iOS 内存管理
Posted xiaoxiaobukuang
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了iOS 内存管理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
内容管理相关问题
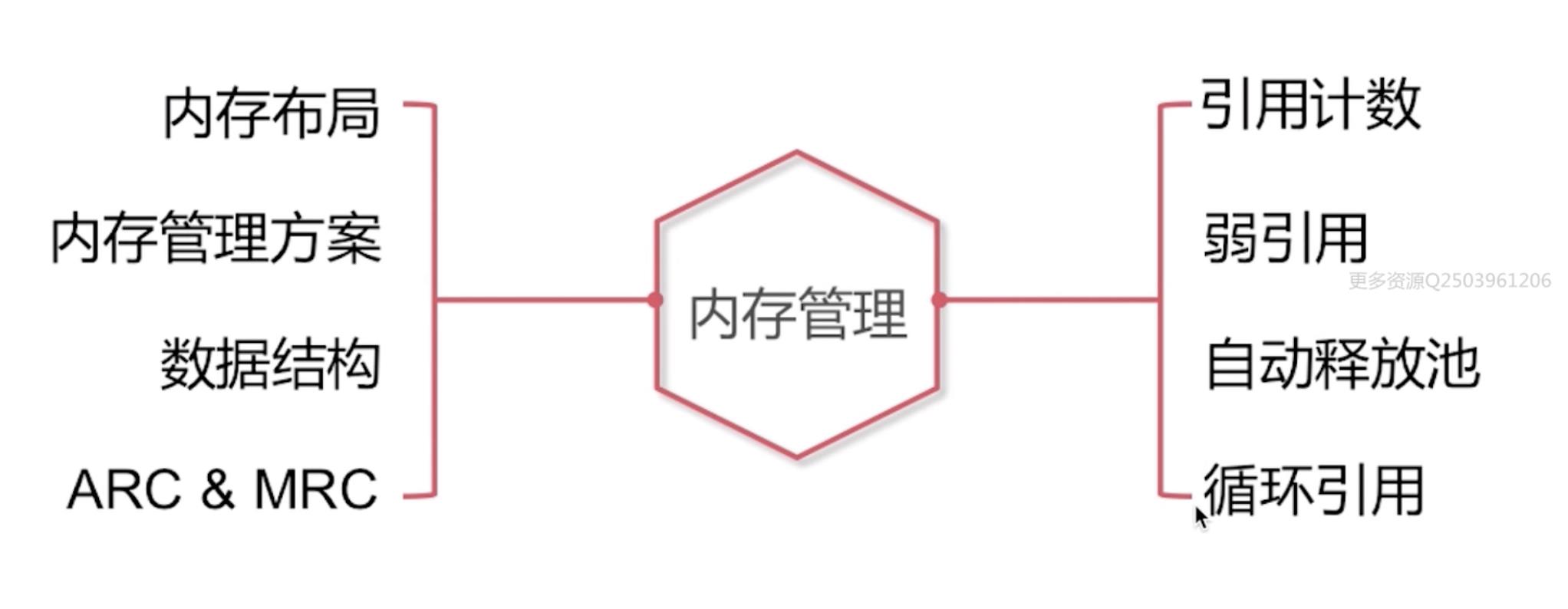
一、内存布局
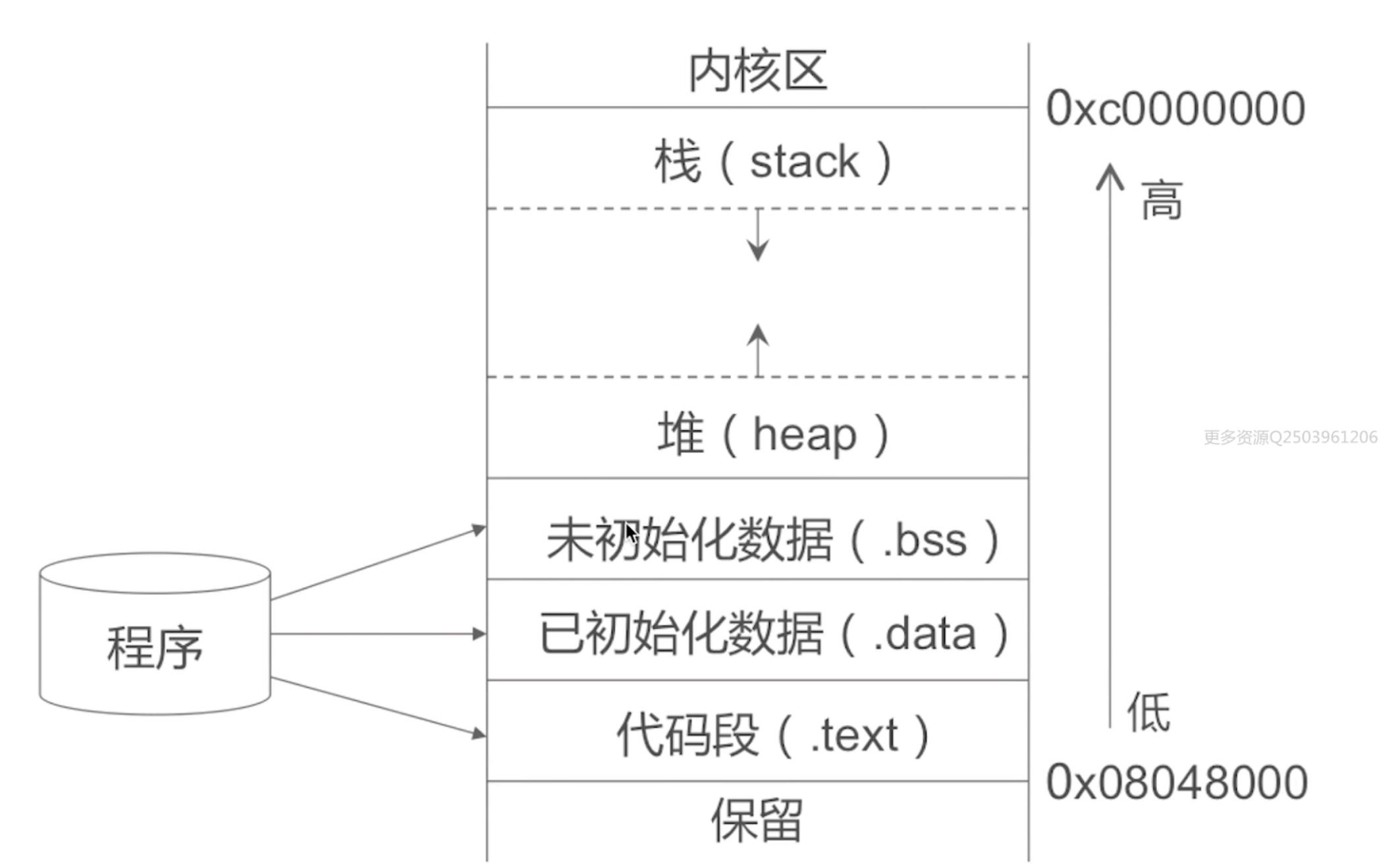
- stack(栈区):方法调用
- heap(堆区):通过alloc等分配的对象
- bss(未初始化数据):未初始化的全局变量等
- data(已初始化数据):已初始化的全局变量等
- text(代码段):程序代码
二、内存管理方案
- TaggedPointer:用于优化NSNumber,NSDate,NSString等小对象的存储。NSNumber指针里边存储的数据是:tag+data,也就是直接将数据存储在指针里。这样做特别节省空间。如果这个数据特别大,指针存储不下这个数,那么会恢复之前的存储方式,存储在堆区,然后指针存放堆区的地址。
- NONPOINTER_ISA:非指针型的isa,对于64位下的,isa 指针占64个比特位,但是其中可能只有32位够用了,剩余的就浪费了,苹果为了不让内存浪费更好的管理内存,剩下的32位,苹果用来存储和内存管理相关的内容,用来节约内存。
- 散列表:引用计数表和弱引用表等
1、NONPOINTER_ISA
在arm64架构下,指针在内存中占8个字节/byte,即64位/bit(1byte=8bit),64比特位中存储的内容有:
- 标记是否是纯的ISA指针,还是非指针型的NOPOINTER_ISA指针indexed
- 标记是否有关联对象has_assoc
- 标记对象是否使用到的C++相关内容,在ARC环境下标记对象是否通过ARC来管理的has_cxx_dtor
- 标记当前对象的类对象的指针地址shiftcls
- magic
- 标记对象是否有弱引用指针weakly_referenced
- 标记对象是否正在进行dealloc操作deallocating
- 标记是否有sitetable结构用于存储引用计数has_sidetable_rc
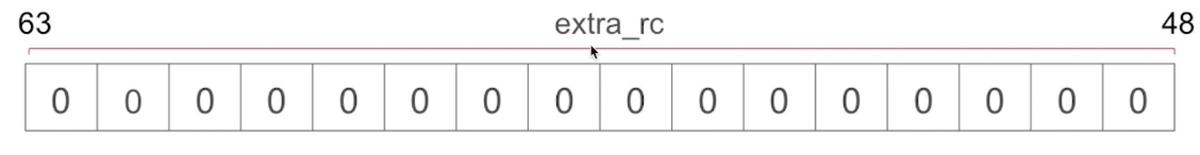
- 标记对象的引用计数(首先会存储在该字段中,当到达上限后,在存入对应的引用计数表中)extra_rc



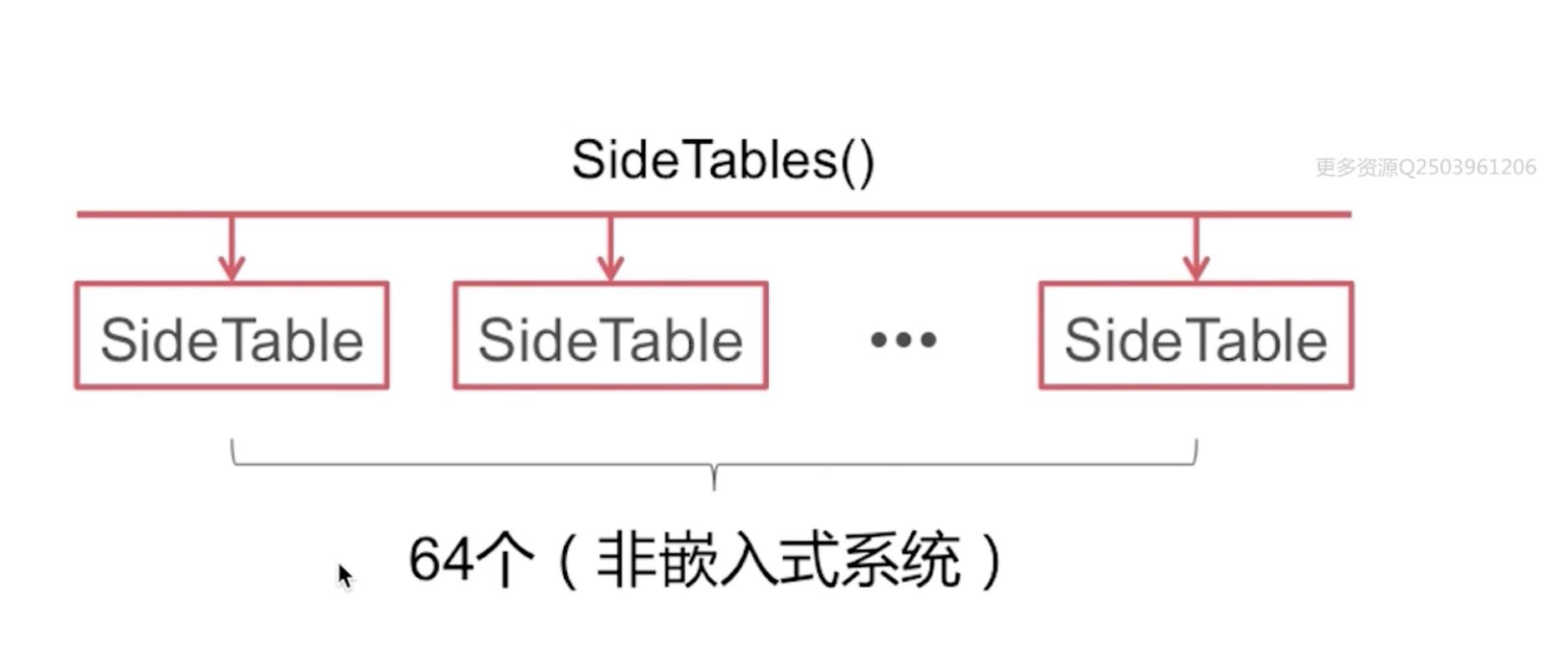
2、散列表方式
SideTables()结构:实际上是一个hash 表,下面挂了很多的 sideTable,sidetable 包括自旋锁(spinlock_t),引用计数表(refcountMap),弱引用表(weak_table_t)。

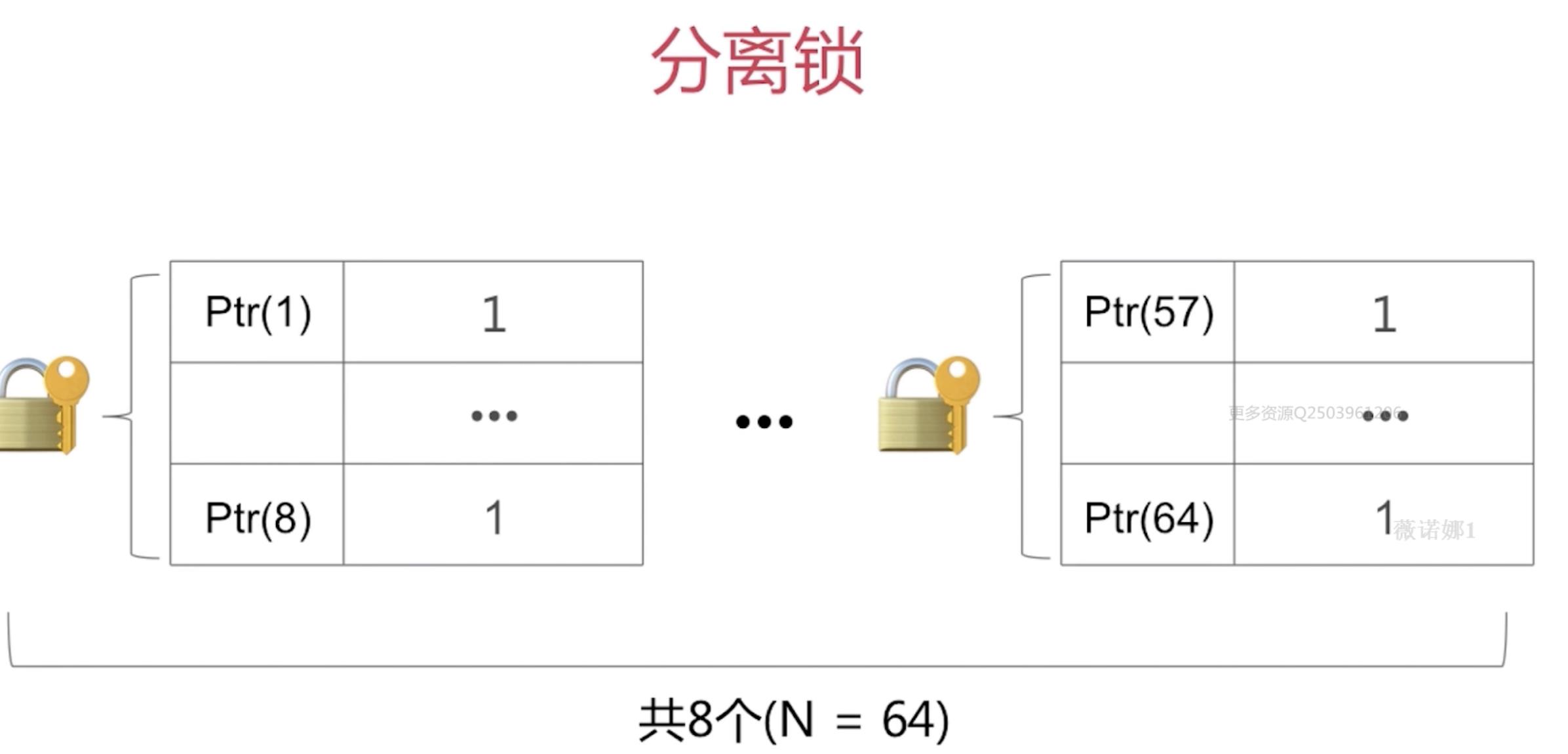
3、怎样实现快速分流
Side Tables的本质是一张Hash表。

通过给定值是对象内存地址,目标值是数组下标索引。
三、数据结构
- Spinlock_t:自旋锁
- RefcountMap:引用计数表
- weak_table_t:弱引用表
1、Spinlock_t(自旋锁)
- Spinlock_t是“忙等”的锁;
- 适用于轻量访问;
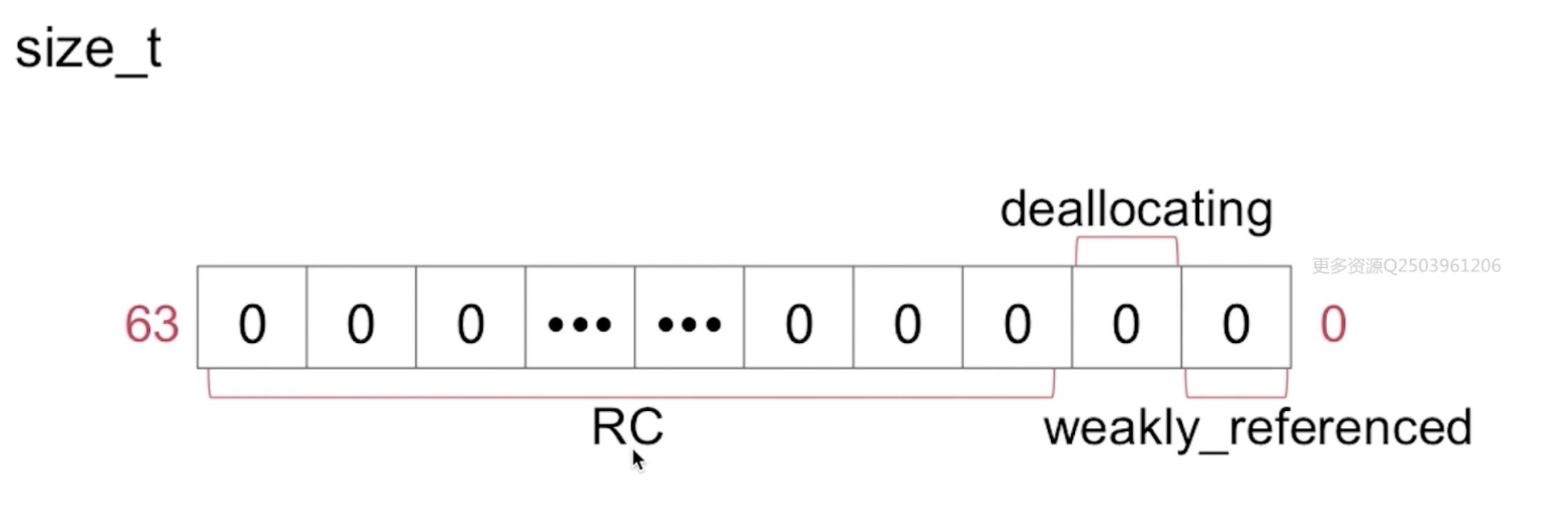
2、RefcountMap(引用计数表)
其实就是hash查找,提高查找效率,插入和查找通过同一个hash函数来获取,避免了循环遍历。ptr->hash->size_t,其中的size_t就是引用计数值,比如用64位存储,第一位表示(weakly_referenced),表示对象是否存在弱引用,下一位表示当前对象是都正在dealoc(deallocating),剩下的位表示引用计数值。

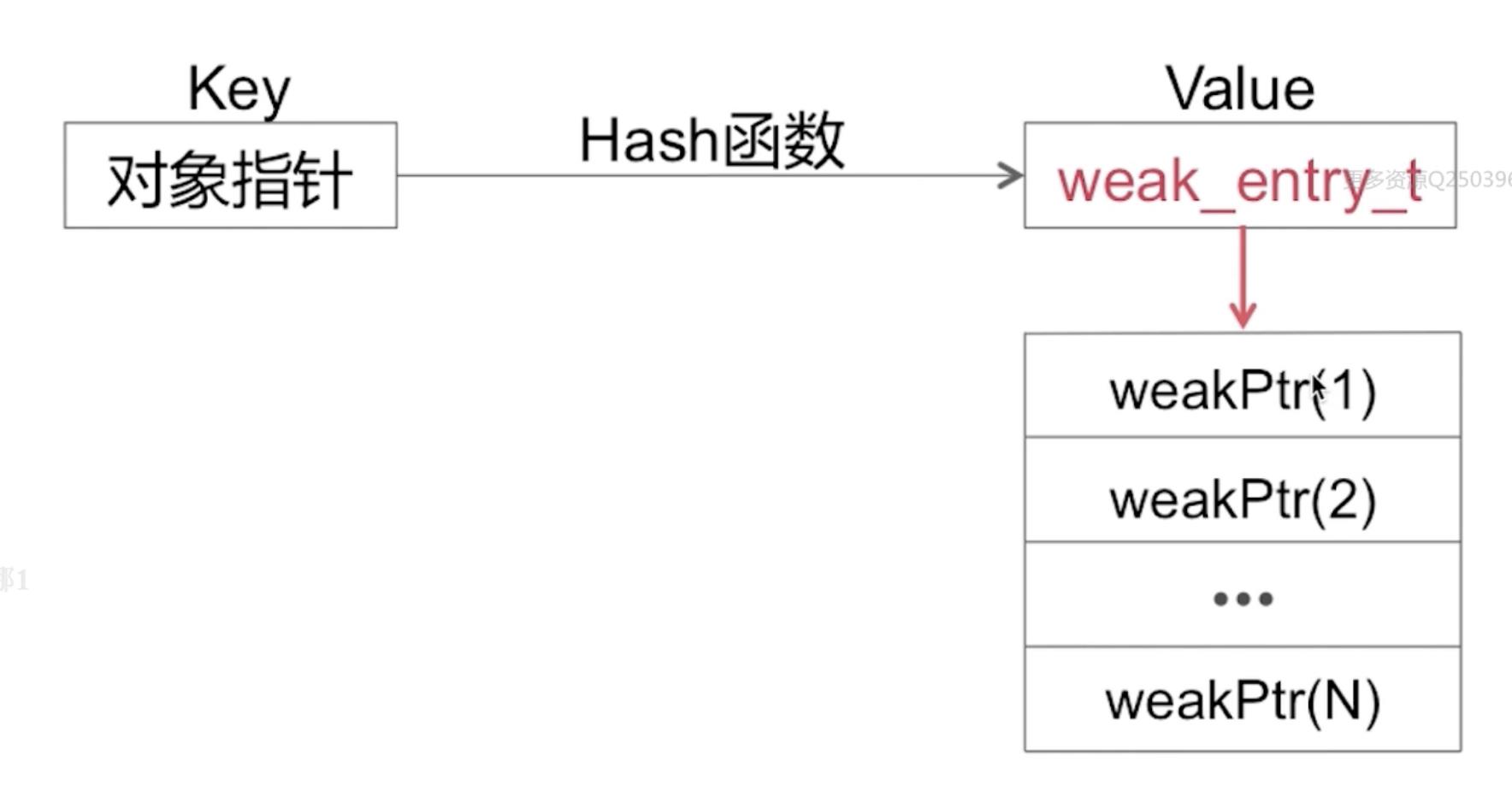
3、weak_table_t(弱引用表)
也是一个hash表,key->hash->weak_entry_t,weak_entry_t,其实是一个结构体数组(weakPtr),比如被weak修饰,就存在这个弱引用表中。
四、ARC & MRC
1、MRC 手动引用计数

- alloc:用来分配一个对象的内存空间;
- retain:可以使一个对象的引用计数+1;
- release:可以使一个对象的引用计数-1;
- retainCount:可以获取当前对象的引用计数值;
- autorelease:当前这个对象会在autoreleasepool结束的时候调用一次release,进行引用计数-1;
- dealloc:在MRC当中需要调用[super dealloc];
2、ARC 自动引用计数
自动引用计数(ARC,Automatic Reference Counting)是指内存管理中对引用采取自动计数的技术;苹果官方说明:
在Objective-C中采用Automatic Reference Counting(ARC)机制,让编译器来进行内存管理。在新一代Apple LLVM编译器中设置ARC为有效状态,就无需再次键入retain或者release代码,这就降低程序崩溃、内存泄露等风险的同时,很大程度上减少了开发程序的工作量。编译器完全清除目标对象,并能立刻释放那些不再被使用的对象。如此一来,引用程序具有可预防性,且能流畅运行,速度也将大幅提升。
- ARC是
LLVM和Runtime协作的结果; - ARC中禁止手动调用
retain/release/retainCount/dealloc。 - ARC中新增
weak、strong属性关键字
3、内存管理
Objective-C提供了三种内存管理方式:
- ①、manual retain-release(MRR,手动管理);
- ②、automatic reference counting(ARC,自动引用计数);
- ③、garbage collection(垃圾回收);
(1)、概要
ObjC采用引用计数(reference counting)的技术来进行管理:
- 1)每个对象都有一个关联的整数,称为引用计数器;
- 2)当代码需要使用该对象时,则将对象的引用计数加1;
- 3)当代码结束使用该对象时,则将对象的引用计数减1;
- 4)当引用计数的值变为0时,表示对象没有被任何代码使用,此时对象将被释放。
与之对应的消息发送方法如下:
- 1)当对象被创建(通过alloc、new或copy等方法)时,其引用计数初始值为1;
- 2)給对象发送retain消息,其引用计数加1;
- 3)給对象发送release消息,其引用计数减1;
- 4)当对象引用计数归0时,ObjC給对象发送dealloc消息销毁对象。
(2)、内存管理的思考方式
- 自己生成的对象,自己持有;
- 非自己生成的对象,自己也能持有;
- 不再需要自己持有的对象时释放;
- 非自己持有的对象无法释放。
对象操作与Objective-C方法的对应
| 对象操作 | Objective-C方法 |
|---|---|
| 生成并持有对象 | alloc/new/copy/mutableCopy |
| 持有对象 | retain方法 |
| 释放对象 | release方法 |
| 废弃对象 | dealloc方法 |
(1)、自己生成的对象,自己持有
- ①、alloc
id obj = [[NSObject alloc]init];
- ②、new
id obj = [NSObject new];
作用同①。
- ③、copy/mutableCopy
copy方法利用基于NSCopying方法约定,由各类实现的copyWithZone:方法生成并持有对象的副本。与copy方法类似,mutableCopy方法利用基于NSMutableCopying方法约定,由各类实现mutableCopyWithZone:方法生成并持有对象的副本。两者的区别在于,copy方法生成不可变更的对象,而mutableCopy方法生成可变更对象。
(2)、非自己生成的对象,自己也能持有
//去的非自己生成并持有的对象
id obj = [NSMutableArray array];
//取得的对象存在,但自己不持有对象
[obj retain];
//自己持有对象
(3)、不再需要自己持有的对象时释放
//自己生成并持有对象
id obj = [[NSMutableArray alloc]init];
//自己持有对象
[obj release];
//释放对象
(4)、非自己持有的对象无法释放
//取得的对象存在,但自己不持有对象
id obj = [NSMutableArray array];
//释放对象导致程序崩溃
[obj release];
五、引用计数管理
实现原理分析
- alloc
- retain
- release
- retainCount
- dealloc
GNUstep是Cocoa框架的互换框架。
1、alloc
经过一系列调用,最终调用了C函数的calloc。此时并没有设置引用计数为1.
2、retain
在非ARC环境下可以使用retain方法对引用计数进行加一操作,调用了_objc_rootRetain(id obj) 函数。
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
size_t& refcntStorage = table.refcnts[this];
refcntStorage += SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;
3、release
在非ARC环境下可以使用release方法对引用计数进行减一操作,调用了_objc_rootRelease(id obj) 函数。
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
RefountMap::iterator it = table.refcnts.find(this);
refcntStorage -= SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;
4、retainCount
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
size_t refcnt_result = 1;
RefcountMap::iterator it = table.refcnts.find(this);
refcnt_result += it->second >> SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;
5、dealloc

- nonpointer_isa:判断当前对象是否拥有非指针型的isa;
- weakly_referenced:判断当前对象是否有weak指针指向他
- has_assoc:判断当前对象是否有关联对象;
- has_cxx_dtor:判断当前对象的内部实现是否涉及到C++的内容,或者是否使用ARC来管理内存;
- has_sidetable_rc:判断当前对象的引用计数是否是通过sidetable当中的引用计数表来维护的;
都为否的时候才可以释放。
object_dispose()的实现
objc_destructInstance()实现:
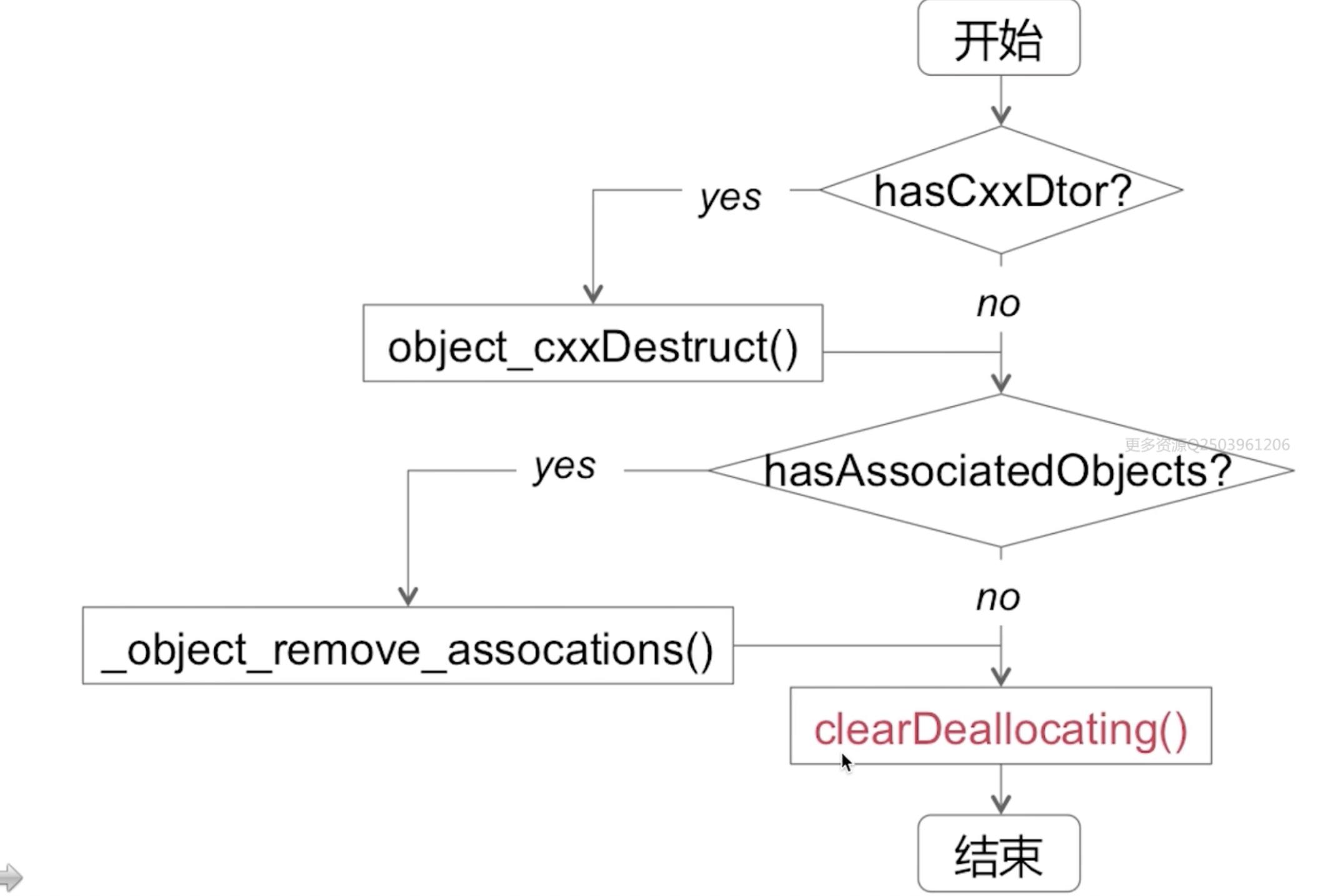
clearDeallocating()实现:
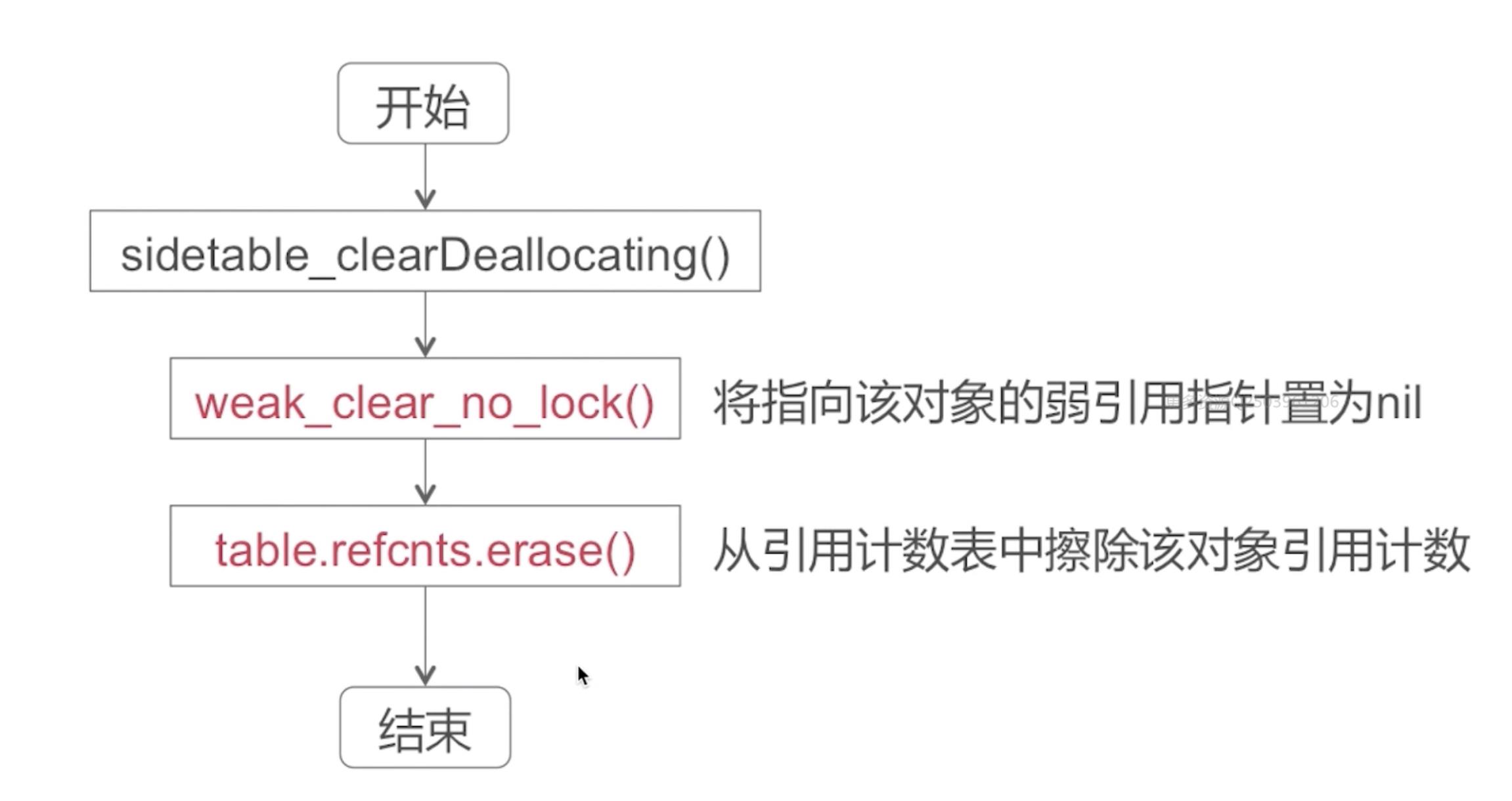
六、弱引用管理
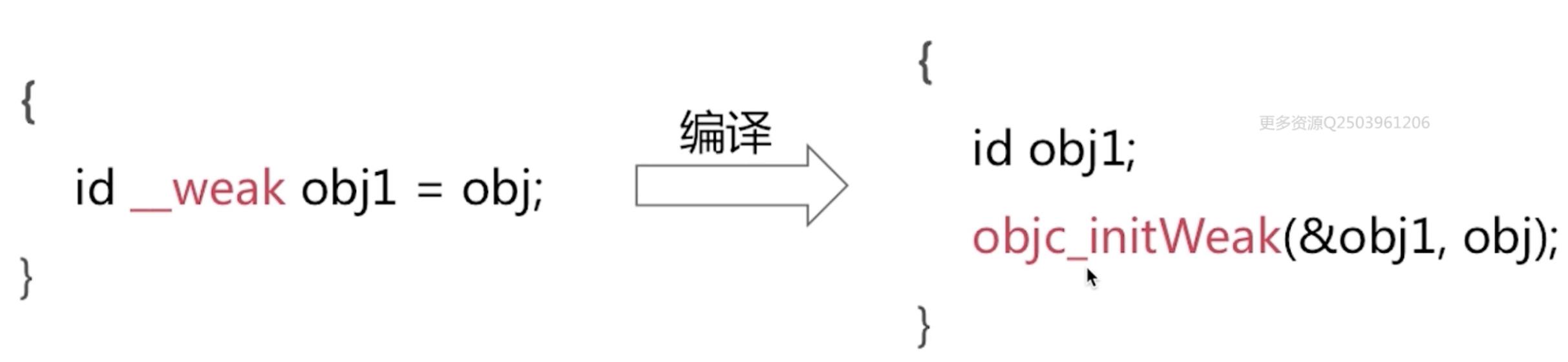
1、添加weak变量

id
objc_initWeak(id *location, id newObj)
if (!newObj)
*location = nil;
return nil;
return storeWeak<DontHaveOld, DoHaveNew, DoCrashIfDeallocating>
(location, (objc_object*)newObj);
storeWeak(id *location, objc_object *newObj)
ASSERT(haveOld || haveNew);
if (!haveNew) ASSERT(newObj == nil);
Class previouslyInitializedClass = nil;
id oldObj;
SideTable *oldTable;
SideTable *newTable;
// Acquire locks for old and new values.
// Order by lock address to prevent lock ordering problems.
// Retry if the old value changes underneath us.
retry:
if (haveOld)
oldObj = *location;
oldTable = &SideTables()[oldObj];
else
oldTable = nil;
if (haveNew)
newTable = &SideTables()[newObj];
else
newTable = nil;
SideTable::lockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable);
if (haveOld && *location != oldObj)
SideTable::unlockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable);
goto retry;
// Prevent a deadlock between the weak reference machinery
// and the +initialize machinery by ensuring that no
// weakly-referenced object has an un-+initialized isa.
if (haveNew && newObj)
Class cls = newObj->getIsa();
if (cls != previouslyInitializedClass &&
!((objc_class *)cls)->isInitialized())
SideTable::unlockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable);
class_initialize(cls, (id)newObj);
// If this class is finished with +initialize then we're good.
// If this class is still running +initialize on this thread
// (i.e. +initialize called storeWeak on an instance of itself)
// then we may proceed but it will appear initializing and
// not yet initialized to the check above.
// Instead set previouslyInitializedClass to recognize it on retry.
previouslyInitializedClass = cls;
goto retry;
// Clean up old value, if any.
if (haveOld)
weak_unregister_no_lock(&oldTable->weak_table, oldObj, location);
// Assign new value, if any.
if (haveNew)
newObj = (objc_object *)
weak_register_no_lock(&newTable->weak_table, (id)newObj, location,
crashIfDeallocating ? CrashIfDeallocating : ReturnNilIfDeallocating);
// weak_register_no_lock returns nil if weak store should be rejected
// Set is-weakly-referenced bit in refcount table.
if (!newObj->isTaggedPointerOrNil())
newObj->setWeaklyReferenced_nolock();
// Do not set *location anywhere else. That would introduce a race.
*location = (id)newObj;
else
// No new value. The storage is not changed.
SideTable::unlockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable);
// This must be called without the locks held, as it can invoke
// arbitrary code. In particular, even if _setWeaklyReferenced
// is not implemented, resolveInstanceMethod: may be, and may
// call back into the weak reference machinery.
callSetWeaklyReferenced((id)newObj);
return (id)newObj;
/**
* Registers a new (object, weak pointer) pair. Creates a new weak
* object entry if it does not exist.
*
* @param weak_table The global weak table.
* @param referent The object pointed to by the weak reference.
* @param referrer The weak pointer address.
*/
id
weak_register_no_lock(weak_table_t *weak_table, id referent_id,
id *referrer_id, WeakRegisterDeallocatingOptions deallocatingOptions)
objc_object *referent = (objc_object *)referent_id;
objc_object **referrer = (objc_object **)referrer_id;
if (referent->isTaggedPointerOrNil()) return referent_id;
// ensure that the referenced object is viable
if (deallocatingOptions == ReturnNilIfDeallocating ||
deallocatingOptions == CrashIfDeallocating)
bool deallocating;
if (!referent->ISA()->hasCustomRR())
deallocating = referent->rootIsDeallocating();
else
// Use lookUpImpOrForward so we can avoid the assert in
// class_getInstanceMethod, since we intentionally make this
// callout with the lock held.
auto allowsWeakReference = (BOOL(*)(objc_object *, SEL))
lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache((id)referent, @selector(allowsWeakReference),
referent->getIsa());
if ((IMP)allowsWeakReference == _objc_msgForward)
return nil;
deallocating =
! (*allowsWeakReference)(referent, @selector(allowsWeakReference));
if (deallocating)
if (deallocatingOptions == CrashIfDeallocating)
_objc_fatal("Cannot form weak reference to instance (%p) of "
"class %s. It is possible that this object was "
"over-released, or is in the process of deallocation.",
(void*)referent, object_getClassName((id)referent));
else
return nil;
// now remember it and where it is being stored
weak_entry_t *entry;
if ((entry = weak_entry_for_referent(weak_table, referent)))
append_referrer(entry, referrer);
else
weak_entry_t new_entry(referent, referrer);
weak_grow_maybe(weak_table);
weak_entry_insert(weak_table, &new_entry);
// Do not set *referrer. objc_storeWeak() requires that the
// value not change.
return referent_id;
2、清除weak变量,同时设置指向为nil

/**
* Called by dealloc; nils out all weak pointers that point to the
* provided object so that they can no longer be used.
*
* @param weak_table
* @param referent The object being deallocated.
*/
void
weak_clear_no_lock(weak_table_t *weak_table, id referent_id)
objc_object *referent = (objc_object *)referent_id;
weak_entry_t *entry = weak_entry_for_referent(weak_table, referent);
if (entry == nil)
/// XXX shouldn't happen, but does with mismatched CF/objc
//printf("XXX no entry for clear deallocating %p\\n", referent);
return;
// zero out references
weak_referrer_t *referrers;
size_t count;
if (entry->out_of_line())
referrers = entry->referrers;
count = TABLE_SIZE(entry);
else
referrers = entry->inline_referrers;
count = WEAK_INLINE_COUNT;
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; ++i)
objc_object **referrer = referrers[i];
if (referrer)
if (*referrer == referent)
*referrer = nil;
else if (*referrer)
_objc_inform("__weak variable at %p holds %p instead of %p. "
"This is probably incorrect use of "
"objc_storeWeak() and objc_loadWeak(). "
"Break on objc_weak_error to debug.\\n",
referrer, (void*)*referrer, (void*)referent);
objc_weak_error();
weak_entry_remove(weak_table, entry);
七、自动释放池
- 是以栈为节点通过双向链表的形式组合而成。
- 是和线程一一对应的。
编辑器会将@autoreleasepool改写为:

autorelease就是自动释放,当給一个对象发送autorelease消息时,方法会在未来某个时间給这个对象发送release消息将其释放,在这个时间段内,对象还是可以使用的。
(1)、原理
对象接收到autorelease消息时,它会被添加到了当前的自动释放池中,当自动释放池被销毁时,会給池里所有的对象发送release消息。
(2)、使用方法
①、生成并持有NSAutoreleasePool对象;
- 使用NSAutoreleasePool来创建
NSAutoreleasePool * pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc]init];
//这里写代码
[pool release];
- 使用@autoreleasepool创建
@autoreleasepool
//这里写代码
②、调用已分配对象的aurorelease实例方法;
③、废弃NSAutoreleasePool对象;

NSAutoreleasePool对象的生命周期相当于C语言变量的作用域。对于所有调用autorelease实例方法的对象,在废弃NSAutoreleasePool对象时,都将调用release实例方法。
在cocoa框架中,程序主循环的NSRunLoop或者在其他程序可运行的地方,对NSAutoreleasePool对象进行生成、持有和废弃处理。
当我们大量产生autorelease对象时,只要不废弃NSAutoreleasePool对象,那么生成的对象就不能被释放。有时候会产生内存不足的情况。
我们可以在必要的地方持有,废弃:
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i)
NSAutoreleasePool *pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init];
***
[pool drain];
八、循环引用
三种循环引用
- 自循环引用
- 相互循环引用
- 多循环引用
1、自循环引用
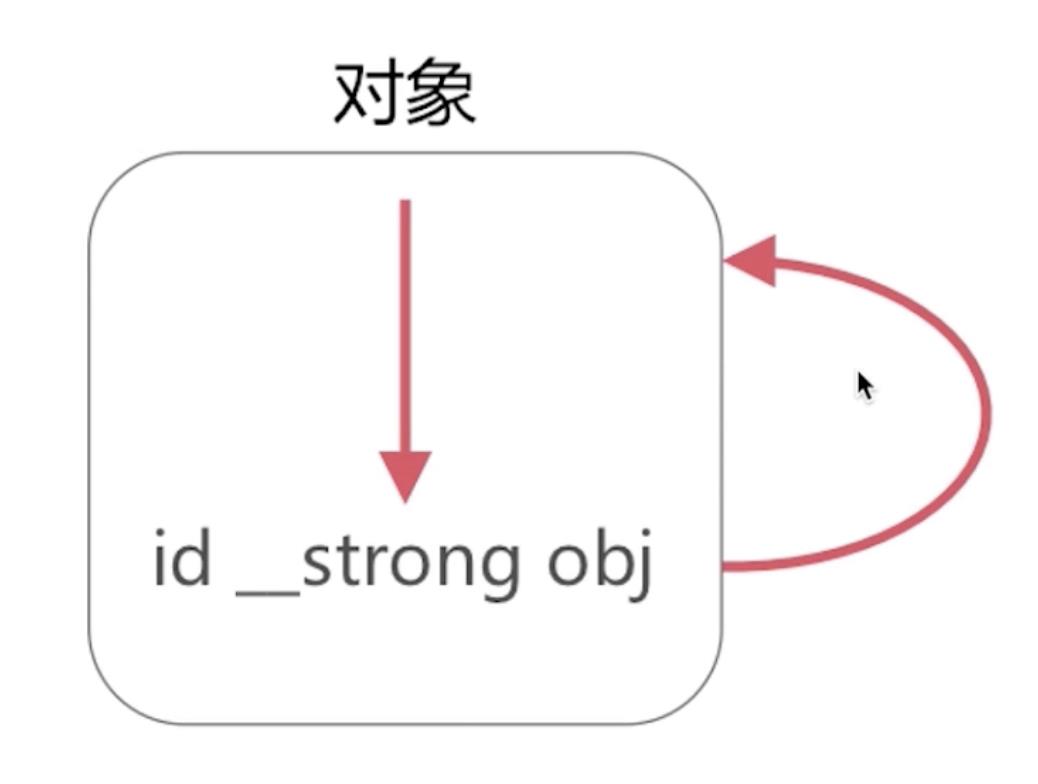
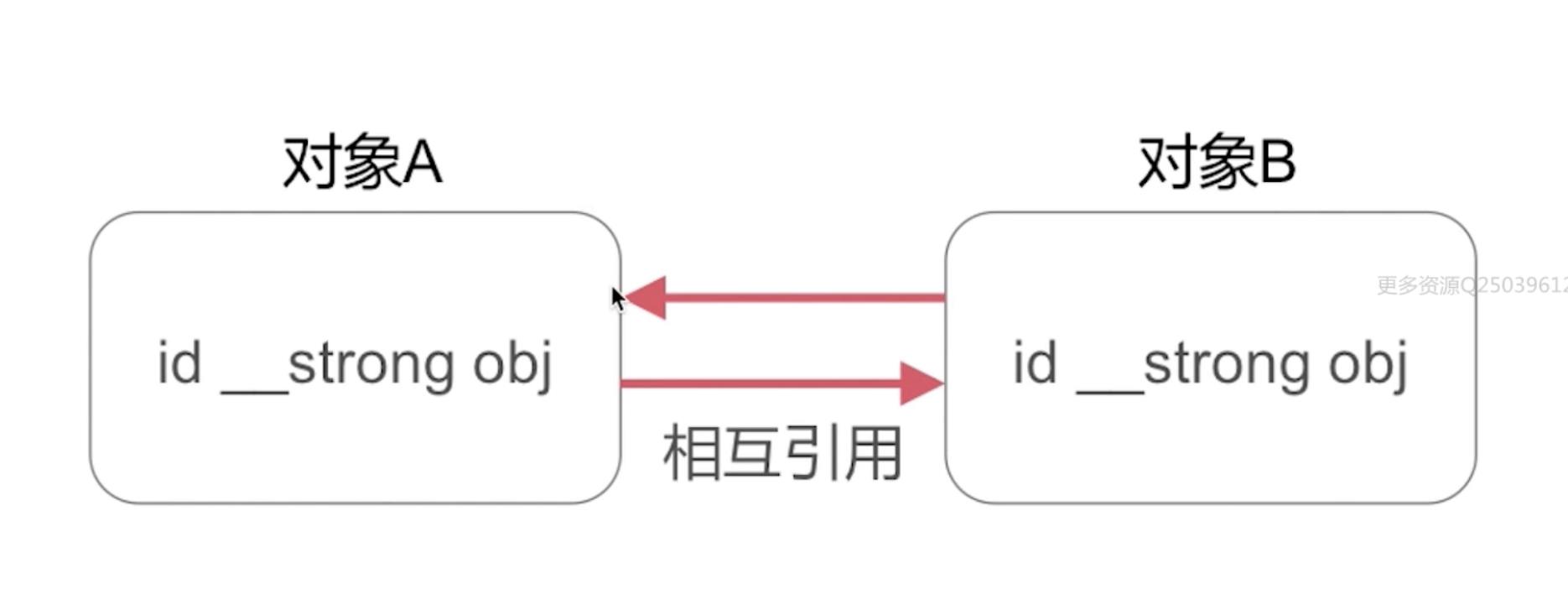
2、相互循环引用
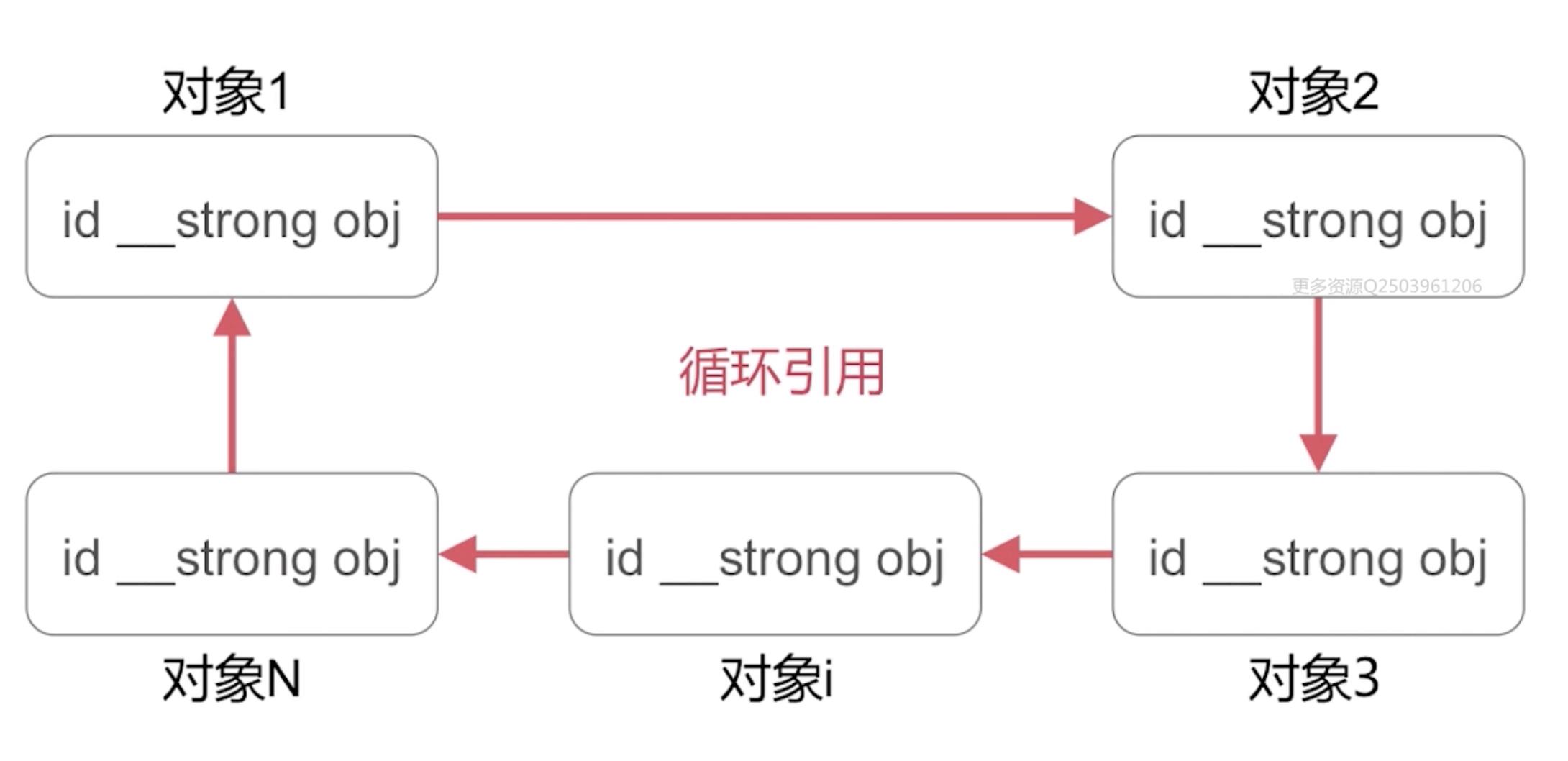
3、多循环引用
4、如何破除循环引用
- 避免产生循环引用
- 在合适的时机手动断环
可能产生循环引用:
- 代理
- Block
- NSTimer
- 大环引用
具体的解决方案:
- __weak
- __block
- __unsafe_unretained
(1)、__weak破解

(2)、__block破解
*注意
- MRC下,__block修饰对象不会增加其引用计数,避免了循环引用;
- ARC下,__block修饰对象会被强引用,无法避免循环引用,需手动解环;
(3)、__unsafe_unretained破解
- 修饰对象不会增加其引用计数,避免了循环引用;
- 如果被释放对象在某一时机被释放,会产生悬垂指针;
5、NSTimer的循环引用问题
假如我们有一个实际的场景,我们有一个页面VC,其有一个轮播图对象,该对象添加了一个成员变量NSTimer,我们添加完成NSTimer之后,给他一个回调函数,这时候NSTimer就强引用了对象。当NSTimer被分配之后,当前的Runloop会对NSTimer进行强引用。

解决方案:
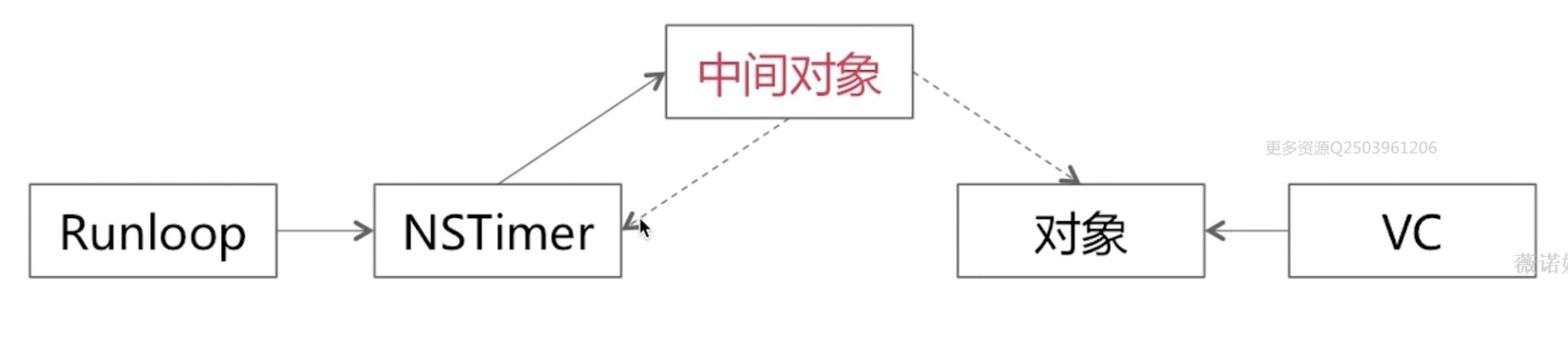
#import "NSTimer+NSWeakTimer.h"
@interface NSTimerWeakObject()
@property (nonatomic, weak) id target;
@property (nonatomic, assign) SEL selector;
@property (nonatomic, weak) NSTimer *timer;
@end
@implementation NSTimerWeakObject
- (void)fire:(NSTimer *)timer
if (self.target)
if ([self.target respondsToSelector:self.selector])
[self.target performSelector:self.selector withObject:timer.userInfo];
else
[self.timer invalidate];
@end
@implementation NSTimer (NSWeakTimer)
+ (NSTimer *)scheduledWeakTimerWithTimeInterval:(NSTimeInterval)ti
target:(id)aTarget
selector:(SEL)aSelector
userInfo:(id)userInfo
repeats:(BOOL)yesOrNo
NSTimerWeakObject *object = [[NSTimerWeakObject alloc]init];
object.target =aTarget;
object.selector = aSelector;
object.timer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:ti target:object selector:@selector(fire:) userInfo:userInfo repeats:yesOrNo];
return object.timer;
@end
以上是关于iOS 内存管理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章