磁盘格式化与性能测试
Posted ggzhangxiaochao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了磁盘格式化与性能测试相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、硬盘相关
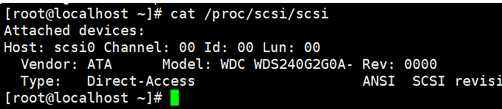
1)查看硬盘的参数,执行cat /proc/scsi/scsi ,显示为ATA,则为SATA的硬盘。
2) 物理硬件设备命名规则
硬件设备在Linux中是以文件形式进行定义和管理,而文件需要命名规范,udev设备管理器在/dev/目录下为所有的设备定义了内核设备的名称,
它是当前Linux默认的设备管理工具,以守护进程的形式运行,通过侦听内核发出来的uevent 来管理/dev目录下的设备文件。
通过命名规范目的是让用户通过设备文件的名字即可猜出设备大致的属性以及分区信息等。
Linux系统中常见的硬件设备文件名称如下:
| 硬件设备 | 文件名称 |
|---|---|
| IDE设备 | /dev/hd[a-d] |
| SCSI/SATA/U 盘 | /dev/sd[a-p] |
| 软驱 | /dev/fd[0-1] |
| 打印机 | /dev/lp[0-15] |
| 光驱 | /dev/cdrom |
| 鼠标 | /dev/mouse |
| 磁带机 | /dev/st0 或/dev/ht0 |
常用的也就SCSI/SATA硬盘或光驱,当进行磁盘扩容等空间管理时会用到磁盘设备,当安装光盘镜像时会用到光驱设备。
硬盘设备一般以“/dev/sd”开头,而一台主机上可以有多块硬盘,因此系统采用 a~p 来代表 16 块不同的硬盘,默认从a开始分配。
分区编号也有一定规则:主分区或扩展分区的编号从 1- 4 ,而逻辑分区从5开始编号。
磁盘在进行测试之前,首先进行分区、格式化文件系统、挂载。
一、磁盘分区
1、执行fdisk -l查看分区的情况。
[root@localhost ~ ]# fdisk - l Disk / dev / sda: 16.1 GB, 16106127360 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors / track, 1958 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System / dev / sda1 * 1 6 48163 + 83 Linux / dev / sda2 7 515 4088542 + 83 Linux / dev / sda3 516 1239 5815530 83 Linux / dev / sda4 1240 1305 530145 5 Extended / dev / sda5 1240 1305 530113 + 82 Linux swap / Solaris
假设/dev/sdb 显示还没有分区,则进行分区。
2、继续执行fdisk /dev/sda进行新建磁盘进行分区
[root@CENTOS100 sdb]# fdisk /dev/sdb The device presents a logical sector size that is smaller than the physical sector size. Aligning to a physical sector (or optimal I/O) size boundary is recommended, or performance may be impacted. Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. Be careful before using the write command. Command (m for help): m Command action a toggle a bootable flag b edit bsd disklabel c toggle the dos compatibility flag d delete a partition g create a new empty GPT partition table G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table l list known partition types m print this menu n add a new partition o create a new empty DOS partition table p print the partition table q quit without saving changes s create a new empty Sun disklabel t change a partition‘s system id u change display/entry units v verify the partition table w write table to disk and exit x extra functionality (experts only)
Command (m for help): n Command action e extended p primary partition ( 1 - 4 ) e Selected partition 1 First cylinder ( 1240 - 1958 , default 1240 ): Using default value 1240 Last cylinder or + size or + sizeM or + sizeK ( 1240 - 1958 , default 1958 ): Using default value 1958 Command (m for help): m
Command (m for help): p #显示分区
Disk /dev/sdb: 2000.4 GB, 2000398934016 bytes, 3907029168 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x15c3159d
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 3907029167 1953513560 83 Linux
Command (m for help): w #记得保存 The partition table has been altered !
3)No free sectors available错误
在继续分区的时候,出现No free sectors available错误,是因为磁盘已经进行了分区,用光了扇区,
需要将已经分好的分区删除(如果不需要重新分区,直接进行格式化)。
[root@CENTOS100 sdb]# fdisk /dev/sdb The device presents a logical sector size that is smaller than the physical sector size. Aligning to a physical sector (or optimal I/O) size boundary is recommended, or performance may be impacted. Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. Be careful before using the write command. Command (m for help): m Command action a toggle a bootable flag b edit bsd disklabel c toggle the dos compatibility flag d delete a partition g create a new empty GPT partition table G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table l list known partition types m print this menu n add a new partition o create a new empty DOS partition table p print the partition table q quit without saving changes s create a new empty Sun disklabel t change a partition‘s system id u change display/entry units v verify the partition table w write table to disk and exit x extra functionality (experts only) Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 2000.4 GB, 2000398934016 bytes, 3907029168 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x15c3159d Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdb1 2048 3907029167 1953513560 83 Linux Command (m for help):m Command (m for help):d #删除分区,执行一次d删除一个分区
二、磁盘格式化
格式化:指将分区格式化成不同的文件系统。那什么是文件系统呢?
文件系统:指操作系统用于明确存储设备或分区上的文件的方法和数据结构:即在存储设备上组织文件的方法。
就好比一个教室,同学们的坐的位置总是与桌子凳子排列的方式有关系。桌子,凳子怎么摆放,就导致了同学坐的位置在哪里。
文件系统存放数据也是这么个道理。
1、Linux系统下的文件类型:
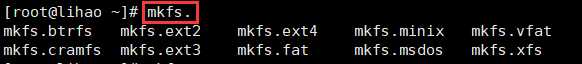
Linux下的文件类型有ext2、ext3、ext4、xfs等等,我们可以使用命令:mkfs. 然后用按TAB、TAB来查看都有哪些文件类型。
2、磁盘的格式化:
在命令行输入mkfs.xfs /dev/sdb1
[root@heimatengyun ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/sdb1 meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize=256 agcount=4, agsize=131072 blks = sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1 = crc=0 data = bsize=4096 blocks=524288, imaxpct=25 = sunit=0 swidth=0 blks naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=0 log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2 = sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1 realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
磁盘在格式化期间出现,ata bus error的错误,请重启机器重新格式化。
三、挂载磁盘
1、挂载磁盘使用之前讲解的mount命令,需要先创建一个挂载点目录。
[root@heimatengyun ~]# mkdir /newDisk [root@heimatengyun ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /newDisk/ [root@heimatengyun ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/centos-root 18G 3.7G 14G 21% / devtmpfs 905M 0 905M 0% /dev tmpfs 914M 80K 914M 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 914M 8.9M 905M 1% /run tmpfs 914M 0 914M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda1 497M 119M 379M 24% /boot /dev/sdb1 2.0G 33M 2.0G 2% /newDisk
2、使用新加的磁盘设备
切换到新加设备所在的目录,添加文件并查看文件及其占用的大小:
[root@heimatengyun ~]# cd /newDisk/ [root@heimatengyun newDisk]# echo ‘test‘>test.txt [root@heimatengyun newDisk]# ll total 4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 Dec 28 18:57 test.txt [root@heimatengyun newDisk]# du -sh /newDisk/ 4.0K /newDisk/
可以看到文件创建成功。
3、使用df -h命令查看挂载状态和硬盘使用量:
[root@heimatengyun ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/centos-root 18G 3.7G 14G 21% / devtmpfs 905M 0 905M 0% /dev tmpfs 914M 80K 914M 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 914M 8.9M 905M 1% /run tmpfs 914M 0 914M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sdb1 2.0G 33M 2.0G 2% /newDisk /dev/sda1 497M 119M 379M 24% /boot
可以看到磁盘挂载成功,至此,说明新挂载的文件没有任何问题,可以正常使用。
4、永久挂载
查看系统的磁盘io性能到底如何,这里使用iostat命令来分析。
Linux系统出现了性能问题,一般我们可以通过top、iostat、free、vmstat等命令来查看初步定位问题。
top整体查看状态,free查看mem和swap,vmstat整体查看,其中iostat可以给我们提供丰富的IO状态数据。
1、关键指标:
rrqm/s: 每秒进行 merge 的读操作数目。即 delta(rmerge)/s
wrqm/s: 每秒进行 merge 的写操作数目。即 delta(wmerge)/s
r/s: 每秒完成的读 I/O 设备次数。即 delta(rio)/s
w/s: 每秒完成的写 I/O 设备次数。即 delta(wio)/s
rsec/s: 每秒读扇区数。即 delta(rsect)/s
wsec/s: 每秒写扇区数。即 delta(wsect)/s
rkB/s: 每秒读K字节数。是 rsect/s 的一半,因为每扇区大小为512字节。(需要计算)
wkB/s: 每秒写K字节数。是 wsect/s 的一半。(需要计算)
avgrq-sz: 平均每次设备I/O操作的数据大小 (扇区)。delta(rsect+wsect)/delta(rio+wio)
avgqu-sz:平均I/O队列长度。即 delta(aveq)/s/1000 (因为aveq的单位为毫秒)。
await: 平均每次设备I/O操作的等待时间 (毫秒)。即 delta(ruse+wuse)/delta(rio+wio)
svctm: 平均每次设备I/O操作的服务时间 (毫秒)。即 delta(use)/delta(rio+wio)
%util: 一秒中有百分之多少的时间用于 I/O 操作,或者说一秒中有多少时间 I/O 队列是非空的。即 delta(use)/s/1000 (因为use的单位为毫秒)
如果 %util 接近 100%,说明产生的I/O请求太多,I/O系统已经满负荷,该磁盘
可能存在瓶颈。
idle小于70% IO压力就较大了,一般读取速度有较多的wait.
同时可以结合vmstat 查看查看b参数()和wa参数(),查看是否存在io等待。
1、基本使用
$iostat -d -k 1 10
其中,参数 -d 表示,显示设备(磁盘)使用状态;-k某些使用block为单位的列强制使用Kilobytes为单位;
1 10表示,数据显示每隔1秒刷新一次,共显示10次。
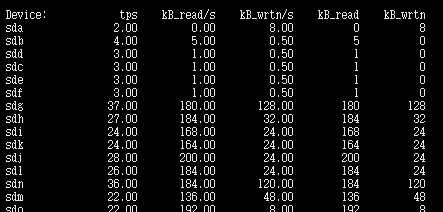
tps:该设备每秒的传输次数(Indicate the number of transfers per second that were issued to the device.)。
“一次传输”意思是“一次I/O请求”。多个逻辑请求可能会被合并为“一次I/O请求”。“一次传输”请求的大小是未知的。
kB_read/s:每秒从设备(drive expressed)读取的数据量;kB_wrtn/s:每秒向设备(drive expressed)写入的数据量;
kB_read:读取的总数据量;kB_wrtn:写入的总数量数据量;这些单位都为Kilobytes。
上面的例子中,我们可以看到磁盘sda以及它的各个分区的统计数据,当时统计的磁盘总TPS是39.29,下面是各个分区的TPS。
(因为是瞬间值,所以总TPS并不严格等于各个分区TPS的总和)
2、-x 参数
使用-x参数我们可以获得更多统计信息。
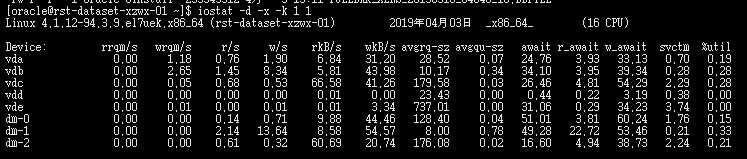
rrqm/s:每秒这个设备相关的读取请求有多少被Merge了(当系统调用需要读取数据的时候,VFS将请求发到各个FS,
如果FS发现不同的读取请求读取的是相同Block的数据,FS会将这个请求合并Merge);wrqm/s:每秒这个设备相关的写入请求有多少被Merge了。
rsec/s:每秒读取的扇区数;wsec/:每秒写入的扇区数。
r/s:The number of read requests that were issued to the device per second;
w/s:The number of write requests that were issued to the device per second;
await:每一个IO请求的处理的平均时间(单位是微秒毫秒)。这里可以理解为IO的响应时间,一般地系统IO响应时间应该低于5ms,如果大于10ms就比较大了。
%util:在统计时间内所有处理IO时间,除以总共统计时间。例如,如果统计间隔1秒,该设备有0.8秒在处理IO,而0.2秒闲置,
那么该设备的%util = 0.8/1 = 80%,所以该参数暗示了设备的繁忙程度。一般地,如果该参数是100%表示设备已经接近满负荷运行了
(当然如果是多磁盘,即使%util是100%,因为磁盘的并发能力,所以磁盘使用未必就到了瓶颈)。
3、常见用法
4. 常见用法
[root@CENTOS100 sdb]# iostat -dkx 1 10 Linux 3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64 (CENTOS100) 01/30/2017 _x86_64_ (8 CPU) Device: rrqm/s wrqm/s r/s w/s rkB/s wkB/s avgrq-sz avgqu-sz await r_await w_await svctm %util sda 0.04 0.05 0.12 3.41 3.20 379.10 216.63 1.49 423.53 14.68 437.31 3.22 1.14 sdb 0.00 0.11 0.01 0.97 0.22 474.93 972.79 0.48 492.19 2.05 496.24 3.66 0.36 dm-0 0.00 0.00 0.13 0.35 2.84 5.68 35.99 0.03 71.89 17.51 91.42 6.28 0.30 dm-1 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.06 0.00 45.59 0.00 8.76 8.76 0.00 5.68 0.00 dm-2 0.00 0.00 0.01 3.11 0.03 373.07 238.94 1.48 473.08 4.30 474.46 3.30 1.03 sdc 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.04 0.00 64.73 0.00 2.74 2.74 0.00 2.32 0.00
dd if=/dev/zero of=test.file bs=2GB count=10
以上是关于磁盘格式化与性能测试的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章