基于逻辑回归信用卡欺诈检测
Posted jiaxinhuang
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于逻辑回归信用卡欺诈检测相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文件读取
import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np %matplotlib inline #由于数据太多,只读取前1000行 data = pd.read_csv("creditcard.csv",nrows=1000) data.head()
数据预处理
缺失值、异常值的处理、删除多余列
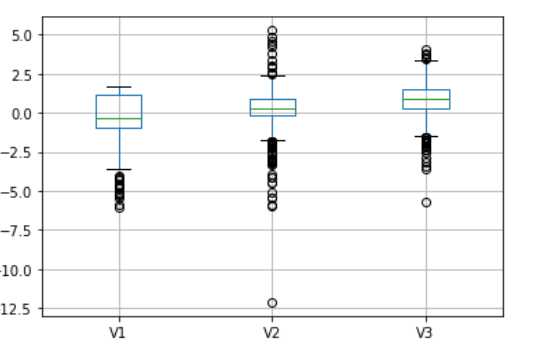
#判断是否有缺失值 data.isnull() #如果有缺失值,是否进行填补 data.fillna(method=‘ffill‘) #判断是否有异常值,可以采用箱型图 data[[‘V1‘,‘V2‘,‘V3‘]].boxplot()
#对于异常值可以删除,或则修改,根据情况而做出判断
#由于time这一列不起作用,可以直接删除,还有种方法是做pca来选择最佳的列,利用pca
data.drop([‘time‘])
特征标准化
主要解决特征因为数值差距过大而导致迭代次数过慢或则结果
#对Amount的那一列数进行特征归一化 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler data[‘normAmount‘] = StandardScaler().fit_transform(data[‘Amount‘].values.reshape(-1, 1))#因为fiy_transform(data),data:2D数据
数据分析阶段
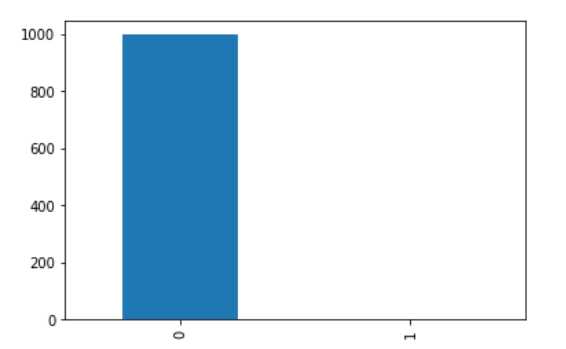
#查看标签的数量 count_classes = pd.value_counts(data[‘Class‘], sort = True) #可以做条形图进行统计
采样方法
因为当数据不足的时候需要采取上采样或者下采样,因为从上图分析可知,类别相差很多,为了预测的正确性,采用过采样的方法,增加类别的样本数量
X = data.loc[:, data.columns != ‘Class‘] y = data.loc[:, data.columns == ‘Class‘] # Number of data points in the minority class number_records_fraud = len(data[data.Class == 1]) fraud_indices = np.array(data[data.Class == 1].index) # Picking the indices of the normal classes normal_indices = data[data.Class == 0].index # Out of the indices we picked, randomly select "x" number (number_records_fraud) random_normal_indices = np.random.choice(normal_indices, number_records_fraud, replace = False) random_normal_indices = np.array(random_normal_indices) print("random_normal_indices:",random_normal_indices) # # Appending the 2 indices under_sample_indices = np.concatenate([fraud_indices,random_normal_indices]) # # Under sample dataset under_sample_data = data.iloc[under_sample_indices,:] X_undersample = under_sample_data.loc[:, under_sample_data.columns != ‘Class‘] y_undersample = under_sample_data.loc[:, under_sample_data.columns == ‘Class‘] # Showing ratio print("Percentage of normal transactions: ", len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class == 0])/len(under_sample_data)) print("Percentage of fraud transactions: ", len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class == 1])/len(under_sample_data)) print("Total number of transactions in resampled data: ", len(under_sample_data))
random_normal_indices: [979 686] Percentage of normal transactions: 0.5 Percentage of fraud transactions: 0.5 Total number of transactions in resampled data: 4
建立预测模型
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # Whole dataset X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.3, random_state = 0) print("Number transactions train dataset: ", len(X_train)) print("Number transactions test dataset: ", len(X_test)) print("Total number of transactions: ", len(X_train)+len(X_test)) # Undersampled dataset X_train_undersample, X_test_undersample, y_train_undersample, y_test_undersample = train_test_split(X_undersample ,y_undersample ,test_size = 0.3 ,random_state = 0) lr = LogisticRegression(C = best_c, penalty = ‘l1‘) lr.fit(X_train_undersample,y_train_undersample.values.ravel()) y_pred_undersample = lr.predict(X_test_undersample.values) # Compute confusion matrix cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test_undersample,y_pred_undersample) np.set_printoptions(precision=2) print("Recall metric in the testing dataset: ", cnf_matrix[1,1]/(cnf_matrix[1,0]+cnf_matrix[1,1]))
以上是关于基于逻辑回归信用卡欺诈检测的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章