分支限界法之单源最短路径问题
Posted cy0628
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了分支限界法之单源最短路径问题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、问题描述
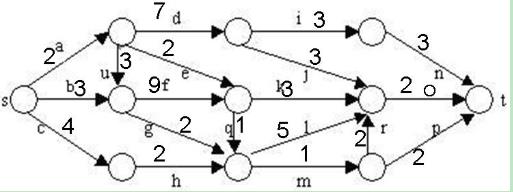
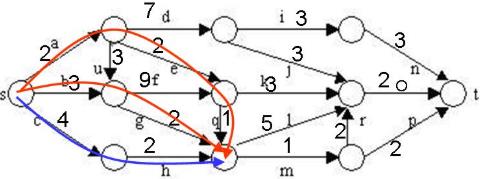
在下图所给的有向图G中,每一边都有一个非负边权。要求图G的从源顶点s到目标顶点t之间的最短路径。
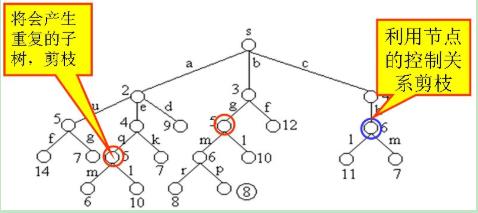
下图是用优先队列式分支限界法解有向图G的单源最短路径问题产生的解空间树。其中,每一个结点旁边的数字表示该结点所对应的当前路长。
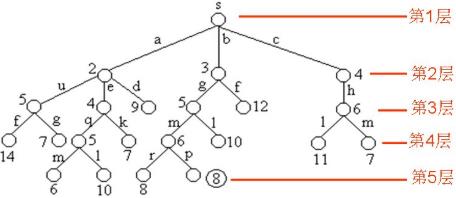
找到一条路径:
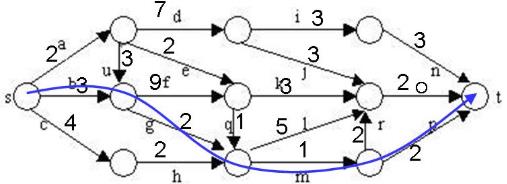
目前的最短路径是8,一旦发现某个结点的下界不小于这个最短路进,则剪枝:
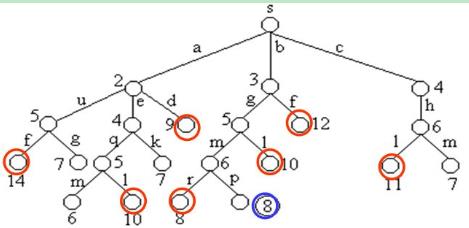
同一个结点选择最短的到达路径:
2.剪枝策略
在算法扩展结点的过程中,一旦发现一个结点的下界不小于当前找到的最短路长,则算法剪去以该结点为根的子树。
在算法中,利用结点间的控制关系进行剪枝。从源顶点s出发,2条不同路径到达图G的同一顶点。由于两条路径的路长不同,因此可以将路长长的路径所对应的树中的结点为根的子树剪去。
3.算法思想
解单源最短路径问题的优先队列式分支限界法用一极小堆来存储活结点表。其优先级是结点所对应的当前路长。
算法从图G的源顶点s和空优先队列开始。结点s被扩展后,它的儿子结点被依次插入堆中。此后,算法从堆中取出具有最小当前路长的结点作为当前扩展结点,并依次检查与当前扩展结点相邻的所有顶点。如果从当前扩展结点i到顶点j有边可达,且从源出发,途经顶点i再到顶点j的所相应的路径的长度小于当前最优路径长度,则将该顶点作为活结点插入到活结点优先队列中。这个结点的扩展过程一直继续到活结点优先队列为空时为止。
代码实现

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <limits> using namespace std; struct node_info { public: node_info (int i,int w) : index (i), weight (w) {} node_info () : index(0),weight(0) {} node_info (const node_info & ni) : index (ni.index), weight (ni.weight) {} friend bool operator < (const node_info& lth,const node_info& rth) { return lth.weight > rth.weight ; // 为了实现从小到大的顺序 } public: int index; // 结点位置 int weight; // 权值 }; struct path_info { public: path_info () : front_index(0), weight (numeric_limits<int>::max()) {} public: int front_index; int weight; }; // single source shortest paths class ss_shortest_paths { public: ss_shortest_paths (const vector<vector<int> >& g,int end_location) :no_edge (-1), end_node (end_location), node_count (g.size()) , graph (g) {} // 打印最短路径 void print_spaths () const { cout << "min weight : " << shortest_path << endl; cout << "path: " ; copy (s_path_index.rbegin(),s_path_index.rend(), ostream_iterator<int> (cout, " ")); cout << endl; } // 求最短路径 void shortest_paths () { vector<path_info> path(node_count); priority_queue<node_info,vector<node_info> > min_heap; min_heap.push (node_info(0,0)); // 将起始结点入队 while (true) { node_info top = min_heap.top (); // 取出最大值 min_heap.pop (); // 已到达目的结点 if (top.index == end_node) { break ; } // 未到达则遍历 for (int i = 0; i < node_count; ++ i) { // 顶点top.index和i间有边,且此路径长小于原先从原点到i的路径长 if (graph[top.index][i] != no_edge && (top.weight + graph[top.index][i]) < path[i].weight) { min_heap.push (node_info (i,top.weight + graph[top.index][i])); path[i].front_index = top.index; path[i].weight = top.weight + graph[top.index][i]; } } if (min_heap.empty()) { break ; } } shortest_path = path[end_node].weight; int index = end_node; s_path_index.push_back(index) ; while (true) { index = path[index].front_index ; s_path_index.push_back(index); if (index == 0) { break; } } } private: vector<vector<int> > graph ; // 图的数组表示 int node_count; // 结点个数 const int no_edge; // 无通路 const int end_node; // 目的结点 vector<int> s_path_index; // 最短路径 int shortest_path; // 最短路径 }; int main() { const int size = 11; vector<vector<int> > graph (size); for (int i = 0;i < size; ++ i) { graph[i].resize (size); } for (int i = 0;i < size; ++ i) { for (int j = 0;j < size; ++ j) { graph[i][j] = -1; } } graph[0][1] = 2; graph[0][2] = 3; graph[0][3] = 4; graph[1][2] = 3; graph[1][5] = 2; graph[1][4] = 7; graph[2][5] = 9; graph[2][6] = 2; graph[3][6] = 2; graph[4][7] = 3; graph[4][8] = 3; graph[5][6] = 1; graph[5][8] = 3; graph[6][9] = 1; graph[6][8] = 5; graph[7][10] = 3; graph[8][10] = 2; graph[9][8] = 2; graph[9][10] = 2; ss_shortest_paths ssp (graph, 10); ssp.shortest_paths (); ssp.print_spaths (); return 0; }
测试数据(图)
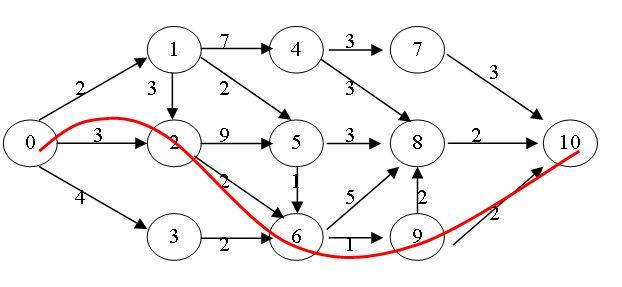
测试结果
min weight : 8
path: 0 2 6 9 10
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/chinazhangjie/archive/2010/11/01/1866136.html
以上是关于分支限界法之单源最短路径问题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章