文本分类-05BiLSTM+Attention
Posted yifanrensheng
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了文本分类-05BiLSTM+Attention相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
- 大纲概述
- 数据集合
- 数据处理
- 预训练word2vec模型
一、大纲概述
文本分类这个系列将会有8篇左右文章,从github直接下载代码,从百度云下载训练数据,在pycharm上导入即可使用,包括基于word2vec预训练的文本分类,与及基于近几年的预训练模型(ELMo,BERT等)的文本分类。总共有以下系列:
word2vec预训练词向量
textCNN 模型
charCNN 模型
Bi-LSTM 模型
Bi-LSTM + Attention 模型
Transformer 模型
ELMo 预训练模型
BERT 预训练模型
模型结构
Bi-LSTM + Attention模型来源于论文Attention-Based Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Relation Classification。
Bi-LSTM + Attention 就是在Bi-LSTM的模型上加入Attention层,在Bi-LSTM中我们会用最后一个时序 的输出向量 作为特征向量,然后进行softmax分类。Attention是先计算每个时序的权重,然后将所有时序 的向量进行加权和作为特征向量,然后进行softmax分类。在实验中,加上Attention确实对结果有所提升。其模型结构如下图:
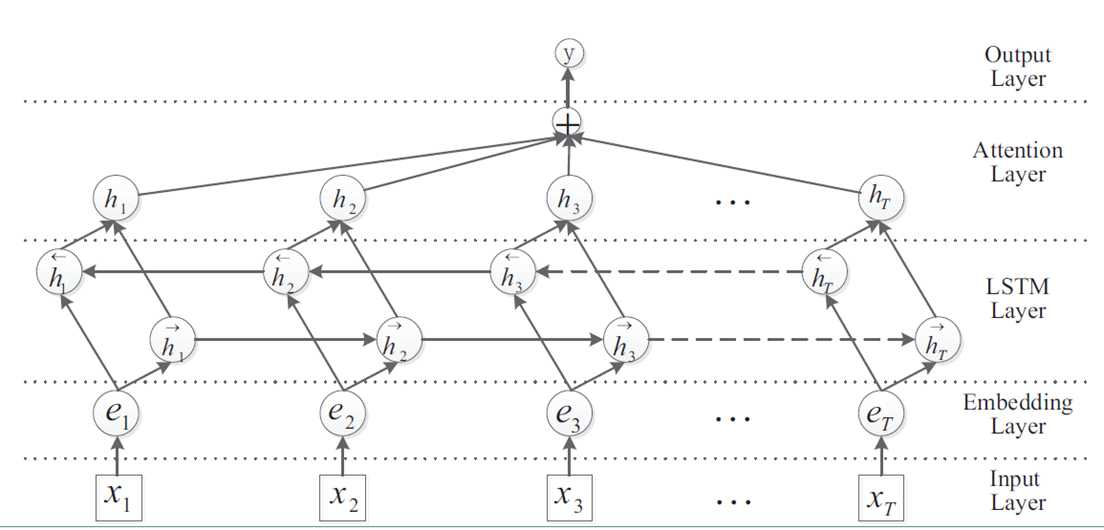
二、数据集合
数据集为IMDB 电影影评,总共有三个数据文件,在/data/rawData目录下,包括unlabeledTrainData.tsv,labeledTrainData.tsv,testData.tsv。在进行文本分类时需要有标签的数据(labeledTrainData),但是在训练word2vec词向量模型(无监督学习)时可以将无标签的数据一起用上。
训练数据地址:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1-XEwx1ai8kkGsMagIFKX_g 提取码:rtz8
三、主要代码
3.1 配置训练参数:parameter_config.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | # Author:yifan #需要的所有导入包,存放留用,转换到jupyter后直接使用 # 1 配置训练参数 class TrainingConfig(object): epoches = 4 evaluateEvery = 100 checkpointEvery = 100 learningRate = 0.001 ? class ModelConfig(object): embeddingSize = 200 hiddenSizes = [256, 128] # LSTM结构的神经元个数 dropoutKeepProb = 0.5 l2RegLambda = 0.0 ? class Config(object): sequenceLength = 200 # 取了所有序列长度的均值 batchSize = 128 dataSource = "../data/preProcess/labeledTrain.csv" stopWordSource = "../data/english" numClasses = 1 # 二分类设置为1,多分类设置为类别的数目 rate = 0.8 # 训练集的比例 training = TrainingConfig() model = ModelConfig() ? # 实例化配置参数对象 config = Config() |
3.2 获取训练数据:get_train_data.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 | # Author:yifan import json from collections import Counter import gensim import pandas as pd import numpy as np import parameter_config # 2 数据预处理的类,生成训练集和测试集 class Dataset(object): def __init__(self, config): self.config = config self._dataSource = config.dataSource self._stopWordSource = config.stopWordSource self._sequenceLength = config.sequenceLength # 每条输入的序列处理为定长 self._embeddingSize = config.model.embeddingSize self._batchSize = config.batchSize self._rate = config.rate self._stopWordDict = {} self.trainReviews = [] self.trainLabels = [] self.evalReviews = [] self.evalLabels = [] self.wordEmbedding = None self.labelList = [] def _readData(self, filePath): """ 从csv文件中读取数据集,就本次测试的文件做记录 """ df = pd.read_csv(filePath) #读取文件,是三列的数据,第一列是review,第二列sentiment,第三列rate if self.config.numClasses == 1: labels = df["sentiment"].tolist() #读取sentiment列的数据, 显示输出01序列数组25000条 elif self.config.numClasses > 1: labels = df["rate"].tolist() #因为numClasses控制,本次取样没有取超过二分类 该处没有输出 review = df["review"].tolist() reviews = [line.strip().split() for line in review] #按空格语句切分 return reviews, labels def _labelToIndex(self, labels, label2idx): """ 将标签转换成索引表示 """ labelIds = [label2idx[label] for label in labels] #print(labels==labelIds) 结果显示为true,也就是两个一样 return labelIds def _wordToIndex(self, reviews, word2idx): """将词转换成索引""" reviewIds = [[word2idx.get(item, word2idx["UNK"]) for item in review] for review in reviews] # print(max(max(reviewIds))) # print(reviewIds) return reviewIds #返回25000个无序的数组 def _genTrainEvalData(self, x, y, word2idx, rate): """生成训练集和验证集 """ reviews = [] # print(self._sequenceLength) # print(len(x)) for review in x: #self._sequenceLength为200,表示长的切成200,短的补齐,x数据依旧是25000 if len(review) >= self._sequenceLength: reviews.append(review[:self._sequenceLength]) else: reviews.append(review + [word2idx["PAD"]] * (self._sequenceLength - len(review))) # print(len(review + [word2idx["PAD"]] * (self._sequenceLength - len(review)))) #以下是按照rate比例切分训练和测试数据: trainIndex = int(len(x) * rate) trainReviews = np.asarray(reviews[:trainIndex], dtype="int64") trainLabels = np.array(y[:trainIndex], dtype="float32") evalReviews = np.asarray(reviews[trainIndex:], dtype="int64") evalLabels = np.array(y[trainIndex:], dtype="float32") return trainReviews, trainLabels, evalReviews, evalLabels ? ? def _getWordEmbedding(self, words): """按照我们的数据集中的单词取出预训练好的word2vec中的词向量 反馈词和对应的向量(200维度),另外前面增加PAD对用0的数组,UNK对应随机数组。 """ wordVec = gensim.models.KeyedVectors.load_word2vec_format("../word2vec/word2Vec.bin", binary=True) vocab = [] wordEmbedding = [] # 添加 "pad" 和 "UNK", vocab.append("PAD") vocab.append("UNK") wordEmbedding.append(np.zeros(self._embeddingSize)) # _embeddingSize 本文定义的是200 wordEmbedding.append(np.random.randn(self._embeddingSize)) # print(wordEmbedding) for word in words: try: vector = wordVec.wv[word] vocab.append(word) wordEmbedding.append(vector) except: print(word + "不存在于词向量中") # print(vocab[:3],wordEmbedding[:3]) return vocab, np.array(wordEmbedding) def _genVocabulary(self, reviews, labels): """生成词向量和词汇-索引映射字典,可以用全数据集""" allWords = [word for review in reviews for word in review] #单词数量5738236 reviews是25000个观点句子【】 subWords = [word for word in allWords if word not in self.stopWordDict] # 去掉停用词 wordCount = Counter(subWords) # 统计词频 sortWordCount = sorted(wordCount.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) #返回键值对,并按照数量排序 # print(len(sortWordCount)) #161330 # print(sortWordCount[:4],sortWordCount[-4:]) # [(‘movie‘, 41104), (‘film‘, 36981), (‘one‘, 24966), (‘like‘, 19490)] [(‘daeseleires‘, 1), (‘nice310‘, 1), (‘shortsightedness‘, 1), (‘unfairness‘, 1)] words = [item[0] for item in sortWordCount if item[1] >= 5] # 去除低频词,低于5的 vocab, wordEmbedding = self._getWordEmbedding(words) self.wordEmbedding = wordEmbedding word2idx = dict(zip(vocab, list(range(len(vocab))))) #生成类似这种{‘I‘: 0, ‘love‘: 1, ‘yanzi‘: 2} uniqueLabel = list(set(labels)) #标签去重 最后就 0 1了 label2idx = dict(zip(uniqueLabel, list(range(len(uniqueLabel))))) #本文就 {0: 0, 1: 1} self.labelList = list(range(len(uniqueLabel))) # 将词汇-索引映射表保存为json数据,之后做inference时直接加载来处理数据 with open("../data/wordJson/word2idx.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f: json.dump(word2idx, f) with open("../data/wordJson/label2idx.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f: json.dump(label2idx, f) return word2idx, label2idx ? ? def _readStopWord(self, stopWordPath): """ 读取停用词 """ with open(stopWordPath, "r") as f: stopWords = f.read() stopWordList = stopWords.splitlines() # 将停用词用列表的形式生成,之后查找停用词时会比较快 self.stopWordDict = dict(zip(stopWordList, list(range(len(stopWordList))))) ? ? def dataGen(self): """ 初始化训练集和验证集 """ # 初始化停用词 self._readStopWord(self._stopWordSource) # 初始化数据集 reviews, labels = self._readData(self._dataSource) # 初始化词汇-索引映射表和词向量矩阵 word2idx, label2idx = self._genVocabulary(reviews, labels) # 将标签和句子数值化 labelIds = self._labelToIndex(labels, label2idx) reviewIds = self._wordToIndex(reviews, word2idx) # 初始化训练集和测试集 trainReviews, trainLabels, evalReviews, evalLabels = self._genTrainEvalData(reviewIds, labelIds, word2idx, self._rate) self.trainReviews = trainReviews self.trainLabels = trainLabels ? ? self.evalReviews = evalReviews self.evalLabels = evalLabels ? ? #获取前些模块的数据 # config =parameter_config.Config() # data = Dataset(config) # data.dataGen() |
3.3 模型构建:mode_structure.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 | import tensorflow as tf import parameter_config config = parameter_config.Config() # 构建模型 3 Bi-LSTM + Attention模型 # 构建模型 class BiLSTMAttention(object): def __init__(self, config, wordEmbedding): # 定义模型的输入 self.inputX = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, config.sequenceLength], name="inputX") self.inputY = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None], name="inputY") self.dropoutKeepProb = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="dropoutKeepProb") # 定义l2损失 l2Loss = tf.constant(0.0) ? # 词嵌入层 with tf.name_scope("embedding"): # 利用预训练的词向量初始化词嵌入矩阵 self.W = tf.Variable(tf.cast(wordEmbedding, dtype=tf.float32, name="word2vec") ,name="W") # 利用词嵌入矩阵将输入的数据中的词转换成词向量,维度[batch_size, sequence_length, embedding_size] self.embeddedWords = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.W, self.inputX) ? # 定义两层双向LSTM的模型结构 with tf.name_scope("Bi-LSTM"): for idx, hiddenSize in enumerate(config.model.hiddenSizes): with tf.name_scope("Bi-LSTM" + str(idx)): # 定义前向LSTM结构 lstmFwCell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(num_units=hiddenSize, state_is_tuple=True), output_keep_prob=self.dropoutKeepProb) # 定义反向LSTM结构 lstmBwCell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(num_units=hiddenSize, state_is_tuple=True), output_keep_prob=self.dropoutKeepProb) ? ? ? ? # 采用动态rnn,可以动态的输入序列的长度,若没有输入,则取序列的全长 # outputs是一个元祖(output_fw, output_bw),其中两个元素的维度都是[batch_size, max_time, hidden_size],fw和bw的hidden_size一样 # self.current_state 是最终的状态,二元组(state_fw, state_bw),state_fw=[batch_size, s],s是一个元祖(h, c) outputs_, self.current_state = tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(lstmFwCell, lstmBwCell, self.embeddedWords, dtype=tf.float32, scope="bi-lstm" + str(idx)) ? # 对outputs中的fw和bw的结果拼接 [batch_size, time_step, hidden_size * 2], 传入到下一层Bi-LSTM中 self.embeddedWords = tf.concat(outputs_, 2) ? # 将最后一层Bi-LSTM输出的结果分割成前向和后向的输出 outputs = tf.split(self.embeddedWords, 2, -1) ? # 在Bi-LSTM+Attention的论文中,将前向和后向的输出相加 with tf.name_scope("Attention"): H = outputs[0] + outputs[1] ? ? # 得到Attention的输出 output = self.attention(H) outputSize = config.model.hiddenSizes[-1] ? # 全连接层的输出 with tf.name_scope("output"): outputW = tf.get_variable( "outputW", shape=[outputSize, config.numClasses], initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer()) ? outputB= tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[config.numClasses]), name="outputB") l2Loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(outputW) l2Loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(outputB) self.logits = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(output, outputW, outputB, name="logits") ? if config.numClasses == 1: self.predictions = tf.cast(tf.greater_equal(self.logits, 0.0), tf.float32, name="predictions") elif config.numClasses > 1: self.predictions = tf.argmax(self.logits, axis=-1, name="predictions") ? # 计算二元交叉熵损失 with tf.name_scope("loss"): ? if config.numClasses == 1: losses = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=self.logits, labels=tf.cast(tf.reshape(self.inputY, [-1, 1]), dtype=tf.float32)) elif config.numClasses > 1: losses = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=self.logits, labels=self.inputY) ? self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses) + config.model.l2RegLambda * l2Loss ? def attention(self, H): """ 利用Attention机制得到句子的向量表示 """ # 获得最后一层LSTM的神经元数量 hiddenSize = config.model.hiddenSizes[-1] ? # 初始化一个权重向量,是可训练的参数 W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([hiddenSize], stddev=0.1)) ? # 对Bi-LSTM的输出用激活函数做非线性转换 M = tf.tanh(H) ? # 对W和M做矩阵运算,W=[batch_size, time_step, hidden_size],计算前做维度转换成[batch_size * time_step, hidden_size] # newM = [batch_size, time_step, 1],每一个时间步的输出由向量转换成一个数字 newM = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(M, [-1, hiddenSize]), tf.reshape(W, [-1, 1])) ? # 对newM做维度转换成[batch_size, time_step] restoreM = tf.reshape(newM, [-1, config.sequenceLength]) ? # 用softmax做归一化处理[batch_size, time_step] self.alpha = tf.nn.softmax(restoreM) ? # 利用求得的alpha的值对H进行加权求和,用矩阵运算直接操作 r = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(H, [0, 2, 1]), tf.reshape(self.alpha, [-1, config.sequenceLength, 1])) ? # 将三维压缩成二维sequeezeR=[batch_size, hidden_size] sequeezeR = tf.reshape(r, [-1, hiddenSize]) ? sentenceRepren = tf.tanh(sequeezeR) ? # 对Attention的输出可以做dropout处理 output = tf.nn.dropout(sentenceRepren, self.dropoutKeepProb) ? return output |
3.4 模型训练:mode_trainning.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 | import os import datetime import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import parameter_config import get_train_data import mode_structure ? ? #获取前些模块的数据 config =parameter_config.Config() data = get_train_data.Dataset(config) data.dataGen() ? ? #4生成batch数据集 def nextBatch(x, y, batchSize): # 生成batch数据集,用生成器的方式输出 perm = np.arange(len(x)) #返回[0 1 2 ... len(x)]的数组 np.random.shuffle(perm) #乱序 x = x[perm] y = y[perm] numBatches = len(x) // batchSize ? ? for i in range(numBatches): start = i * batchSize end = start + batchSize batchX = np.array(x[start: end], dtype="int64") batchY = np.array(y[start: end], dtype="float32") yield batchX, batchY ? ? # 5 定义计算metrics的函数 """ 定义各类性能指标 """ def mean(item: list) -> float: """ 计算列表中元素的平均值 :param item: 列表对象 :return: """ res = sum(item) / len(item) if len(item) > 0 else 0 return res ? ? def accuracy(pred_y, true_y): """ 计算二类和多类的准确率 :param pred_y: 预测结果 :param true_y: 真实结果 :return: """ if isinstance(pred_y[0], list): pred_y = [item[0] for item in pred_y] corr = 0 for i in range(len(pred_y)): if pred_y[i] == true_y[i]: corr += 1 acc = corr / len(pred_y) if len(pred_y) > 0 else 0 return acc ? ? def binary_precision(pred_y, true_y, positive=1): """ 二类的精确率计算 :param pred_y: 预测结果 :param true_y: 真实结果 :param positive: 正例的索引表示 :return: """ corr = 0 pred_corr = 0 for i in range(len(pred_y)): if pred_y[i] == positive: pred_corr += 1 if pred_y[i] == true_y[i]: corr += 1 ? ? prec = corr / pred_corr if pred_corr > 0 else 0 return prec ? ? def binary_recall(pred_y, true_y, positive=1): """ 二类的召回率 :param pred_y: 预测结果 :param true_y: 真实结果 :param positive: 正例的索引表示 :return: """ corr = 0 true_corr = 0 for i in range(len(pred_y)): if true_y[i] == positive: true_corr += 1 if pred_y[i] == true_y[i]: corr += 1 ? ? rec = corr / true_corr if true_corr > 0 else 0 return rec ? ? def binary_f_beta(pred_y, true_y, beta=1.0, positive=1): """ 二类的f beta值 :param pred_y: 预测结果 :param true_y: 真实结果 :param beta: beta值 :param positive: 正例的索引表示 :return: """ precision = binary_precision(pred_y, true_y, positive) recall = binary_recall(pred_y, true_y, positive) try: f_b = (1 + beta * beta) * precision * recall / (beta * beta * precision + recall) except: f_b = 0 return f_b ? ? def multi_precision(pred_y, true_y, labels): """ 多类的精确率 :param pred_y: 预测结果 :param true_y: 真实结果 :param labels: 标签列表 :return: """ if isinstance(pred_y[0], list): pred_y = [item[0] for item in pred_y] ? ? precisions = [binary_precision(pred_y, true_y, label) for label in labels] prec = mean(precisions) return prec ? ? def multi_recall(pred_y, true_y, labels): """ 多类的召回率 :param pred_y: 预测结果 :param true_y: 真实结果 :param labels: 标签列表 :return: """ if isinstance(pred_y[0], list): pred_y = [item[0] for item in pred_y] ? ? recalls = [binary_recall(pred_y, true_y, label) for label in labels] rec = mean(recalls) return rec ? ? def multi_f_beta(pred_y, true_y, labels, beta=1.0): """ 多类的f beta值 :param pred_y: 预测结果 :param true_y: 真实结果 :param labels: 标签列表 :param beta: beta值 :return: """ if isinstance(pred_y[0], list): pred_y = [item[0] for item in pred_y] ? ? f_betas = [binary_f_beta(pred_y, true_y, beta, label) for label in labels] f_beta = mean(f_betas) return f_beta ? ? def get_binary_metrics(pred_y, true_y, f_beta=1.0): """ 得到二分类的性能指标 :param pred_y: :param true_y: :param f_beta: :return: """ acc = accuracy(pred_y, true_y) recall = binary_recall(pred_y, true_y) precision = binary_precision(pred_y, true_y) f_beta = binary_f_beta(pred_y, true_y, f_beta) return acc, recall, precision, f_beta ? ? def get_multi_metrics(pred_y, true_y, labels, f_beta=1.0): """ 得到多分类的性能指标 :param pred_y: :param true_y: :param labels: :param f_beta: :return: """ acc = accuracy(pred_y, true_y) recall = multi_recall(pred_y, true_y, labels) precision = multi_precision(pred_y, true_y, labels) f_beta = multi_f_beta(pred_y, true_y, labels, f_beta) return acc, recall, precision, f_beta ? ? # 6 训练模型 # 生成训练集和验证集 trainReviews = data.trainReviews trainLabels = data.trainLabels evalReviews = data.evalReviews evalLabels = data.evalLabels wordEmbedding = data.wordEmbedding labelList = data.labelList ? ? # 定义计算图 with tf.Graph().as_default(): ? ? session_conf = tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True, log_device_placement=False) session_conf.gpu_options.allow_growth=True session_conf.gpu_options.per_process_gpu_memory_fraction = 0.9 # 配置gpu占用率 ? ? sess = tf.Session(config=session_conf) ? # 定义会话 with sess.as_default(): bilstmattention = mode_structure.BiLSTMAttention(config, wordEmbedding) globalStep = tf.Variable(0, name="globalStep", trainable=False) # 定义优化函数,传入学习速率参数 optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(config.training.learningRate) # 计算梯度,得到梯度和变量 gradsAndVars = optimizer.compute_gradients(bilstmattention.loss) # 将梯度应用到变量下,生成训练器 trainOp = optimizer.apply_gradients(gradsAndVars, global_step=globalStep) ? # 用summary绘制tensorBoard gradSummaries = [] for g, v in gradsAndVars: if g is not None: tf.summary.histogram("{}/grad/hist".format(v.name), g) tf.summary.scalar("{}/grad/sparsity".format(v.name), tf.nn.zero_fraction(g)) ? outDir = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.curdir, "summarys")) print("Writing to {} ".format(outDir)) ? lossSummary = tf.summary.scalar("loss", bilstmattention.loss) summaryOp = tf.summary.merge_all() ? trainSummaryDir = os.path.join(outDir, "train") trainSummaryWriter = tf.summary.FileWriter(trainSummaryDir, sess.graph) ? evalSummaryDir = os.path.join(outDir, "eval") evalSummaryWriter = tf.summary.FileWriter(evalSummaryDir, sess.graph) ? ? # 初始化所有变量 saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables(), max_to_keep=5) ? # 保存模型的一种方式,保存为pb文件 savedModelPath = "../model/bilstm-atten/savedModel" if os.path.exists(savedModelPath): os.rmdir(savedModelPath) builder = tf.saved_model.builder.SavedModelBuilder(savedModelPath) ? sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) ? ? def trainStep(batchX, batchY): """ 训练函数 """ feed_dict = { bilstmattention.inputX: batchX, bilstmattention.inputY: batchY, bilstmattention.dropoutKeepProb: config.model.dropoutKeepProb } _, summary, step, loss, predictions = sess.run( [trainOp, summaryOp, globalStep, bilstmattention.loss, bilstmattention.predictions], feed_dict) timeStr = datetime.datetime.now().isoformat() ? if config.numClasses == 1: acc, recall, prec, f_beta = get_binary_metrics(pred_y=predictions, true_y=batchY) ? ? elif config.numClasses > 1: acc, recall, prec, f_beta = get_multi_metrics(pred_y=predictions, true_y=batchY, labels=labelList) ? trainSummaryWriter.add_summary(summary, step) ? return loss, acc, prec, recall, f_beta ? ? def devStep(batchX, batchY): """ 验证函数 """ feed_dict = { bilstmattention.inputX: batchX, bilstmattention.inputY: batchY, bilstmattention.dropoutKeepProb: 1.0 } summary, step, loss, predictions = sess.run( [summaryOp, globalStep, bilstmattention.loss, bilstmattention.predictions], feed_dict) ? if config.numClasses == 1: ? acc, precision, recall, f_beta = get_binary_metrics(pred_y=predictions, true_y=batchY) elif config.numClasses > 1: acc, precision, recall, f_beta = get_multi_metrics(pred_y=predictions, true_y=batchY, labels=labelList) ? evalSummaryWriter.add_summary(summary, step) ? return loss, acc, precision, recall, f_beta ? for i in range(config.training.epoches): # 训练模型 print("start training model") for batchTrain in nextBatch(trainReviews, trainLabels, config.batchSize): loss, acc, prec, recall, f_beta = trainStep(batchTrain[0], batchTrain[1]) ? currentStep = tf.train.global_step(sess, globalStep) print("train: step: {}, loss: {}, acc: {}, recall: {}, precision: {}, f_beta: {}".format( currentStep, loss, acc, recall, prec, f_beta)) if currentStep % config.training.evaluateEvery == 0: print(" Evaluation:") ? losses = [] accs = [] f_betas = [] precisions = [] recalls = [] ? for batchEval in nextBatch(evalReviews, evalLabels, config.batchSize): loss, acc, precision, recall, f_beta = devStep(batchEval[0], batchEval[1]) losses.append(loss) accs.append(acc) f_betas.append(f_beta) precisions.append(precision) recalls.append(recall) ? time_str = datetime.datetime.now().isoformat() print("{}, step: {}, loss: {}, acc: {},precision: {}, recall: {}, f_beta: {}".format(time_str, currentStep, mean(losses), mean(accs), mean(precisions), mean(recalls), mean(f_betas))) ? if currentStep % config.training.checkpointEvery == 0: # 保存模型的另一种方法,保存checkpoint文件 path = saver.save(sess, "../model/bilstm-atten/model/my-model", global_step=currentStep) print("Saved model checkpoint to {} ".format(path)) ? inputs = {"inputX": tf.saved_model.utils.build_tensor_info(bilstmattention.inputX), "keepProb": tf.saved_model.utils.build_tensor_info(bilstmattention.dropoutKeepProb)} ? ? outputs = {"predictions": tf.saved_model.utils.build_tensor_info(bilstmattention.predictions)} ? ? prediction_signature = tf.saved_model.signature_def_utils.build_signature_def(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, method_name=tf.saved_model.signature_constants.PREDICT_METHOD_NAME) legacy_init_op = tf.group(tf.tables_initializer(), name="legacy_init_op") builder.add_meta_graph_and_variables(sess, [tf.saved_model.tag_constants.SERVING], signature_def_map={"predict": prediction_signature}, legacy_init_op=legacy_init_op) ? ? builder.save() |
3.5 预测:predict.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 | # Author:yifan import os import csv import time import datetime import random import json from collections import Counter from math import sqrt import gensim import pandas as pd import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score import parameter_config config =parameter_config.Config() ? ? #7预测代码 x = "this movie is full of references like mad max ii the wild one and many others the ladybug′s face it′s a clear reference or tribute to peter lorre this movie is a masterpiece we′ll talk much more about in the future" # x = "his movie is the same as the third level movie. There‘s no place to look good" # x = "This film is not good" #最终反馈为0 # x = "This film is bad" #最终反馈为0 ? ? x = "this movie is full of references like mad max ii the wild one and many others the ladybug′s face it′s a clear reference or tribute to peter lorre this movie is a masterpiece we′ll talk much more about in the future" ? ? # 注:下面两个词典要保证和当前加载的模型对应的词典是一致的 with open("../data/wordJson/word2idx.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: word2idx = json.load(f) ? with open("../data/wordJson/label2idx.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: label2idx = json.load(f) idx2label = {value: key for key, value in label2idx.items()} ? xIds = [word2idx.get(item, word2idx["UNK"]) for item in x.split(" ")] if len(xIds) >= config.sequenceLength: xIds = xIds[:config.sequenceLength] else: xIds = xIds + [word2idx["PAD"]] * (config.sequenceLength - len(xIds)) ? ? graph = tf.Graph() with graph.as_default(): gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.333) session_conf = tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True, log_device_placement=False, gpu_options=gpu_options) sess = tf.Session(config=session_conf) ? ? with sess.as_default(): checkpoint_file = tf.train.latest_checkpoint("../model/bilstm-atten/model/") saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("{}.meta".format(checkpoint_file)) saver.restore(sess, checkpoint_file) ? ? # 获得需要喂给模型的参数,输出的结果依赖的输入值 inputX = graph.get_operation_by_name("inputX").outputs[0] dropoutKeepProb = graph.get_operation_by_name("dropoutKeepProb").outputs[0] ? ? # 获得输出的结果 predictions = graph.get_tensor_by_name("output/predictions:0") ? ? pred = sess.run(predictions, feed_dict={inputX: [xIds], dropoutKeepProb: 1.0})[0] ? ? # print(pred) pred = [idx2label[item] for item in pred] print(pred) |
结果

相关代码可见:https://github.com/yifanhunter/NLP_textClassifier
主要参考:
【1】 https://home.cnblogs.com/u/jiangxinyang/
以上是关于文本分类-05BiLSTM+Attention的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章