Chapter0 - opencv基本操作
Posted rongyupan
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Chapter0 - opencv基本操作相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Chapter0 - opencv基本操作
环境简介
- 操作系统:Linux-mint-20.03
- 工具:
miniconda3, jupyter-notebook,python=3.8
为了保证独立性,使用miniconda3新建python环境;
以下所有代码都在Jupyter notebook中编写、运行成功;
导入opencv和numpy
import cv2
import numpy as np
读取图片
# read picture
img_colored = cv2.imread("opencv.png", 1) # colored image.
img_gray = cv2.imread("opencv.png", 0) # Black and white image.
print(img_gray, ‘
‘, type(img_gray), ‘
‘, img_gray.shape)
[[255 255 255 ... 255 255 255]
[255 255 255 ... 255 255 255]
[255 255 255 ... 255 255 255]
...
[255 255 255 ... 255 255 255]
[255 255 255 ... 255 255 255]
[255 255 255 ... 255 255 255]]
<class ‘numpy.ndarray‘>
(610, 570)
导入的图片显示的像素信息是:689×549,即长度689,高度549;
但是在使用.shape方法时,返回的是矩阵信息,即行×列,就要变成549×689了。
图片读取后的数据类型为np.ndarray,意味着我们可以通过操作numpy、pandas等工具,来操作图像。
print(img_colored, "
img_colored.shape:", img_colored.shape)
[[[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
...
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]]
[[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
...
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]]
[[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
...
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]]
...
[[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
...
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]]
[[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
...
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]]
[[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
...
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]
[255 255 255]]]
img_colored.shape: (610, 570, 3)
如何理解610×570×3
从矩阵的形式来看,有610个"元素",每个元素是570x3维的矩阵;
从图像的角度来看,先按行分割(610),每一行有616列,每列元素都有RGB三种属性,所以是616×3;
展示图片
# show image
cv2.namedWindow("opencv", cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)
cv2.imshow("opencv", img_gray) # "Penguins": title of image
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows() # 关闭所有窗口;
运行结果

cv.namedWindow("input",cv.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)
-
作用:会先生成一个窗口,这个窗口的顶部栏会加上
Penguins这个字样; -
配合
cv.imshow("Penguins", src),因为这两个的标题是一致的(都为Penguins),所以会放在同一个窗口中显示;如果这两个的标题并不一致,那么会出现两个窗口; -
必须配合
waitKey()和destroyAllWindows()使用!不然会卡死! -
其实如果不是特别要求显示效果,
namedWindow()选配。
waitKey(time_period)
-
等待用户事件,使窗口一直保持静态,直到用户在窗口界面随便按一下键盘,窗口才会自动关闭;
-
time_period: 单位毫秒ms,如果没有用户操作,在time_peroid毫秒后执行下一步操作;比如这里是cv2.destroyAllWindows(),关闭所有窗口; -
time_peroid=0代表一直保持窗口静态; -
一定要用按键盘退出,而不是手动关闭,不然会一直卡死的;
图片缩放
# resize image
img_resized = cv2.resize(img_gray, (600,500))
cv2.imshow("Resized", img_resized)
# resize image to one half
img_resized_half = cv2.resize(img_gray, (int(img_gray.shape[1]/2), int(img_gray.shape[0]/2)))
cv2.imshow("Resized to half", img_resized_half)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
运行结果
-
Resized to half

-
Resized

注意
- 这里的
(600, 500)代表图片的长度和高度,而不是矩阵,对应矩阵应该是:500×600; - 这里的操作是缩放而不是裁剪;
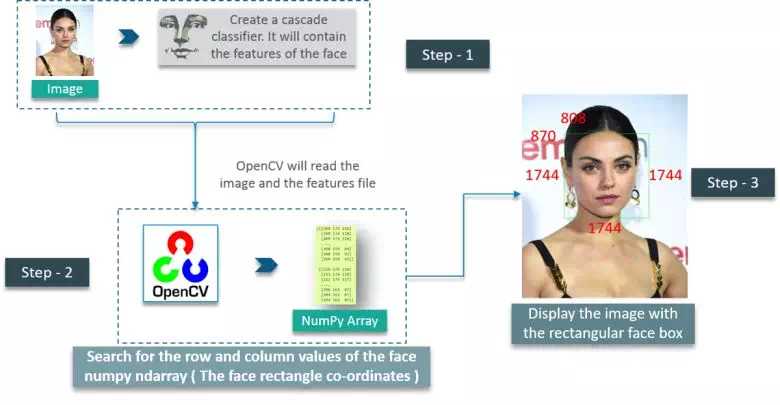
应用举例:用opencv进行人脸检测
检测的大致过程
- 创建级联分类器(Cascade Classifier),作用是提取面部特征数据,往往使用XML文件来保存面部特征数据;
- 用OpenCV读取图像,这也是个把图像-->NumPy数组的过程;
- 结合面部特征数据,对这些数组进行搜索,得到面部矩形的坐标;
- 使用矩形面框显示图像;
以上是关于Chapter0 - opencv基本操作的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章