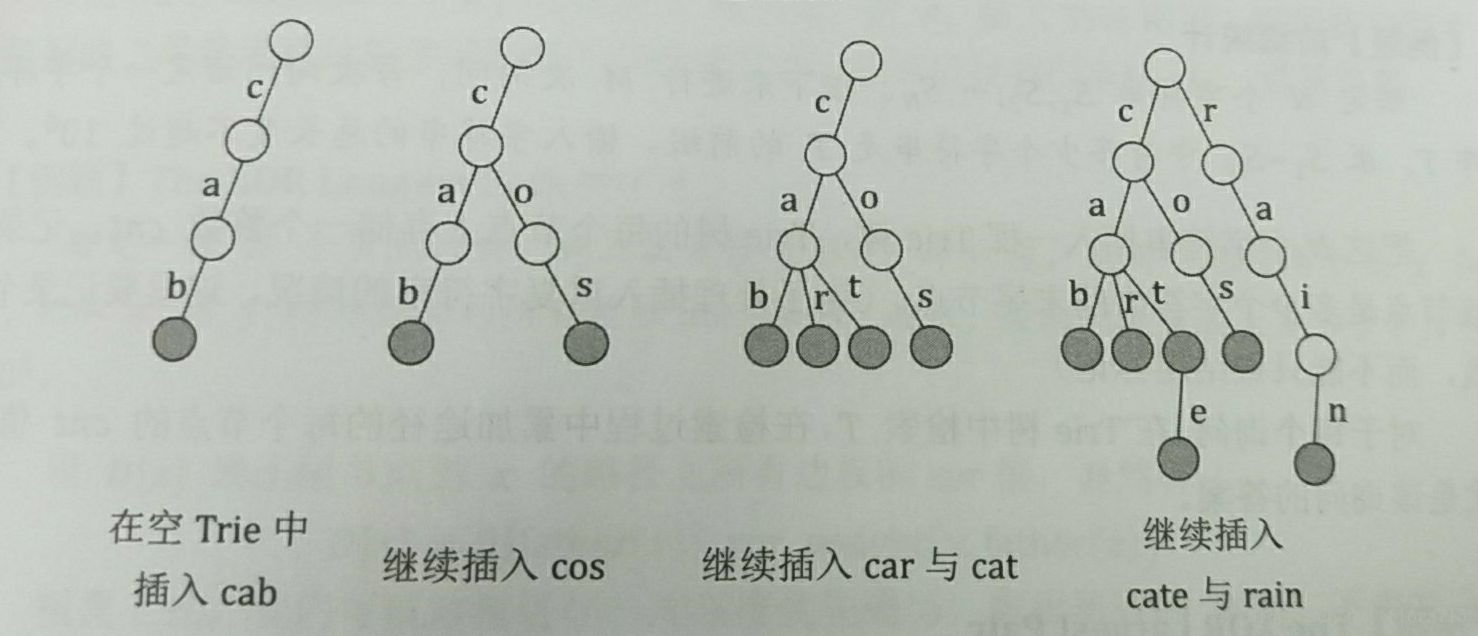
暖*墟 #trie# 字典树的运用
Posted floraloveryuuji
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了暖*墟 #trie# 字典树的运用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Trie,又称字典树
是一种用于实现字符串快速检索的多叉树结构。
每个节点都拥有若干个字符指针,若在插入或检索字符串时扫描到一个字符c ,
就沿着当前节点的c这个字符指针,走向该指针指的节点。
下面我们来详细讨论Trie的基本操作过程。
初始化
一棵空Trie仅包含一个根节点,该点的字符指针均指向空。
********* 根节点表示空串。*********
插入
当需要插入一个字符串S时,我们令一个指针P起初指向根节点。
然后,依次扫描S中的每个字符c。
1.若P的c字符指针指向一个已经存在的节点Q,则令P=Q。
2.若P的c字符指针指向空,则新建一个节点Q,令P的c字符指针指向Q,然后令P=Q。
当S中的字符扫描完毕时,在当前节点P上标记它是一个字符串的末尾。
检索
当需要检索一个字符串S在Trie中是否存在时,我们令一个指针P起初指向根节点,
然后依次扫描S中的每个字符c:
1.若P的c字符指针指向空,则说明S没有被插入过Trie,结束检索。
2.若P的的c字符指针指向一个已经存在的节点Q,则令P=Q。
当S中的字符扫描完毕时,若当前节点P被标记为一个字符串的末尾,
则说明S在Trie中存在,否则说明S没有被插入过Trie。
即先将字符传入字典树中,查询的时候从根节点向下层寻找(每层26个字母)。
任意一个线结点所表示的字符串,都是实际字符串集合中某些串的前缀。
——> 利用串的公共前缀,节约空间。可以看做26叉树(全是小写英文字母)。

bool tail[SIZE]; //串尾元素 int trie[SIZE][26],tot=1; //SIZE:字符串最大长度(层数) //tot为节点编号,用它可以在trie数组中表示某层的某字母是否存在 void insert(char* str){ //插入一个字符串 int len=strlen(str),p=1; //p初始化为根节点 for(int k=0;k<len;k++){ int ch=str[k]-‘a‘; //小写字符组成串的某个字符,变成数字 if(trie[p][ch]==0) trie[p][ch]=++tot; //trie存编号tot //↑↑↑不存在此层的这个字符,新建结点,转移边 p=trie[p][ch]; //指针移动,连接下一个位置 } tail[p]=true; //s中字符扫描完毕,p标记的是字符串的末位字符(的编号) } bool searchs(char* str){ //检索字符串是否存在 int len=strlen(str),p=1; //p初始化为根节点 for(int k=0;k<len;k++){ p=trie[p][str[k]-‘a‘]; //寻找下一处字符 //trie[lastp][ch1]=nowp; //trie[nowp][ch2]=nextp; //nowp=trie[nowp][ch2]=nextp; 即寻找下一处字符的编号 if(p==0) return false; //某层字符没有编号,不存在,即串也不存在 } return tail[p]; //判断最后一个字符 }
字典树trie 例题
#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【电话簿】 poj 3630 多组数据,每组n个长度不超过10的数字串, 问是否存在数字串S,T。使得S是T的前缀。 */ //构建Trie,过程中可以顺便判断答案 const int maxn=1e5+9; int trie[maxn][10]; //数字只有0~9 int n,tot,T; bool tail[maxn]; char s[20]; //每个串长度不超过10 void clears(){ //初始化清零 memset(trie,0,sizeof(trie)); memset(tail,false,sizeof(tail)); } bool insert(char* s){ //插入一个字符串T,判断S是不是它的前缀 int len=strlen(s),p=1; //p初始化为根节点 bool flag=false; for(int k=0;k<len;k++){ int ch=s[k]-‘0‘; //小写字符组成串的某个字符,变成数字 if(trie[p][ch]==0) trie[p][ch]=++tot; //trie存编号tot //↑↑↑不存在此层的这个字符,新建结点,转移边 else if(k==len-1) flag=true; //没有插入任何新节点 p=trie[p][ch]; //指针移动,连接下一个位置 if(tail[p]) flag=true; //经过某个有标记的结点,即完成了某个串 } tail[p]=true; //s中字符插入完毕,p标记的是字符串的末位字符(的编号) return flag; } int main(){ scanf("%d",&T); while(T--){ scanf("%d",&n); tot=1; //tot是编号数 clears(); bool ans=false; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%s",s); if(insert(s)) ans=true; } if(ans) puts("YES"); else puts("NO"); } return 0; }
(2)【按位异或】 bzoj 4260

#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【按位异或】 bzoj 4260 */ /*【分析】设l[i]表示1<=l<=r<=i的最大a[l]^a[l+1]^...^a[r], r[i]表示i<=l<=r<=n的最大a[l]^a[l+1]^...^a[r], 则结果为最大的l[i]+r[i+1]。问题转化为求l[i]和r[i]。 设x[i]表示a[0]^a[1]^...^a[i](a[0]=0),那么l[i]=max(x[i]^x[j])(j<i) */ /*【求一组数中两个数 异或 得到的最大值】 把每个整数看成长度为31的二进制01串(在前面补0), 并把31位的串插进一棵trie树(最低二进制位为叶节点), 进行类似查找的过程:沿着“与当前位相反的字符指针”向下层访问。 如果“与ai当前位相反的字符指针”指向空节点,就访问ai当前位指针。 根据xor运算“相同=0,不同=1”,求出异或值最大的ai和aj。 */ const int maxn=4e5+9; int trie[maxn<<5][2]; //数字只有0~9 int n,tot=1,l[maxn],r[maxn],a[maxn]; void clears(){ //初始化清零 memset(trie,0,sizeof(trie)); } void insert(int x){ //插入一个二进制数 //将当前的前/后缀异或和化为31位二进制数,插入trie树 int p=1; //p初始化为根节点 for(int i=1<<30;i;i>>=1){ //每次除二 int c=(x&i)? 1:0; if(trie[p][c]==0) trie[p][c]=++tot; //trie存编号tot //↑↑↑不存在此层的这个字符,新建结点,转移边 p=trie[p][c]; //指针移动,连接下一个位置 } } int finds(int x){ //找目前最大的两数异或和 int p=1,ans=0; for(int i=1<<30;i;i>>=1){ //从高位到低位,尽量让异或和高位为1 int c=(x&i)? 0:1; //每一位反过来 if(trie[p][c]){ //这一位记录过,可以继续 ans+=i; p=trie[p][c]; //查询与相反相连的下一位 } else p=trie[p][!c]; //否则这一位只能为0,连接与相同相连的下一位 } return ans; } int main(){ int now,ans=0; scanf("%d",&n); insert(now=0); //存a[0]的异或值 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d",&a[i]); now^=a[i]; //now为a[0]~a[i]的异或和 insert(now); l[i]=max(l[i-1],finds(now)); //l[i]表示1<=l<=r<=i的最大a[l]^a[l+1]^...^a[r] } clears(); tot=1; insert(now=0); //重新初始化 for(int i=n;i>=1;i--){ now^=a[i]; //now为a[n]~a[i]的异或和 insert(now); r[i]=max(r[i+1],finds(now)); //r[i]表示i<=l<=r<=n的最大a[l]^a[l+1]^...^a[r] } for(int i=1;i<n;i++) ans=max(ans,l[i]+r[i+1]); printf("%d ",ans); return 0; }
(3)【IMMEDIATE DECODABILITY】poj 1056
#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【IMMEDIATE DECODABILITY】poj 1056 给你一些字符串,每组数据以9结尾,判断给出的字符串中, 是否存在一个字符串是另外一个字符串的前缀(如:01为010的前缀); 如果存在至少一组这种情况输出:Set %d is not immediately decodable ; 不存在则输出:Set %d is immediately decodable 。 */ //构建Trie,过程中可以顺便判断答案 const int maxn=1e5+9; int trie[maxn][10]; //数字只有0~9 int tot=1; bool tail[maxn]; char s[20]; //每个串长度不超过10 void clears(){ //初始化清零 memset(trie,0,sizeof(trie)); memset(tail,false,sizeof(tail)); } bool insert(char* s){ //插入一个字符串T,判断S是不是它的前缀 int len=strlen(s),p=1; //p初始化为根节点 bool flag=false; for(int k=0;k<len;k++){ int ch=s[k]-‘0‘; //小写字符组成串的某个字符,变成数字 if(trie[p][ch]==0) trie[p][ch]=++tot; //trie存编号tot //↑↑↑不存在此层的这个字符,新建结点,转移边 else if(k==len-1) flag=true; //没有插入任何新节点 p=trie[p][ch]; //指针移动,连接下一个位置 if(tail[p]) flag=true; //经过某个有标记的结点,即完成了某个串 } tail[p]=true; //s中字符插入完毕,p标记的是字符串的末位字符(的编号) return flag; } int main(){ int kase=1,flag=0; while(scanf("%s",s)!=EOF){ if(s[0]==‘9‘){ if(!flag) printf("Set %d is immediately decodable ",kase++); else printf("Set %d is not immediately decodable ",kase++); flag=0; tot=1; clears(); continue; } if(!flag&&insert(s)) flag=1; } return 0; }
(4)【L语言】bzoj 1212
#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【bzoj 1212】L语言 标点符号的出现晚于文字的出现,所以以前的语言都是没有标点的。 现在你要处理的就是一段没有标点的文章。一段文章T是由若干小写字母构成。 一个单词W也是由若干小写字母构成。一个字典D是若干个单词的集合。 我们称一段文章T在某个字典D下是可以被理解的,是指如果文章T可以被分成若干部分, 且每一个部分都是字典D中的单词。 例如字典D中包括单词{‘is’, ‘name’, ‘what’, ‘your’}, 则文章‘whatisyourname’是在字典D下可以被理解的,因为它可以分成4个单词:‘what’, ‘is’, ‘your’, ‘name’, 且每个单词都属于字典D,而文章‘whatisyouname’ 在字典D下不能被理解, 但可以在字典D’=D+{‘you’}下被理解。这段文章的一个前缀‘whatis’, 也可以在字典D下被理解 而且是在字典D下能够被理解的最长的前缀。 给定一个字典D,你的程序需要判断若干段文章在字典D下是否能够被理解。 并给出其在字典D下能够被理解的最长前缀的位置。 */ //【分析】令f[i]表示到i的前缀能否被理解,那么答案就是f[i]==1时最大的i。 // 如果f[i]==1,这个串就可以从i+1开始匹配一个新单词,设trie上匹配到一个长度为j的单词,那么f[i+j]=1。 const int maxn=(1<<20)+10; int n,m,len,f[maxn]; char s[maxn]; struct trie{ int tot,ch[2010][26];bool ok[maxn]; void insert(){ int p=0,len=strlen(s); for(int i=0;i<len;p=ch[p][s[i]-‘a‘],i++) if(!ch[p][s[i]-‘a‘]) ch[p][s[i]-‘a‘]=++tot; ok[p]=1; //队尾标记 } }T; int work(int t){ int ans=0; len=strlen(s+1); f[0]=t; for(int i=0;i<=len;i++){ if(f[i]!=t) continue; else ans=i; for(int p=0,j=i+1;j<=len;j++){ p=T.ch[p][s[j]-‘a‘]; if (!p) break; if (T.ok[p]) f[j]=t; } } return ans; } int main(){ scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%s",s),T.insert(); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) scanf("%s",s+1),printf("%d ",work(i)); return 0; }
(5)bzoj 1590 / bzoj 4567 / bzoj 1954
——时间划过风的轨迹,那个少年,还在等你。
以上是关于暖*墟 #trie# 字典树的运用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章