UVA-11437 Triangle Fun(梅涅劳斯定理)(三等分点)
Posted pixel-teee
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了UVA-11437 Triangle Fun(梅涅劳斯定理)(三等分点)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题意:如下是一个三角形ABC.(点D,E和F是三角形ABC的三等分点,)求(三角形PQR)的面积。
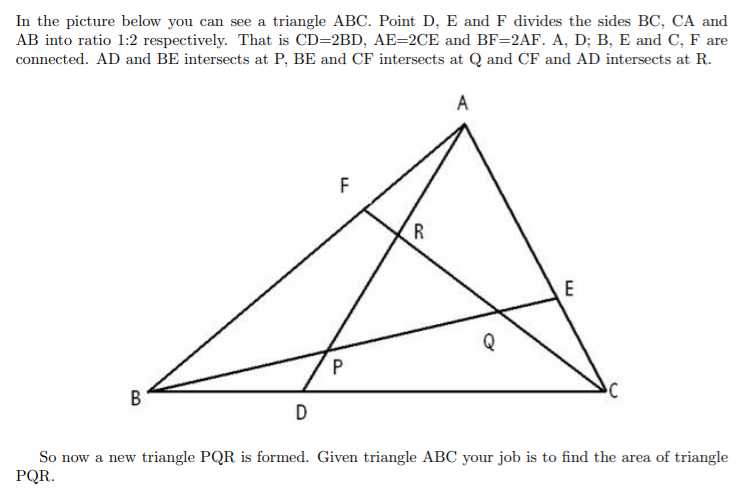
分析:三等分点的坐标可以推导出来,比如求D的坐标,D的坐标为((frac{2 * B.x + C.x}{3}, frac{2 * B.y + C.y}{3})),然后求出(三个交点P, R, Q),求出向量(vec{pr})和(vec{pq})的夹角,然后利用公式(frac{1}{2}*|pr|*|pq|*sinangle{RPQ})求出三角形面积。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const double eps = 1e-10;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
struct Point
{
double x, y;
Point(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
};
typedef Point Vector;
//向量 + 向量 = 向量, 点 + 向量 = 点
Vector operator + (Vector A, Vector B) { return Vector(A.x + B.x, A.y + B.y); }
//点 - 点 = 向量
Vector operator - (Point A, Point B) { return Vector(A.x - B.x, A.y - B.y); }
//向量 * 标量 = 向量
Vector operator * (Vector A, double p) { return Vector(A.x * p, A.y * p); }
//向量 / 数 = 向量
Vector operator / (Vector A, double p) { return Vector(A.x / p, A.y / p); }
double Dot(Vector A, Vector B) { return A.x * B.x + A.y * B.y; }
double Cross(Vector A, Vector B) { return A.x * B.y - A.y * B.x; }
double Length(Vector A) { return sqrt(Dot(A, A)); }
Vector Normal(Vector A)
{
double L = Length(A);
return Vector(-A.y / L, A.x / L);
}
int dcmp(double x)
{
if (fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
else return x < 0 ? -1 : 1;
}
bool operator<(const Point& a, const Point& b)
{
return dcmp(a.x - b.x) < 0 || dcmp(a.x - b.x) == 0 && dcmp(a.y - b.y) < 0;
}
bool operator == (const Point& a, const Point& b)
{
return dcmp(a.x - b.x) == 0 && dcmp(a.y - b.y) == 0;
}
Point GetLineIntersection(Point P, Vector v, Point Q, Vector w)
{
Vector u = P - Q;
double t = Cross(w, u) / Cross(v, w);
return P + v * t;
}
struct Line {
Point p;
Vector v;
Line(Point p, Vector v) :p(p), v(v) { }
//直线上的点坐标
Point point(double t) {
return p + v * t;
}
//平移直线d距离
Line move(double d) {
return Line(p + Normal(v) * d, v);
}
};
Point GetLineIntersection(Line a, Line b)
{
return GetLineIntersection(a.p, a.v, b.p, b.v);
}
double angle(Vector v)
{
return atan2(v.y, v.x);
}
void out(Point a)
{
cout << a.x << a.y << endl;
}
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
for (int i = 1; i <= t; ++i)
{
double ax, ay, bx, by, cx, cy;
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &ax, &ay, &bx, &by, &cx, &cy);
Point A(ax, ay), B(bx, by), C(cx, cy);
//f点(A, B的三等分点)
Point F((2 * A.x + B.x) / 3, (2 * A.y + B.y) / 3);
//d点(B, C的三等分点)
Point D((2 * B.x + C.x) / 3, (2 * B.y + C.y) / 3);
//e点(A, C的三等分点)
Point E((2 * C.x + A.x) / 3, (2 * C.y + A.y) / 3);
//直线ad
Line ad(A, A - D);
//直线be
Line be(B, B - E);
//直线cf
Line cf(C, C - F);
Point p = GetLineIntersection(ad, be);
Point q = GetLineIntersection(be, cf);
Point r = GetLineIntersection(ad, cf);
Line pr(p, p - r);
Line pq(p, p - q);
double ang2 = angle(pq.v);
double ang1 = angle(pr.v) - ang2;
//pr和pq的夹角
double ang = acos(Dot(pr.v, pq.v) / Length(pr.v) / Length(pq.v));
//余弦定理
double s = 1.0 / 2.0 * Length(pr.v) * Length(pq.v) * sin(ang);
printf("%.0lf
", s);
}
return 0;
}
以上是关于UVA-11437 Triangle Fun(梅涅劳斯定理)(三等分点)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章