AQS解析与实战
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了AQS解析与实战相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
前段时间在面试,发现面试官都有问到同步器AQS的相关问题。AQS为Java中几乎所有的锁和同步器提供一个基础框架,派生出如ReentrantLock、Semaphore、CountDownLatch等AQS全家桶。本文基于AQS原理的几个核心点,谈谈对AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的理解,并实现一个自定义同步器。
AQS原理面试题的核心回答要点
- state 状态的维护。
- CLH队列
- ConditionObject通知
- 模板方法设计模式
- 独占与共享模式。
- 自定义同步器。
- AQS全家桶的一些延伸,如:ReentrantLock等。
AQS的类图结构
AQS全称是AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,即抽象同步队列。下面看一下AQS的类图结构: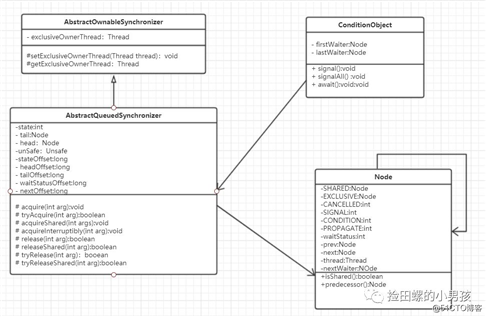
为了方便下面几个关键点的理解,大家先熟悉一下AQS的类图结构。
state 状态的维护
在
AQS
中维持了一个单一的共享状态
state
,来实现同步器同步。看一下
state
的相关代码如下:state源码
/**
* The synchronization state.
*/
private
volatile
int
state
;
/**
* Returns the current value of synchronization state.
* This operation has memory semantics of a {@code volatile} read.
* @return current state value
*/
protected
final
int
getState
()
{
return
state
;
}
/**
* Sets the value of synchronization state.
* This operation has memory semantics of a {@code volatile} write.
* @param newState the new state value
*/
protected
final
void
setState
(
int
newState
)
{
state
=
newState
;
}
/**
* Atomically sets synchronization state to the given updated
* value if the current state value equals the expected value.
* This operation has memory semantics of a {@code volatile} read
* and write.
*
* @param expect the expected value
* @param update the new value
* @return {@code true} if successful. False return indicates that the actual
* value was not equal to the expected value.
*/
protected
final
boolean
compareAndSetState
(
int
expect
,
int
update
)
{
// See below for intrinsics setup to support this
return
unsafe
.
compareAndSwapInt
(
this
,
stateOffset
,
expect
,
update
);
}state 源码设计几个回答要点:
- state用volatile修饰,保证多线程中的可见性。
- getState()和setState()方法采用final修饰,限制AQS的子类重写它们两。
- compareAndSetState()方法采用乐观锁思想的CAS算法,也是采用final修饰的,不允许子类重写。
CLH队列
谈到CLH队列,我们结合以上state状态,先来看一下AQS原理图:
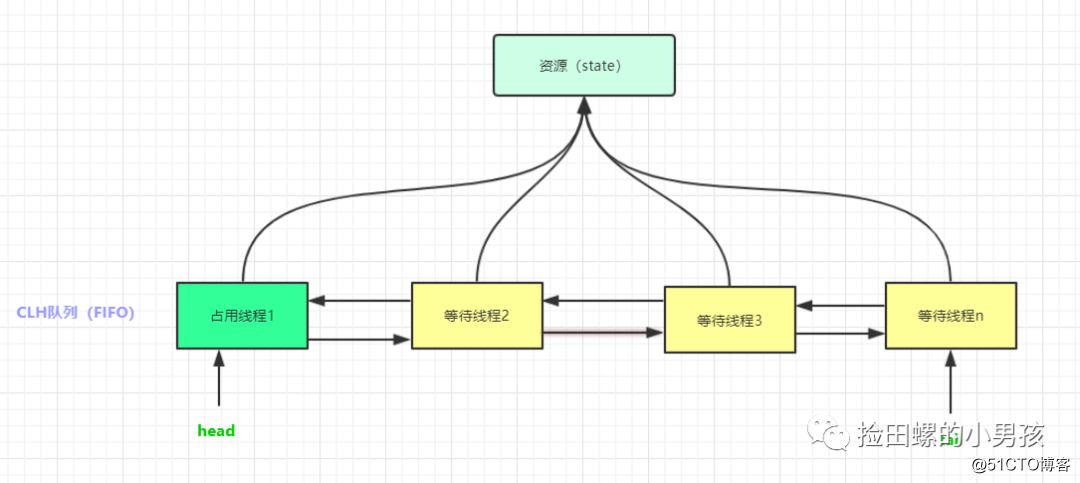
CLH(Craig, Landin, and Hagersten locks) 同步队列 是一个FIFO双向队列,其内部通过节点head和tail记录队首和队尾元素,队列元素的类型为Node。AQS依赖它来完成同步状态state的管理,当前线程如果获取同步状态失败时,AQS则会将当前线程已经等待状态等信息构造成一个节点(Node)并将其加入到CLH同步队列,同时会阻塞当前线程,当同步状态释放时,会把首节点唤醒(公平锁),使其再次尝试获取同步状态。
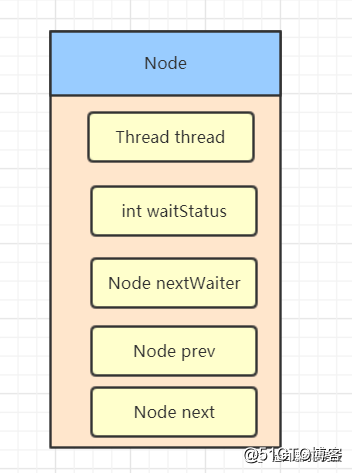
Node节点
CLH同步队列中,一个节点表示一个线程,它保存着线程的引用(thread)、状态(waitStatus)、前驱节点(prev)、后继节点(next),condition队列的后续节点(nextWaiter)如下图:
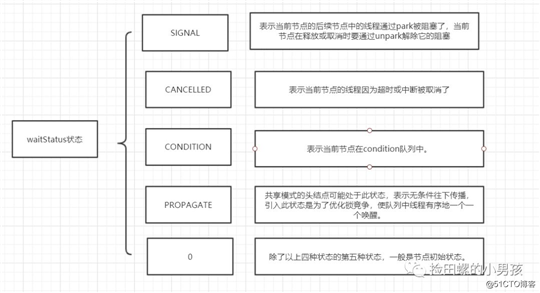
waitStatus几种状态状态:
我们再看一下CLH队列入列以及出列的代码:
入列
CLH队列入列就是tail指向新节点、新节点的prev指向当前最后的节点,当前最后一个节点的next指向当前节点。addWaiter方法如下:
//构造Node
private
Node
addWaiter
(
Node
mode
)
{
Node
node
=
new
Node
(
Thread
.
currentThread
(),
mode
);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure(快速尝试添加尾节点)
Node
pred
=
tail
;
if
(
pred
!=
null
)
{
node
.
prev
=
pred
;
//CAS设置尾节点
if
(
compareAndSetTail
(
pred
,
node
))
{
pred
.
next
=
node
;
return
node
;
}
}
//多次尝试
enq
(
node
);
return
node
;
}由以上代码可得,addWaiter设置尾节点失败的话,调用enq(Node node)方法设置尾节点,enq方法如下:
private
Node
enq
(
final
Node
node
)
{
//死循环尝试,知道成功为止
for
(;;)
{
Node
t
=
tail
;
//tail 不存在,设置为首节点
if
(
t
==
null
)
{
// Must initialize
if
(
compareAndSetHead
(
new
Node
()))
tail
=
head
;
}
else
{
node
.
prev
=
t
;
if
(
compareAndSetTail
(
t
,
node
))
{
t
.
next
=
node
;
return
t
;
}
}
}
}出列
首节点的线程释放同步状态后,将会唤醒它的后继节点(next),而后继节点将会在获取同步状态成功时将自己设置为首节点。可以看一下以下两段源码:
Node
h
=
head
;
if
(
h
!=
null
&&
h
.
waitStatus
!=
0
)
unparkSuccessor
(
h
);
private
void
unparkSuccessor
(
Node
node
)
{
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int
ws
=
node
.
waitStatus
;
if
(
ws
<
0
)
compareAndSetWaitStatus
(
node
,
ws
,
0
);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node
s
=
node
.
next
;
if
(
s
==
null
||
s
.
waitStatus
>
0
)
{
s
=
null
;
for
(
Node
t
=
tail
;
t
!=
null
&&
t
!=
node
;
t
=
t
.
prev
)
if
(
t
.
waitStatus
<=
0
)
s
=
t
;
}
if
(
s
!=
null
)
LockSupport
.
unpark
(
s
.
thread
);
}CLH核心几个回答要点
- 双向链表入列出列
- CAS算法设置尾节点+死循环自旋。
CAS算法,可以看一下我工作实战中仿造CAS算法解决并发问题的实现https://juejin.im/post/5d0616ade51d457756536791
ConditionObject
ConditionObject简介
我们都知道,synchronized控制同步的时候,可以配合Object的wait()、notify(),notifyAll() 系列方法可以实现等待/通知模式。而Lock呢?它提供了条件Condition接口,配合await(),signal(),signalAll() 等方法也可以实现等待/通知机制。ConditionObject实现了Condition接口,给AQS提供条件变量的支持 。
Condition队列与CLH队列的那些事
我们先来看一下图:
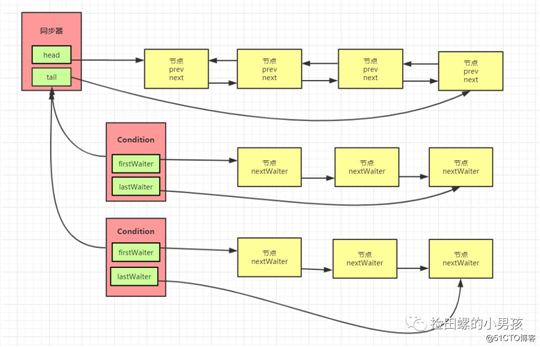
ConditionObject队列与CLH队列的爱恨情仇:
- 调用了await()方法的线程,会被加入到conditionObject等待队列中,并且唤醒CLH队列中head节点的下一个节点。
- 线程在某个ConditionObject对象上调用了singnal()方法后,等待队列中的firstWaiter会被加入到AQS的CLH队列中,等待被唤醒。
- 当线程调用unLock()方法释放锁时,CLH队列中的head节点的下一个节点(在本例中是firtWaiter),会被唤醒。
区别:
- ConditionObject对象都维护了一个单独的等待队列 ,AQS所维护的CLH队列是同步队列,它们节点类型相同,都是Node。
独占与共享模式。
AQS支持两种同步模式:独占式和共享式。
独占式
同一时刻仅有一个线程持有同步状态,如ReentrantLock。又可分为公平锁和非公平锁。
公平锁: 按照线程在队列中的排队顺序,有礼貌的,先到者先拿到锁。
非公平锁: 当线程要获取锁时,无视队列顺序直接去抢锁,不讲道理的,谁抢到就是谁的。
acquire(int arg)是独占式获取同步状态的方法,我们来看一下源码:
- acquire(long arg)方法
public
final
void
acquire
(
long
arg
)
{
if
(!
tryAcquire
(
arg
)
&&
acquireQueued
(
addWaiter
(
Node
.
EXCLUSIVE
),
arg
))
selfInterrupt
();
}- addWaiter方法
//构造Node
private
Node
addWaiter
(
Node
mode
)
{
Node
node
=
new
Node
(
Thread
.
currentThread
(),
mode
);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure(快速尝试添加尾节点)
Node
pred
=
tail
;
if
(
pred
!=
null
)
{
node
.
prev
=
pred
;
//CAS设置尾节点
if
(
compareAndSetTail
(
pred
,
node
))
{
pred
.
next
=
node
;
return
node
;
}
}
//多次尝试
enq
(
node
);
return
node
;
}- acquireQueued(final Node node, long arg)方法
final
boolean
acquireQueued
(
final
Node
node
,
long
arg
)
{
boolean
failed
=
true
;
try
{
boolean
interrupted
=
false
;
for
(;;)
{
final
Node
p
=
node
.
predecessor
();
if
(
p
==
head
&&
tryAcquire
(
arg
))
{
setHead
(
node
);
p
.
next
=
null
;
// help GC
failed
=
false
;
return
interrupted
;
}
if
(
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire
(
p
,
node
)
&&
parkAndCheckInterrupt
())
interrupted
=
true
;
}
}
finally
{
if
(
failed
)
cancelAcquire
(
node
);
}
}- selfInterrupt()方法
static
void
selfInterrupt
()
{
Thread
.
currentThread
().
interrupt
();
}结合源代码,可得acquire(int arg)方法流程图,如下: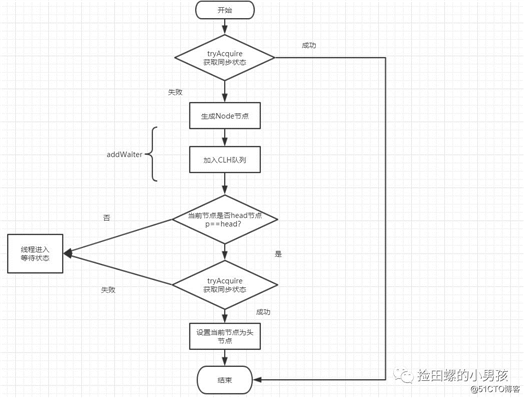
共享式
多个线程可同时执行,如Semaphore/CountDownLatch等都是共享式的产物。
acquireShared(long arg)是共享式获取同步状态的方法,可以看一下源码:
public
final
void
acquireShared
(
long
arg
)
{
if
(
tryAcquireShared
(
arg
)
<
0
)
doAcquireShared
(
arg
);
}由上可得,先调用tryAcquireShared(int arg)方法尝试获取同步状态,如果获取失败,调用doAcquireShared(int arg)自旋方式获取同步状态,方法源码如下:
private
void
doAcquireShared
(
long
arg
)
{
final
Node
node
=
addWaiter
(
Node
.
SHARED
);
boolean
failed
=
true
;
try
{
boolean
interrupted
=
false
;
for
(;;)
{
final
Node
p
=
node
.
predecessor
();
if
(
p
==
head
)
{
long
r
=
tryAcquireShared
(
arg
);
if
(
r
>=
0
)
{
setHeadAndPropagate
(
node
,
r
);
p
.
next
=
null
;
// help GC
if
(
interrupted
)
selfInterrupt
();
failed
=
false
;
return
;
}
}
if
(
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire
(
p
,
node
)
&&
parkAndCheckInterrupt
())
interrupted
=
true
;
}
}
finally
{
if
(
failed
)
cancelAcquire
(
node
);
}
}AQS的模板方法设计模式
模板方法模式
模板方法模式: 在一个方法中定义一个算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。模板方法使得子类可以在不改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义算法中的某些步骤。
模板方法模式生活中的例子: 假设我们要去北京旅游,那么我们可以坐高铁或者飞机,或者火车,那么定义交通方式的抽象类,可以有以下模板:买票->安检->乘坐xx交通工具->到达北京。让子类继承该抽象类,实现对应的模板方法。
AQS定义的一些模板方法如下:
isHeldExclusively()//该线程是否正在独占资源。只有用到condition才需要去实现它。
tryAcquire(int)//独占方式。尝试获取资源,成功则返回true,失败则返回false。
tryRelease(int)//独占方式。尝试释放资源,成功则返回true,失败则返回false。tryAcquireShared(int)//共享方式。尝试获取资源。负数表示失败;0表示成功,但没有剩余可用资源;正数表示成功,且有剩余资源。
tryReleaseShared(int)//共享方式。尝试释放资源,成功则返回true,失败则返回false。
简言之,就是AQS提供tryAcquire,tryAcquireShared等模板方法,给子类实现自定义的同步器。
自定义同步器。
基于以上分析,我们都知道state,CLH队列,ConditionObject队列 等这些关键点,你要实现自定义锁的话,首先需要确定你要实现的是独占锁还是共享锁,定义原子变量state的含义,再定义一个内部类去继承AQS,重写对应的模板方法。
我们来看一下基于 AQS 实现的不可重入的独占锁的demo,来自《Java并发编程之美》:
public
class
NonReentrantLock
implements
Lock
,
Serializable
{
//内部类,自定义同步器
static
class
Sync
extends
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
{
//是否锁已经被持有
public
boolean
isHeldExclusively
()
{
return
getState
()
==
1
;
}
//如果state为0 则尝试获取锁
public
boolean
tryAcquire
(
int
arg
)
{
assert
arg
==
1
;
//CAS设置状态,能保证操作的原子性,当前为状态为0,操作成功状态改为1
if
(
compareAndSetState
(
0
,
1
)){
//设置当前独占的线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread
(
Thread
.
currentThread
());
return
true
;
}
return
false
;
}
//尝试释放锁,设置state为0
public
boolean
tryRelease
(
int
arg
)
{
assert
arg
==
1
;
//如果同步器同步器状态等于0,则抛出监视器非法状态异常
if
(
getState
()
==
0
)
throw
new
IllegalMonitorStateException
();
//设置独占锁的线程为null
setExclusiveOwnerThread
(
null
);
//设置同步状态为0
setState
(
0
);
return
true
;
}
//返回Condition,每个Condition都包含了一个Condition队列
Condition
newCondition
(){
return
new
ConditionObject
();
}
}
//创建一个Sync来做具体的工作
private
final
Sync
sync
=
new
Sync
();
@Override
public
void
lock
()
{
sync
.
acquire
(
1
);
}
public
boolean
isLocked
()
{
return
sync
.
isHeldExclusively
();
}
@Override
public
void
lockInterruptibly
()
throws
InterruptedException
{
sync
.
acquireInterruptibly
(
1
);
}
@Override
public
boolean
tryLock
()
{
return
sync
.
tryAcquire
(
1
);
}
@Override
public
boolean
tryLock
(
long
time
,
TimeUnit
unit
)
throws
InterruptedException
{
return
sync
.
tryAcquireNanos
(
1
,
unit
.
toNanos
(
time
));
}
@Override
public
void
unlock
()
{
sync
.
release
(
1
);
}
@Override
public
Condition
newCondition
()
{
return
sync
.
newCondition
();
}
}NonReentrantLockDemoTest:
public
class
NonReentrantLockDemoTest
{
private
static
NonReentrantLock
nonReentrantLock
=
new
NonReentrantLock
();
public
static
void
main
(
String
[]
args
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
10
;
i
++)
{
Thread
thread
=
new
Thread
(()
->
{
nonReentrantLock
.
lock
();
try
{
System
.
out
.
println
(
Thread
.
currentThread
().
getName
());
Thread
.
sleep
(
3000
);
}
catch
(
InterruptedException
e
)
{
e
.
printStackTrace
();
}
finally
{
nonReentrantLock
.
unlock
();
}
});
thread
.
start
();
}
}
}运行结果:
AQS全家桶实战
AQS派生出如ReentrantLock、Semaphore等AQS全家桶,接下来可以看一下它们的使用案例。
ReentrantLock
ReentrantLock介绍
- ReentrantLock为重入锁,能够对共享资源能够重复加锁,是实现Lock接口的一个类。
- ReentrantLock支持公平锁和非公平锁两种方式
ReentrantLock案例
使用ReentrantLock来实现个简单线程安全的list,如下:
public
class
ReentrantLockList
{
// 线程不安全的list
private
ArrayList
<
String
>
array
=
new
ArrayList
<>();
//独占锁
private
volatile
ReentrantLock
lock
=
new
ReentrantLock
();
//添加元素
public
void
add
(
String
e
){
lock
.
lock
();
try
{
array
.
add
(
e
);
}
finally
{
lock
.
unlock
();
}
}
//删除元素
public
void
remove
(
String
e
){
lock
.
lock
();
try
{
array
.
remove
(
e
);
}
finally
{
lock
.
unlock
();
}
}
//获取元素
public
String
get
(
int
index
){
lock
.
lock
();
try
{
return
array
.
get
(
index
);
}
finally
{
lock
.
unlock
();
}
}
}Semaphore
Semaphore介绍
- Semaphore也叫信号量,可以用来控制资源并发访问的线程数量,通过协调各个线程,以保证合理的使用资源。
Semaphore案例
Java多线程有一到比较经典的面试题:ABC三个线程顺序输出,循环10遍。
public
class
ABCSemaphore
{
private
static
Semaphore
A
=
new
Semaphore
(
1
);
private
static
Semaphore
B
=
new
Semaphore
(
1
);
private
static
Semaphore
C
=
new
Semaphore
(
1
);
static
class
ThreadA
extends
Thread
{
@Override
public
void
run
()
{
try
{
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
10
;
i
++)
{
A
.
acquire
();
System
.
out
.
print
(
"A"
);
B
.
release
();
}
}
catch
(
InterruptedException
e
)
{
e
.
printStackTrace
();
}
}
}
static
class
ThreadB
extends
Thread
{
@Override
public
void
run
()
{
try
{
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
10
;
i
++)
{
B
.
acquire
();
System
.
out
.
print
(
"B"
);
C
.
release
();
}
}
catch
(
InterruptedException
e
)
{
e
.
printStackTrace
();
}
}
}
static
class
ThreadC
extends
Thread
{
@Override
public
void
run
()
{
try
{
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
10
;
i
++)
{
C
.
acquire
();
System
.
out
.
print
(
"C"
);
A
.
release
();
}
}
catch
(
InterruptedException
e
)
{
e
.
printStackTrace
();
}
}
}
public
static
void
main
(
String
[]
args
)
throws
InterruptedException
{
// 开始只有A可以获取, BC都不可以获取, 保证了A最先执行
B
.
acquire
();
C
.
acquire
();
new
ThreadA
().
start
();
new
ThreadB
().
start
();
new
ThreadC
().
start
();
}参考
- 《Java并发编程之美》
- 【死磕Java并发】—–J.U.C之AQS
以上是关于AQS解析与实战的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章