多线程
Posted dissipate
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了多线程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
from threading import Event,Thread
import logging,time
FORMAT=‘%(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s‘
logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO)
def boss(event:Event):
logging.info(‘boss is waitting‘)
event.wait()
logging.info(‘boss: work is done‘)
def worker(event:Event,count=10):
logging.info(‘worker start‘)
cups=[]
while True:
cups.append(1)
time.sleep(0.5)
logging.info(‘append 1‘)
if len(cups)>=10:
event.set()
break
logging.info(‘worker finished, cups={}‘.format(cups))
event=Event()
w=Thread(target=worker,args=(event,))
b=Thread(target=boss,args=(event,))
w.start()
b.start()
使用同一个Event对象的标记flag
event.wait()就是等到flag变为True,或等到超时返回False,不限制等待时间
from threading import Event,Thread
import logging,time
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
def do(event:Event,interval:int):
while not event.wait(interval):
logging.info(‘do sth‘)
e=Event()
Thread(target=do,args=(e,3)).start()
# e.wait(10)
time.sleep(10)
e.set()
print(‘main exited‘)
wait优于sleep,wait会主动出让时间片,其它线程可以调度,而sleep会占用时间片,不出让
Timer类的实现
from threading import Thread,Event
import logging,datetime
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
def add(x:int,y:int):
logging.info(x+y)
class Timer():
def __init__(self,interval,fn,*args,**kwargs):
self.interval=interval
self.fn=fn
self.args=args
self.kwargs=kwargs
self.event=Event()
def start(self):
Thread(target=self.__run).start()
def cancel(self):
self.event.set()
def __run(self):
start=datetime.datetime.now()
logging.info(‘waiting‘)
self.event.wait(self.interval)
if not self.event.is_set():
self.fn(*self.args,**self.kwargs)
delta=(datetime.datetime.now()-start).total_seconds()
logging.info(‘finished {}‘.format(delta))
t=Timer(5,add,3,9)
t.start()
e=Event()
e.wait(3)
t.cancel()
Lock:
lock 存在共享资源争抢的地方都可以使用索,从而保证只有一个使用者可以完全使用这个资源
import logging,threading
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
cups=[]
lock=threading.Lock()
def w(lock:threading.Lock,n=100):
while True:
lock.acquire()
count=len(cups)
logging.info(count)
if count>=n:
lock.release()
break
cups.append(1)
lock.release()
logging.info(‘{} produce‘.format(threading.current_thread()))
for b in range(10):
threading.Thread(target=w,args=(lock,20)).start()
threading.Event().wait(1)
print(len(cups))
print(threading.enumerate())
import threading,logging,time
FORMAT=‘%(name)s %(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s‘
logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO)
cups=[]
def worker(count=10):
logging.info(‘produce cups‘)
flag=True
while True:
if len(cups)>=count:
flag=False
time.sleep(0.001)
if not flag:
break
if flag:
cups.append(1)
logging.info(‘{} done,cups: {}‘.format(threading.current_thread(),len(cups)))
for _ in range(10):
threading.Thread(target=worker,args=(20,)).start()
threading.Event().wait(1)
print(len(cups))
Lock
一旦线程获得锁,其它试图获得锁的线程将被 阻塞,
| acquire(blocking=True,timeout=-1) | 默认阻塞,可以设置阻塞超时时间,非阻塞时,timeout禁止设置,成功获取锁,返回True,否则返回False |
| release() | 释放锁,可以从任何线程调用release(),已上锁的Lock会被重置为unlocked,未上锁调用release(),抛出RuntimeError异常 |
Counter类
import threading,time
class C:
def __init__(self):
self.__val=0
@property
def value(self):
return self.__val
def inc(self):
lock.acquire()
self.__val+=1
lock.release()
def dec(self):
lock.acquire()
self.__val-=1
lock.release()
lock=threading.Lock()
def run(c:C,count=100):
for _ in range(count):
for p in range(-50,50):
if p<0:
# lock.acquire()
c.dec()
# lock.release()
else:
# lock.acquire()
c.inc()
# lock.release()
c=C()
c1=10
c2=10000
for b in range(c1):
threading.Thread(target=run,args=(c,c2)).start()
# time.sleep(0.001)
print(c.value)
while True:
time.sleep(0.5)
print(threading.enumerate())
print(c.value)
类中加锁 或者 操作加锁
通过with 或 try finally确保锁释放
import threading,time
class C:
def __init__(self):
self.__val=0
self.__lock=threading.Lock()
@property
def value(self):
with self.__lock:
return self.__val
def inc(self):
try:
self.__lock.acquire()
self.__val+=1
finally:
self.__lock.release()
def dec(self):
try:
self.__lock.acquire()
self.__val-=1
finally:
self.__lock.release()
def dec(self):
with self.__lock:
self.__val-=1
def run(c:C,count=100):
for _ in range(count):
for p in range(-50,50):
if p<0:
c.inc()
else:
c.dec()
c=C()
c1=10
c2=1000
for _ in range(c1):
threading.Thread(target=run,args=(c,c2)).start()
while True:
if threading.active_count() == 1:
print(threading.enumerate())
print(c.value)
else:
print(threading.enumerate())
time.sleep(0.5)
import threading,logging,time
FORMAT=‘%(name)s %(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s‘
logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO)
cups=[]
def worker(lock:threading.Lock,task=100):
while True:
if lock.acquire(blocking=False):
count=len(cups)
logging.info(‘number of cups: {}‘.format(count))
if count>=task: # 每个子线程必须执行此退出条件
lock.release()
break
cups.append(1)
lock.release()
logging.info(‘{} produce {} cup‘.format(threading.current_thread().name,len(cups)))
time.sleep(0.5)
logging.info(‘worker end,number of cups: {}‘.format(len(cups)))
lock=threading.Lock()
for _ in range(10):
threading.Thread(target=worker,args=(lock,40)).start()
while True:
if threading.active_count() == 1:
print(threading.enumerate())
print(len(cups))
else:
print(threading.enumerate())
time.sleep(1)
import threading,logging,time
FORMAT=‘%(asctime)-15s [%(threadName)s %(thread)8d] %(message)s‘
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT)
def worker(tasks):
for task in tasks:
time.sleep(0.01) # 强行切换线程,使任务依次执行
if task.lock.acquire(blocking=False):
logging.info(‘{} {} acquire success‘.format(threading.current_thread(),task.name))
else:
logging.info(‘{} {} acquire failed‘.format(threading.current_thread(),task.name))
class Task:
def __init__(self,name):
self.name=name
self.lock=threading.Lock()
tasks=[Task(‘task-{}‘.format(p)) for p in range(10)]
for b in range(5):
threading.Thread(target=worker,name=‘worker-{}‘.format(b),args=(tasks,)).start()
可重入锁RLock Reentrant Lock
线程相关锁
线程A获得可重入锁,并可以多次获取成功,不会阻塞,最后要在线程A中做和acquire()次数相同的release()
import threading
lock=threading.RLock()
ret=lock.acquire()
print(ret)
ret=lock.acquire(timeout=5)
print(ret)
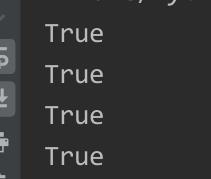
print(lock.acquire(True))
print(lock.acquire(False))
import threading
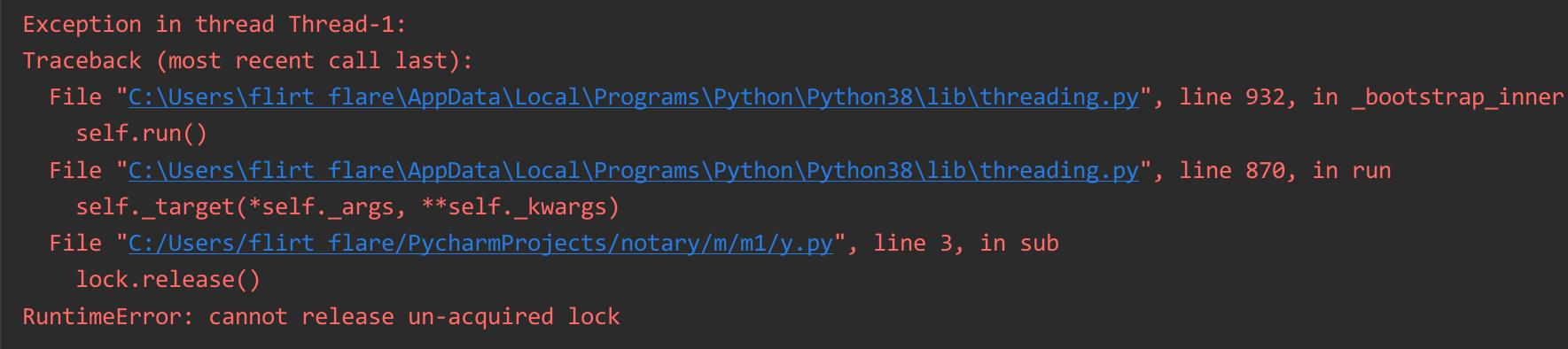
def sub(lock:threading.RLock):
lock.release()
lock=threading.RLock()
print(lock.acquire())
print(lock.acquire(timeout=3))
threading.Thread(target=sub,args=(lock,)).start()
import threading,time
lock=threading.RLock()
print(lock.acquire())
print(‘~‘*80)
print(lock.acquire(blocking=True))
print(lock.acquire(blocking=False))
print(lock.acquire(timeout=3))
# for _ in range(5): # RuntimeError
# lock.release()
# print(lock.acquire(blocking=False,timeout=3)) # ValueError
for _ in range(4): # 使Timer线程不阻塞
lock.release()
def sub(lock:threading.RLock):
print(‘{}: {}‘.format(threading.current_thread(),lock.acquire()))
print(‘{}: {}‘.format(threading.current_thread(),lock.acquire()))
print(lock.release())
print(lock.release())
# print(lock.release())
threading.Timer(2,sub,args=(lock,)).start()
不同线程获取同一个RLock时会阻塞
threading.Condition:
import threading,logging,random
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=‘%(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s‘)
class Dispatcher:
def __init__(self):
self.data=0
self.event=threading.Event()
self.cond=threading.Condition()
def produce(self):
for b in range(100):
with self.cond:
self.data=random.randint(1,100)
logging.info(‘produce {}‘.format(self.data))
# self.cond.notify_all()
self.cond.notify(2)
self.event.wait(1)
def consume(self):
while True:
with self.cond:
self.cond.wait()
logging.info(‘thread {} consume {}‘.format(threading.current_thread(),self.data))
# self.event.wait(0.5)
v=Dispatcher()
# threading.Thread(target=v.produce).start()
# threading.Event().wait(3)
# threading.Thread(target=v.consume).start()
# threading.Thread(target=v.consume).start()
for b in range(5):
threading.Thread(target=v.consume,name=‘consumer-{}‘.format(b)).start()
threading.Thread(target=v.produce).start()
import threading,logging,random
FORMAT=‘%(asctime)s [%(threadName)s %(thread)d] %(message)s‘
logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.CRITICAL)
class Dispatcher:
def __init__(self):
self.data=None
self.event=threading.Event()
def produce(self,total):
for _ in range(total):
data=random.randrange(1,100)
logging.critical(data)
self.data=data
self.event.wait(1)
self.event.set() # 结束consume的endless loop
def consume(self):
while not self.event.is_set():
logging.critical(‘received {}‘.format(self.data))
self.data=None
self.event.wait(0.5)
v=Dispatcher()
threading.Thread(target=v.consume,name=‘consumer‘).start()
threading.Event().wait(2)
threading.Thread(target=v.produce,args=(10,),name=‘producer‘).start()
import threading,logging,time
FORMAT=‘%(name)s %(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s‘
logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO)
cups=[]
def worker(lock:threading.Lock,task=100):
while True:
if lock.acquire(blocking=False):
count=len(cups)
logging.info(‘number of cups: {}‘.format(count))
if count>=task: # 每个子线程必须执行此退出条件
lock.release()
break
cups.append(1)
lock.release()
logging.info(‘{} produce {} cup‘.format(threading.current_thread().name,len(cups)))
time.sleep(0.5)
logging.info(‘worker end,number of cups: {}‘.format(len(cups)))
lock=threading.Lock()
for _ in range(10):
threading.Thread(target=worker,args=(lock,40)).start()
while True:
if threading.active_count() == 1:
print(threading.enumerate())
print(len(cups))
else:
print(threading.enumerate())
time.sleep(1)
import threading,logging,random
FORMAT=‘%(asctime)s [ %(threadName)s %(thread)d ] %(message)s‘
logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.ERROR)
class Dispatcher:
def __init__(self):
self.data=None
self.event=threading.Event()
self.cond=threading.Condition()
def produce(self,total):
for _ in range(total):
with self.cond:
data=random.randint(1,100)
logging.error(data)
self.data=data
self.cond.notify_all()
self.event.wait(1)
self.event.set()
print(88888888888888888888888888)
with self.cond: # notify最后一次使consumer结束循环
self.cond.notify_all()
def consumer(self):
while not self.event.is_set():
with self.cond:
print(3333333333)
self.cond.wait()
print(444444444444444444444)
logging.error(‘received {}‘.format(self.data))
self.data=None
self.event.wait(0.5)
print(self.event.is_set())
v=Dispatcher()
threading.Thread(target=v.produce,args=(5 ,),name=‘producer‘).start()
threading.Event().wait(1)
threading.Thread(target=v.consumer,name=‘consumer‘).start()
以上是关于多线程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章