字节流
Posted maxuefeng
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了字节流相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
字节输出流:
OutputStream此抽象类,是表示输出字节流的所有类的超类。以Stream结尾的都是输出字节流。
成员方法:
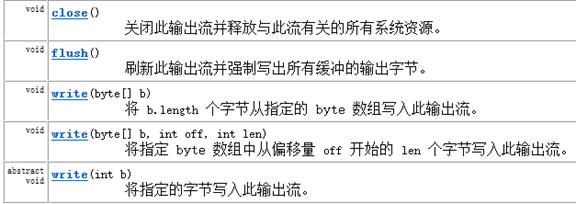
FileOutputStream类:
OutputStream有很多子类,其中子类FileOutputStream可用来写入数据到文件。FileOutputStream类,即文件输出流,是用于将数据写入 File的输出流。
构造方法:

public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //明确目的地 //如果目的地文件不存在,则会创建。 //如果目的地为文件存在,则会覆盖。 //new FileOutputStream("D:\\io0803\\demo10.txt",true); //(目的地地址,是否续写) FileOutputStream fos= new FileOutputStream("D:\\io0803\\demo10.txt",true); //写一个字节 fos.write(49); fos.write(48); fos.write(48); //写一个字节数组 byte[] bytes={-65,-66,-67,-68}; fos.write(bytes); //写字节数组中指定字节 fos.write(bytes, 1, 2); //换行 fos.write("你好吗 我很号".getBytes()); //释放资源 fos.close(); } }
处理异常:
public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //明确目的地 //如果目的地文件不存在,则会创建。 //如果目的地为文件存在,则会覆盖。 //new FileOutputStream("D:\\io0803\\demo10.txt",true); //(目的地地址,是否续写) //写一个字节 FileOutputStream fos=null; try { fos= new FileOutputStream("D:\\io0803\\demo10.txt",true); fos.write(49); fos.write(48); fos.write(48); //写一个字节数组 byte[] bytes={-65,-66,-67,-68}; fos.write(bytes); //写字节数组中指定字节 fos.write(bytes, 1, 2); //换行 fos.write("你好吗 我很号".getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //释放资源 if(fos!=null){ try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
字节输入流:
InputStream此抽象类,是表示字节输入流的所有类的超类。
成员方法:

int read():读取一个字节并返回,没有字节返回-1.
int read(byte[]): 读取一定量的字节数,并存储到字节数组中,返回读取到的字节数。
FileInputStream类:
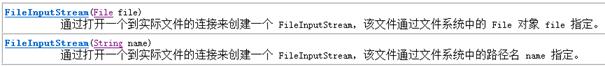
InputStream有很多子类,其中子类FileInputStream可用来读取文件内容。FileInputStream 从文件系统中的某个文件中获得输入字节。
构造方法:
成员方法:


public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建字节输入流对象,明确数据源(从哪读); FileInputStream fis= new FileInputStream("D:\\io0803\\demo10.txt"); //读一个字节 int len=0; while((len=fis.read())!=-1){ System.out.println((char)len); } //释放资源 fis.close(); } }
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建字节输入流对象,明确数据源 FileInputStream fis= new FileInputStream("D:\\io0803\\demo10.txt"); //一个字节数组一个字节数组读 byte[] bytes=new byte[2]; int len=0; while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len)); } //释放资源 fis.close(); } }
一个字节一个字节的复制文件代码:
public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //明确数据源 FileInputStream fis= new FileInputStream("D:\\io0803\\demo10.txt"); //明确目的地 FileOutputStream fos= new FileOutputStream("D:\\io0803\\a\\demo10.txt"); //开始复制(一个字节) int len=0; while((len=fis.read())!=-1){ //写一个字节 fos.write(len); } //释放资源 fis.close(); fos.close(); } }
一个数组一个数组的复制文件:
public class Demo06 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //明确数据源 FileInputStream fis= new FileInputStream("D:\\io0803\\demo10.txt"); //明确目的地 FileOutputStream fos= new FileOutputStream("D:\\io0803\\a\\b\\demo09.txt"); //开始复制(一个数组) byte bytes[]=new byte[1024]; int len=0; while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ fos.write(bytes,0,len); } //释放资源 fis.close(); fos.close(); } }
以上是关于字节流的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章