spring AOP解析之xml方式详解
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring AOP解析之xml方式详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

<aop:config>标签解析
aop名称空间的解析器是AopNamespaceHandler
// 这里我们可以看到注册了几个解析器,重点关注ConfigBeanDefinitionParser

在ConfigBeanDefinitionParser的parse方法中对aop:config下面的三个直接子标签pointcut、advisor、aspect分别进行解析
List<Element> childElts = DomUtils.getChildElements(element);
for (Element elt: childElts) {
String localName = parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(elt);
if (POINTCUT.equals(localName)) {
parsePointcut(elt, parserContext);
}
else if (ADVISOR.equals(localName)) {
parseAdvisor(elt, parserContext);
}
else if (ASPECT.equals(localName)) {
parseAspect(elt, parserContext);
}
}
pointcut标签解析
private AbstractBeanDefinition parsePointcut(Element pointcutElement, ParserContext parserContext) {
String id = pointcutElement.getAttribute(ID);
String expression = pointcutElement.getAttribute(EXPRESSION);
AbstractBeanDefinition pointcutDefinition = null;
try {
this.parseState.push(new PointcutEntry(id));
// 创建BeanDefinition,下边详解
pointcutDefinition = createPointcutDefinition(expression);
pointcutDefinition.setSource(parserContext.extractSource(pointcutElement));
String pointcutBeanName = id;
if (StringUtils.hasText(pointcutBeanName)) {
// 这里是注册bean
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(pointcutBeanName, pointcutDefinition);
}
else {
pointcutBeanName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(pointcutDefinition);
}
parserContext.registerComponent(
new PointcutComponentDefinition(pointcutBeanName, pointcutDefinition, expression));
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return pointcutDefinition;
}
protected AbstractBeanDefinition createPointcutDefinition(String expression) {
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(AspectJExpressionPointcut.class);
beanDefinition.setScope(BeanDefinition.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE);
beanDefinition.setSynthetic(true);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(EXPRESSION, expression);
return beanDefinition;
}
我们可以看到RootBeanDefinition的beanClass是AspectJExpressionPointcut,也就是getBean时会实例化AspectJExpressionPointcut,并且为其设置了属性值expression如execution(* com.wjz.service.*.*(..))
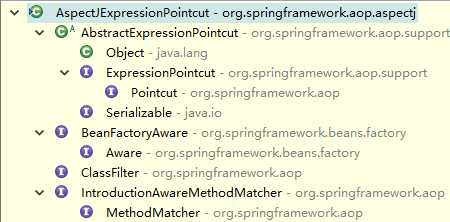
我们来看一下AspectJExpressionPointcut的继承结构。这个类同时实现了ClassFilter和MethodMatcher接口执行类匹配和方法匹配逻辑。它有一个expression属性设置表达式,AspectJ最终会把该表达式解析成一个PointcutExpression对象执行相关的语义。后文详解
aspect标签解析
aspect标签的解析要相对复杂一些,解析它下面的所有通知子标签(aop:before、aop:after等标签)
String aspectId = aspectElement.getAttribute(ID);
String aspectName = aspectElement.getAttribute(REF);
// 获得所有的通知子标签
NodeList nodeList = aspectElement.getChildNodes();
boolean adviceFoundAlready = false;
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nodeList.item(i);
// 判断是否是通知标签如before,after-returning
if (isAdviceNode(node, parserContext)) {
if (!adviceFoundAlready) {
adviceFoundAlready = true;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(aspectName)) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"<aspect> tag needs aspect bean reference via ‘ref‘ attribute when declaring advices.",
aspectElement, this.parseState.snapshot());
return;
}
beanReferences.add(new RuntimeBeanReference(aspectName));
}
// 解析并注册通知子标签,后文详解
AbstractBeanDefinition advisorDefinition = parseAdvice(
aspectName, i, aspectElement, (Element) node, parserContext, beanDefinitions, beanReferences);
beanDefinitions.add(advisorDefinition);
}
}
AspectComponentDefinition aspectComponentDefinition = createAspectComponentDefinition(
aspectElement, aspectId, beanDefinitions, beanReferences, parserContext);
parserContext.pushContainingComponent(aspectComponentDefinition);
List<Element> pointcuts = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(aspectElement, POINTCUT);
for (Element pointcutElement : pointcuts) {
parsePointcut(pointcutElement, parserContext);
}
parserContext.popAndRegisterContainingComponent();
private AbstractBeanDefinition parseAdvice(
String aspectName, int order, Element aspectElement, Element adviceElement, ParserContext parserContext,
List<BeanDefinition> beanDefinitions, List<BeanReference> beanReferences) {
try {
this.parseState.push(new AdviceEntry(parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(adviceElement)));
// 通知标签的方法属性(method属性)会被解析成一个MethodLocatingFactoryBean类型的bean,并设置了methodName属性值
// 为AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice等的构造函数的形参作准备
RootBeanDefinition methodDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(MethodLocatingFactoryBean.class);
methodDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("targetBeanName", aspectName);
methodDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("methodName", adviceElement.getAttribute("method"));
methodDefinition.setSynthetic(true);
// 创建AspectInstanceFactory的一个实例,为AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice等的构造函数的形参作准备
RootBeanDefinition aspectFactoryDef = new RootBeanDefinition(SimpleBeanFactoryAwareAspectInstanceFactory.class);
aspectFactoryDef.getPropertyValues().add("aspectBeanName", aspectName);
aspectFactoryDef.setSynthetic(true);
// 准备AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice等的构造函数,后文详解
AbstractBeanDefinition adviceDef = createAdviceDefinition(
adviceElement, parserContext, aspectName, order, methodDefinition, aspectFactoryDef,
beanDefinitions, beanReferences);
// 解析通知子标签为AspectJPointcutAdvisor对象
RootBeanDefinition advisorDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(AspectJPointcutAdvisor.class);
advisorDefinition.setSource(parserContext.extractSource(adviceElement));
// 设置AspectJPointcutAdvisor中的AbstractAspectJAdvice的构造函数参数信息
advisorDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(adviceDef);
if (aspectElement.hasAttribute(ORDER_PROPERTY)) {
advisorDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(
ORDER_PROPERTY, aspectElement.getAttribute(ORDER_PROPERTY));
}
// 注册通知子标签
parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(advisorDefinition);
return advisorDefinition;
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
private AbstractBeanDefinition createAdviceDefinition(
Element adviceElement, ParserContext parserContext, String aspectName, int order,
RootBeanDefinition methodDef, RootBeanDefinition aspectFactoryDef,
List<BeanDefinition> beanDefinitions, List<BeanReference> beanReferences) {
// getAdviceClass()方法获得AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice、AspectJAfterReturningAdvice等
RootBeanDefinition adviceDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(getAdviceClass(adviceElement, parserContext));
adviceDefinition.setSource(parserContext.extractSource(adviceElement));
// 添加属性值
adviceDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(ASPECT_NAME_PROPERTY, aspectName);
adviceDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(DECLARATION_ORDER_PROPERTY, order);
if (adviceElement.hasAttribute(RETURNING)) {
adviceDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(
RETURNING_PROPERTY, adviceElement.getAttribute(RETURNING));
}
if (adviceElement.hasAttribute(THROWING)) {
adviceDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(
THROWING_PROPERTY, adviceElement.getAttribute(THROWING));
}
if (adviceElement.hasAttribute(ARG_NAMES)) {
adviceDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(
ARG_NAMES_PROPERTY, adviceElement.getAttribute(ARG_NAMES));
}
// 准备AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice等构造函数所需的参数,为构造函数反射得到AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice做准备
ConstructorArgumentValues cav = adviceDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues();
cav.addIndexedArgumentValue(METHOD_INDEX, methodDef);
// 获得pointcut-ref属性值
Object pointcut = parsePointcutProperty(adviceElement, parserContext);
if (pointcut instanceof BeanDefinition) {
cav.addIndexedArgumentValue(POINTCUT_INDEX, pointcut);
beanDefinitions.add((BeanDefinition) pointcut);
}
else if (pointcut instanceof String) {
RuntimeBeanReference pointcutRef = new RuntimeBeanReference((String) pointcut);
cav.addIndexedArgumentValue(POINTCUT_INDEX, pointcutRef);
beanReferences.add(pointcutRef);
}
cav.addIndexedArgumentValue(ASPECT_INSTANCE_FACTORY_INDEX, aspectFactoryDef);
return adviceDefinition;
}
AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice等的构造函数为

advisor标签解析
private void parseAdvisor(Element advisorElement, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 创建advisor标签对应的BeanDefinition,后文详解
AbstractBeanDefinition advisorDef = createAdvisorBeanDefinition(advisorElement, parserContext);
String id = advisorElement.getAttribute(ID);
try {
this.parseState.push(new AdvisorEntry(id));
String advisorBeanName = id;
// 注册bean
if (StringUtils.hasText(advisorBeanName)) {
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(advisorBeanName, advisorDef);
}
else {
advisorBeanName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(advisorDef);
}
// 获得pointcut-ref属性值,添加属性
Object pointcut = parsePointcutProperty(advisorElement, parserContext);
if (pointcut instanceof BeanDefinition) {
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add(POINTCUT, pointcut);
parserContext.registerComponent(
new AdvisorComponentDefinition(advisorBeanName, advisorDef, (BeanDefinition) pointcut));
}
else if (pointcut instanceof String) {
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add(POINTCUT, new RuntimeBeanReference((String) pointcut));
parserContext.registerComponent(
new AdvisorComponentDefinition(advisorBeanName, advisorDef));
}
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
private AbstractBeanDefinition createAdvisorBeanDefinition(Element advisorElement, ParserContext parserContext) {
// getBean时实例化一个DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor
RootBeanDefinition advisorDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor.class);
advisorDefinition.setSource(parserContext.extractSource(advisorElement));
String adviceRef = advisorElement.getAttribute(ADVICE_REF);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(adviceRef)) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"‘advice-ref‘ attribute contains empty value.", advisorElement, this.parseState.snapshot());
}
else {
advisorDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(
ADVICE_BEAN_NAME, new RuntimeBeanNameReference(adviceRef));
}
if (advisorElement.hasAttribute(ORDER_PROPERTY)) {
advisorDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(
ORDER_PROPERTY, advisorElement.getAttribute(ORDER_PROPERTY));
}
return advisorDefinition;
}
以上是关于spring AOP解析之xml方式详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章