深入理解系统调用
Posted fengyakk
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了深入理解系统调用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、实验目的
1.找一个系统调用,系统调用号为学号最后2位相同的系统调用,本人学号最后两位为80,即要测试的系统调用号为80
2.通过汇编指令触发该系统调用
3.通过gdb跟踪该系统调用的内核处理过程
4.重点阅读分析系统调用入口的保存现场、恢复现场和系统调用返回,以及重点关注系统调用过程中内核堆栈状态的变化
二、环境准备
安装开发工具:
sudo apt install build-essential sudo apt install qemu # install QEMU sudo apt install libncurses5-dev bison ?ex libssl-dev libelf-dev
下载内核源码:(本人的多线程下载老是出现问题,于是直接去网站下载了linux-5.4.34.tar.xz)
sudo apt install axel axel -n 20 https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v5.x/ linux-5.4.34.tar.xz xz -d linux-5.4.34.tar.xz tar -xvf linux-5.4.34.tar cd linux-5.4.34
配置内核选项:
make defconfig #Default configuration is based on ‘x86_64_defconfig‘ make menuconfig #打开debug相关选项 Kernel hacking ---> Compile-time checks and compiler options ---> [*] Compile the kernel with debug info [*] Provide GDB scripts for kernel debugging [*] Kernel debugging #关闭KASLR,否则会导致打断点失败 Processor type and features ----> [] Randomize the address of the kernel image (KASLR)
编译和运行内核:
make -j$(nproc)
# 测试一下内核能不能正常加载运行,因为没有文件系统最终会kernel panic
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage
制作根文件系统:
axel -n 20 https://busybox.net/downloads/busybox-1.31.1.tar.bz2 tar -jxvf busybox-1.31.1.tar.bz2 cd busybox-1.31.1 make menucon?g #记得要编译成静态链接,不?动态链接库。 Settings ---> [*] Build static binary (no shared libs) #然后编译安装,默认会安装到源码?录下的 _install ?录中。 make -j$(nproc) && make install
制作内存根文件系统镜像:
mkdir rootfs cd rootfs cp ../busybox-1.31.1/_install/* ./ -rf mkdir dev proc sys home sudo cp -a /dev/{null,console,tty,tty1,tty2,tty3,tty4} dev/
准备init脚本文件放在根文件系统跟目录下(rootfs/init),添加如下内容到init文件:
#!/bin/sh mount -t proc none /proc mount -t sysfs none /sys echo "Wellcome MyOS!" echo "--------------------" cd home
/bin/sh
给init脚本添加可执行权限:
chmod +x init
打包成内存根文件系统镜像:
find . -print0 | cpio --null -ov --format=newc | gzip -9 > ../rootfs.cpio.gz
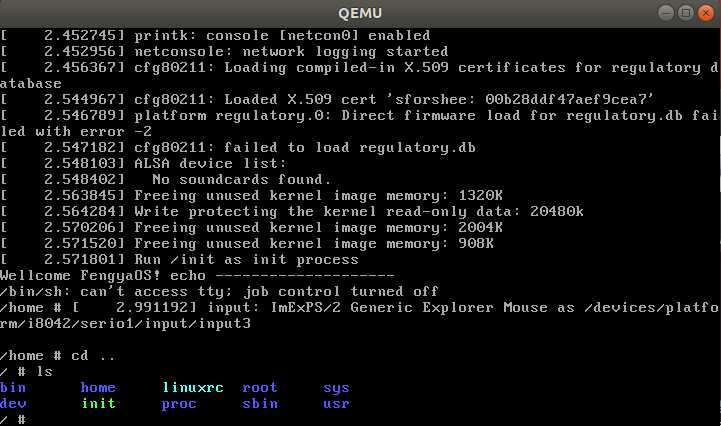
测试挂载根文件系统,看内核启动完成后是否执行init脚本:
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.cpio.gz
运行结果如下所示:
三、查看系统调用并编写调用汇编代码
1. 打开/linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_64.tbl
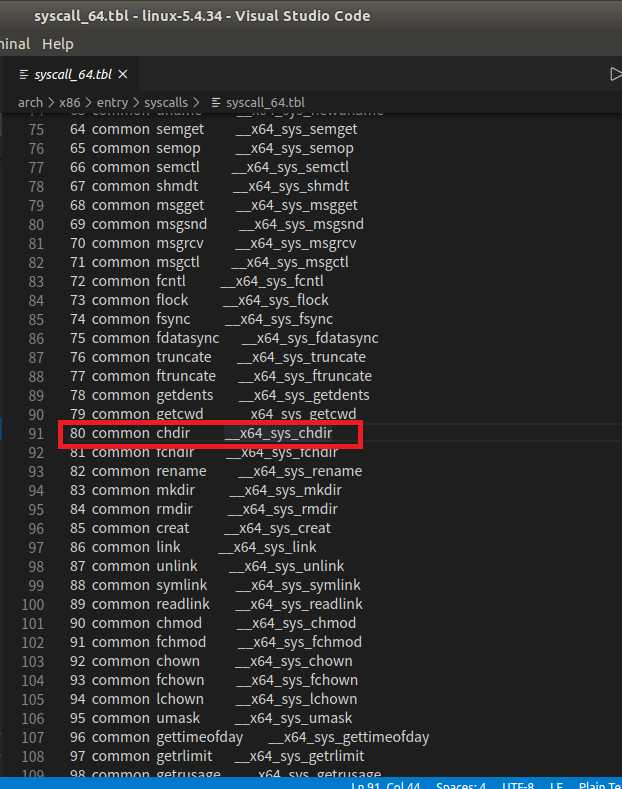
查表可见,系统调用号为80的命令为chdir,作用是改变当前进程的工作路径。
2.编写汇编调用代码
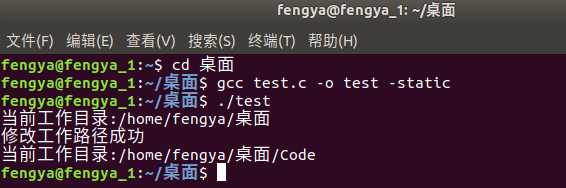
首先写一个非汇编版本的:
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> int main() { char path[30]; char name[30]="/home/fengya/桌面/Code"; //这个路径必须存在,否则肯定修改路径失败 int res; getcwd(path,30); printf("当前工作目录:%s ",path); res=chdir(name); if( res == 0 ) { printf("修改工作路径成功 "); getcwd(path,30); printf("当前工作目录:%s ",path); } else { printf("修改工作路径失败"); return 1; } }
编译运行结果如下所示:
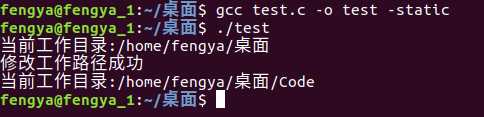
现在将代码中的系统调用换成用汇编代码触发:
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> int main() { char path[30]; char name[30]="/home/fengya/桌面/Code"; int res; getcwd(path,30); printf("当前工作目录:%s ",path); //res=chdir(name); asm volatile( "movq %1, %%rdi " // 参数1 "movl $0x50,%%eax " // 传递系统调用号80 "syscall " // 系统调用 "movq %%rax,%0 " // 结果存到%0 就是res中 :"=m"(res) // 输出 :"a"(name) //输入 ); if( res == 0 ) { printf("修改工作路径成功 "); getcwd(path,30); printf("当前工作目录:%s ",path); } else { printf("修改工作路径失败"); return 1; } }
编译运行结果如下:
3.将代码放入rootfs/home目录下(注意路径要改成在qemu系统中存在的路径,否则之后运行无法成功修改路径),重新制作根文件系统
?nd . -print0 | cpio --null -ov --format=newc | gzip -9 > ../rootfs.cpio.gz
四、GDB调试与分析
1. 纯命令行启动qemu
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.cpio.gz -S -s -nographic -append "console=ttyS0"
此时停留在以下界面
2.打开另一个终端,进入linux-5.4.34文件夹,输入:
gdb vmlinux
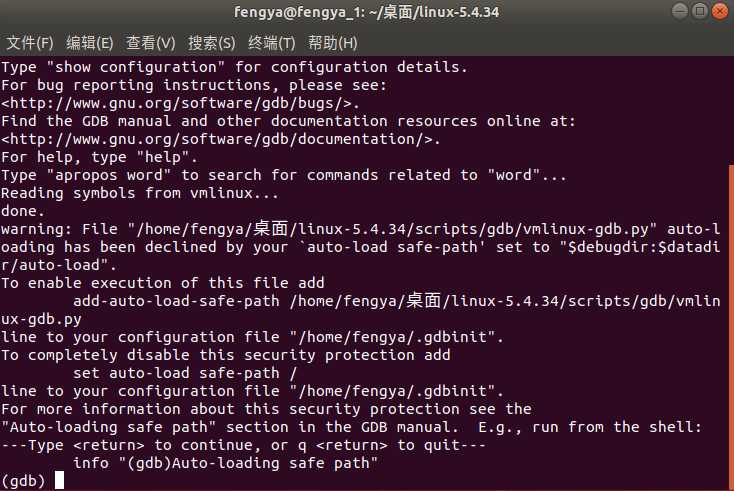
在gdb中运行:
target remote:1234
然后再gdb输入命令c,使得虚拟机继续执行,到初始界面
然后在qemu中测试之前放入的系统调用代码是否可以正常执行:
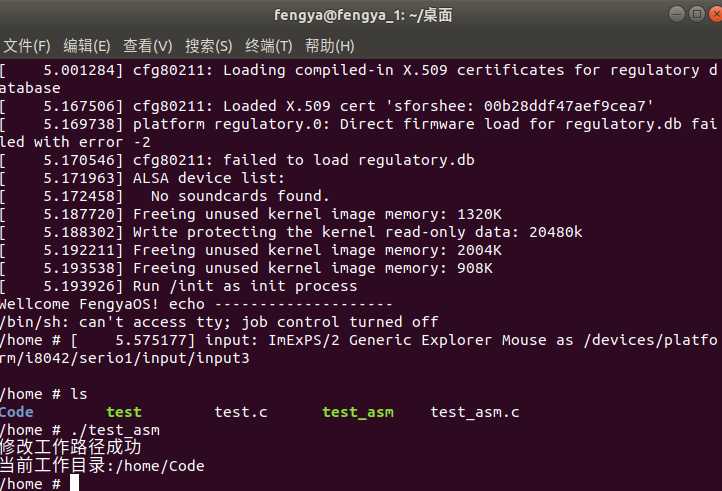
然后在gdb中给80号系统调用__x64_sys_chdir打上断点:
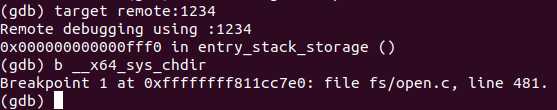
然后输入c(continue)继续运行,因为系统启动过程中也会多次调用chdir,因此需要多次输入c
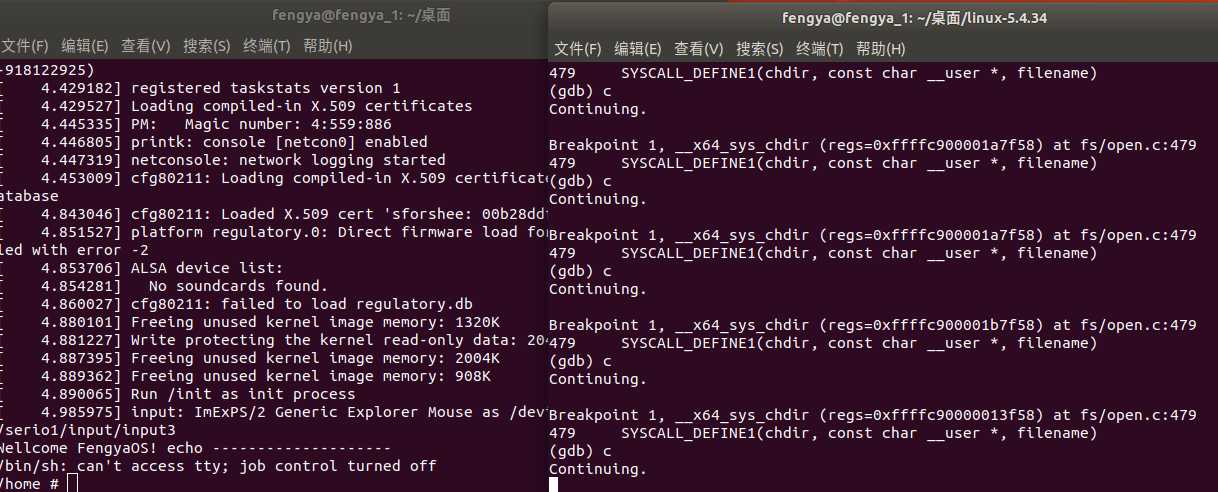
运行编写好的调用系统调用的代码,并进行gdb单步调试(输入n逐行执行)
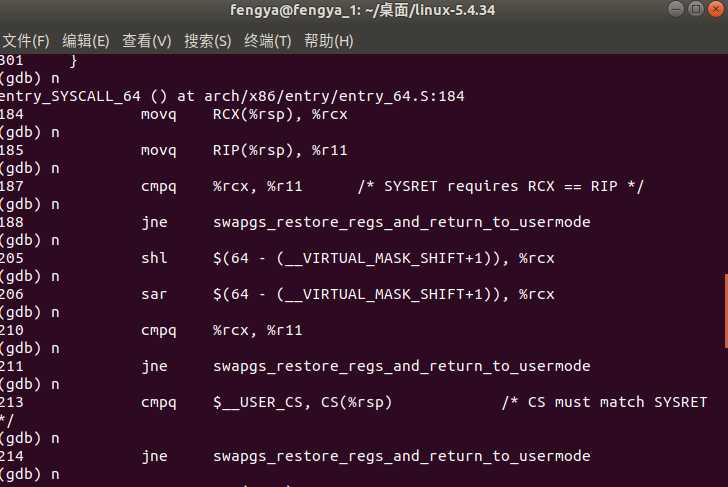
五、结果分析
通过断点进行单步调试,运行结果如下所示:
(gdb) n do_syscall_64 (nr=18446612682183950656, regs=0xffffc900001b7f58) at arch/x86/entry/common.c:300 300 syscall_return_slowpath(regs); (gdb) n 301 } (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:184 184 movq RCX(%rsp), %rcx (gdb) n 185 movq RIP(%rsp), %r11 (gdb) n 187 cmpq %rcx, %r11 /* SYSRET requires RCX == RIP */ (gdb) n 188 jne swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (gdb) n 205 shl $(64 - (__VIRTUAL_MASK_SHIFT+1)), %rcx (gdb) n 206 sar $(64 - (__VIRTUAL_MASK_SHIFT+1)), %rcx (gdb) n 210 cmpq %rcx, %r11 (gdb) n 211 jne swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (gdb) n 213 cmpq $__USER_CS, CS(%rsp) /* CS must match SYSRET */ (gdb) n 214 jne swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (gdb) n 216 movq R11(%rsp), %r11 (gdb) n 217 cmpq %r11, EFLAGS(%rsp) /* R11 == RFLAGS */ (gdb) n 218 jne swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (gdb) n 238 testq $(X86_EFLAGS_RF|X86_EFLAGS_TF), %r11 (gdb) n 239 jnz swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (gdb) n 243 cmpq $__USER_DS, SS(%rsp) /* SS must match SYSRET */ (gdb) n 244 jne swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (gdb) n 253 POP_REGS pop_rdi=0 skip_r11rcx=1 (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:259 259 movq %rsp, %rdi (gdb) n 260 movq PER_CPU_VAR(cpu_tss_rw + TSS_sp0), %rsp (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:262 262 pushq RSP-RDI(%rdi) /* RSP */ (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:263 263 pushq (%rdi) /* RDI */ (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:271 271 SWITCH_TO_USER_CR3_STACK scratch_reg=%rdi (gdb) n 273 popq %rdi (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:274 274 popq %rsp (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:275 275 USERGS_SYSRET64 (gdb) n 0x0000000000400ba5 in ?? ()
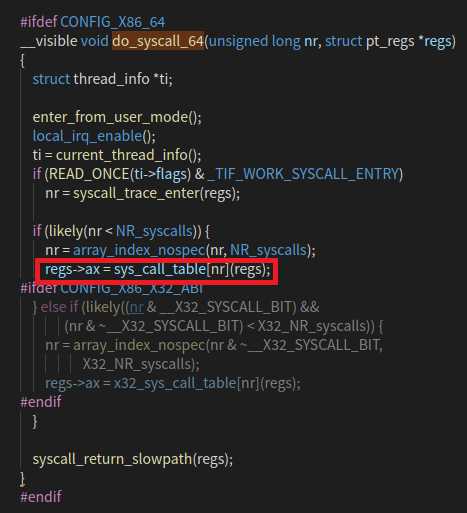
1.汇编指令触发系统调用,找到函数中断入口,执行 entry_SYSCALL_64() ,通过 swapgs 指令保存现场,触发 do_syscall_64 。
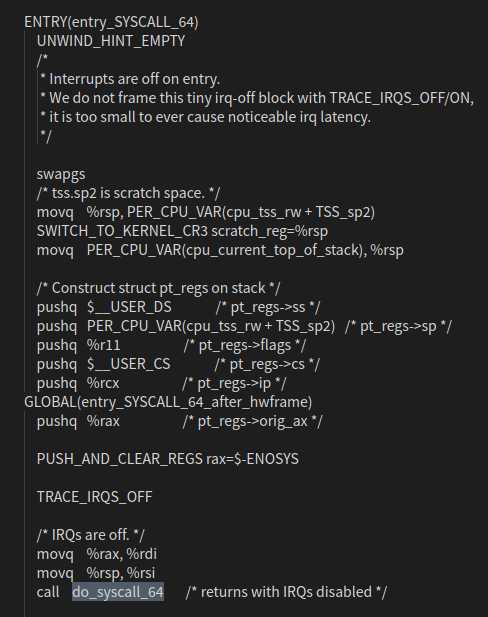
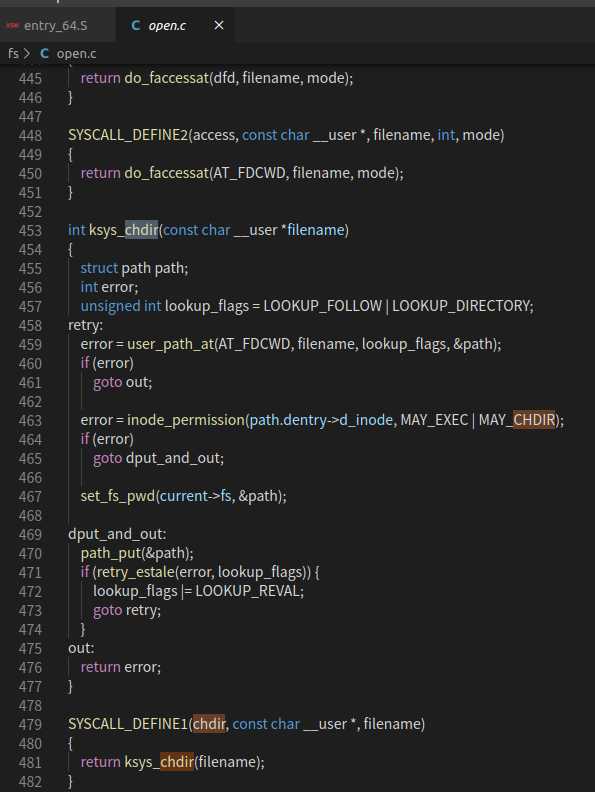
2.通过 do_syscall_64 函数得到了 系统调用号,执行系统调用内容。然后程序跳到 fs/open.c文件,触发了 ksys_chdir() 函数,执行完毕后,又跳回了do_syscall_64 中的 syscall_return_slowpath() ,准备进行现场恢复操作,并准备跳回用户态。
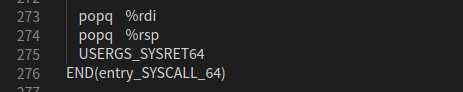
3.最后回到 entry_SYSCALL_64() 执行 popq ,完成堆栈切换。
以上是关于深入理解系统调用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章