循环序列模型-week1编程题1(一步步搭建循环神经网络)
Posted cxq1126
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了循环序列模型-week1编程题1(一步步搭建循环神经网络)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.循环神经网络的前向传播
1.1RNN单元

向量化m个样本,x<t>的维度为(nx,m),a<t>的维度为(na,m)
1 import numpy as np 2 from rnn_utils import * 3 4 #单步前向传播 5 def rnn_cell_forward(xt, a_prev, parameters): 6 """ 7 Implements a single forward step of the RNN-cell as described in Figure (2) 8 9 Arguments: 10 xt -- your input data at timestep "t", numpy array of shape (n_x, m). 11 a_prev -- Hidden state at timestep "t-1", numpy array of shape (n_a, m) 12 parameters -- python dictionary containing: 13 Wax -- Weight matrix multiplying the input, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_x) 14 Waa -- Weight matrix multiplying the hidden state, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a) 15 Wya -- Weight matrix relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, n_a) 16 ba -- Bias, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1) 17 by -- Bias relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, 1) 18 Returns: 19 a_next -- next hidden state, of shape (n_a, m) 20 yt_pred -- prediction at timestep "t", numpy array of shape (n_y, m) 21 cache -- tuple of values needed for the backward pass, contains (a_next, a_prev, xt, parameters) 22 """ 23 # Retrieve parameters from "parameters" 24 Wax = parameters["Wax"] 25 Waa = parameters["Waa"] 26 Wya = parameters["Wya"] 27 ba = parameters["ba"] 28 by = parameters["by"] 29 30 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈2 lines) 31 # compute next activation state using the formula given above 32 a_next = np.tanh(np.dot(Waa, a_prev) + np.dot(Wax, xt) + ba) 33 # compute output of the current cell using the formula given above 34 yt_pred = softmax(np.dot(Wya, a_next) + by) 35 ### END CODE HERE ### 36 37 # store values you need for backward propagation in cache 38 cache = (a_next, a_prev, xt, parameters) 39 return a_next, yt_pred, cache
1.2RNN的前向传播
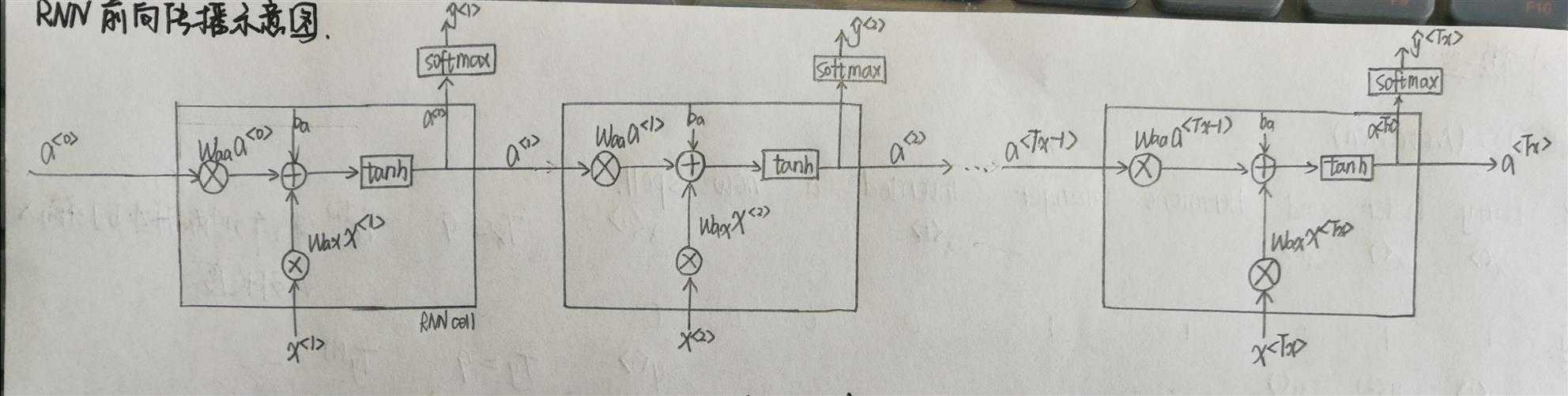
1 def rnn_forward(x, a0, parameters): 2 """ 3 Implement the forward propagation of the recurrent neural network described in Figure (3). 4 5 Arguments: 6 x -- Input data for every time-step, of shape (n_x, m, T_x). 7 a0 -- Initial hidden state, of shape (n_a, m) 8 parameters -- python dictionary containing: 9 Waa -- Weight matrix multiplying the hidden state, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a) 10 Wax -- Weight matrix multiplying the input, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_x) 11 Wya -- Weight matrix relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, n_a) 12 ba -- Bias numpy array of shape (n_a, 1) 13 by -- Bias relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, 1) 14 15 Returns: 16 a -- Hidden states for every time-step, numpy array of shape (n_a, m, T_x) 17 y_pred -- Predictions for every time-step, numpy array of shape (n_y, m, T_x) 18 caches -- tuple of values needed for the backward pass, contains (list of caches, x) 19 """ 20 # Initialize "caches" which will contain the list of all caches 21 caches = [] 22 23 # Retrieve dimensions from shapes of x and Wy 24 n_x, m, T_x = x.shape 25 n_y, n_a = parameters["Wya"].shape 26 27 ### START CODE HERE ### 28 # initialize "a" and "y" with zeros (≈2 lines) 29 a=np.zeros((n_a,m,T_x)) 30 y_pred=np.zeros((n_y,m,T_x)) 31 32 # Initialize a_next (≈1 line) 33 a_next=a0 34 35 # loop over all time-steps 36 for t in range(T_x): 37 # Update next hidden state, compute the prediction, get the cache (≈1 line) 38 a_next, yt_pred, cache=rnn_cell_forward(x[:,:,t], a_next, parameters) 39 # Save the value of the new "next" hidden state in a (≈1 line) 40 a[:,:,t]=a_next 41 # Save the value of the prediction in y (≈1 line) 42 y_pred[:,:,t]=yt_pred 43 # Append "cache" to "caches" (≈1 line) 44 caches.append(cache) 45 ### END CODE HERE ### 46 47 # store values needed for backward propagation in cache 48 caches = (caches, x) 49 return a, y_pred, caches
2.LSTM网络的前向传播
对更新门的理解:

2.1LSTM单元
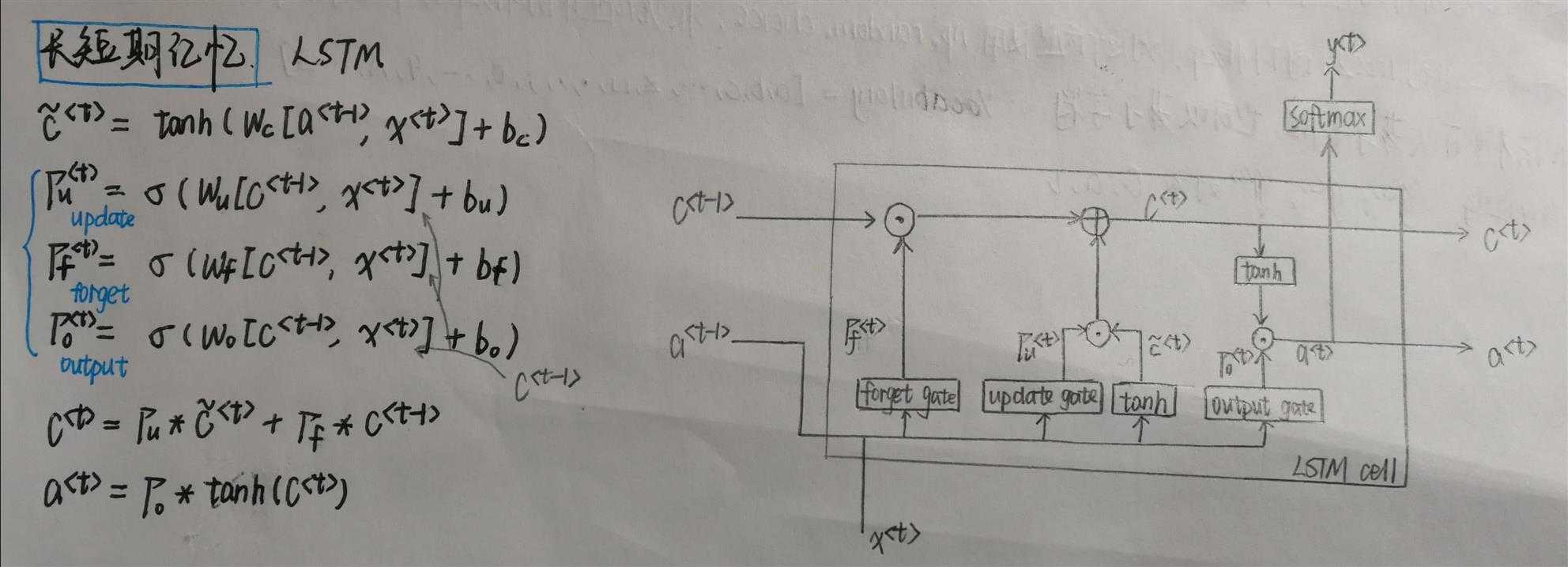
1 def lstm_cell_forward(xt, a_prev, c_prev, parameters): 2 """ 3 Implement a single forward step of the LSTM-cell as described in Figure (4) 4 5 Arguments: 6 xt -- your input data at timestep "t", numpy array of shape (n_x, m). 7 a_prev -- Hidden state at timestep "t-1", numpy array of shape (n_a, m) 8 c_prev -- Memory state at timestep "t-1", numpy array of shape (n_a, m) 9 parameters -- python dictionary containing: 10 Wf -- Weight matrix of the forget gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 11 bf -- Bias of the forget gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1) 12 Wi -- Weight matrix of the update gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 13 bi -- Bias of the update gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1) 14 Wc -- Weight matrix of the first "tanh", numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 15 bc -- Bias of the first "tanh", numpy array of shape (n_a, 1) 16 Wo -- Weight matrix of the output gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 17 bo -- Bias of the output gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1) 18 Wy -- Weight matrix relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, n_a) 19 by -- Bias relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, 1) 20 21 Returns: 22 a_next -- next hidden state, of shape (n_a, m) 23 c_next -- next memory state, of shape (n_a, m) 24 yt_pred -- prediction at timestep "t", numpy array of shape (n_y, m) 25 cache -- tuple of values needed for the backward pass, contains (a_next, c_next, a_prev, c_prev, xt, parameters) 26 27 Note: ft/it/ot stand for the forget/update/output gates, cct stands for the candidate value (c tilde), 28 c stands for the memory value 29 """ 30 # Retrieve parameters from "parameters" 31 Wf = parameters["Wf"] 32 bf = parameters["bf"] 33 Wi = parameters["Wi"] 34 bi = parameters["bi"] 35 Wc = parameters["Wc"] 36 bc = parameters["bc"] 37 Wo = parameters["Wo"] 38 bo = parameters["bo"] 39 Wy = parameters["Wy"] 40 by = parameters["by"] 41 42 # Retrieve dimensions from shapes of xt and Wy 43 n_x, m = xt.shape 44 n_y, n_a = Wy.shape 45 46 ### START CODE HERE ### 47 # Concatenate a_prev and xt (≈3 lines) 48 contact=np.zeros((n_a+n_x,m)) 49 contact[:n_a,:] = a_prev 50 contact[n_a:,:] = xt 51 52 # Compute values for ft, it, cct, c_next, ot, a_next using the formulas given figure (4) (≈6 lines) 53 ft = sigmoid(np.dot(Wf, contact) + bf) 54 it = sigmoid(np.dot(Wi,contact) + bi) 55 cct = np.tanh(np.dot(Wc,contact) + bc) 56 c_next = it * cct + ft * c_prev 57 ot = sigmoid(np.dot(Wo,contact) + bo) 58 a_next = ot * np.tanh(c_next) 59 60 # Compute prediction of the LSTM cell (≈1 line) 61 yt_pred = softmax(np.dot(Wy, a_next) + by) 62 ### END CODE HERE ### 63 64 # store values needed for backward propagation in cache 65 cache = (a_next, c_next, a_prev, c_prev, ft, it, cct, ot, xt, parameters) 66 return a_next, c_next, yt_pred, cache
2.2LSTM的前向传播
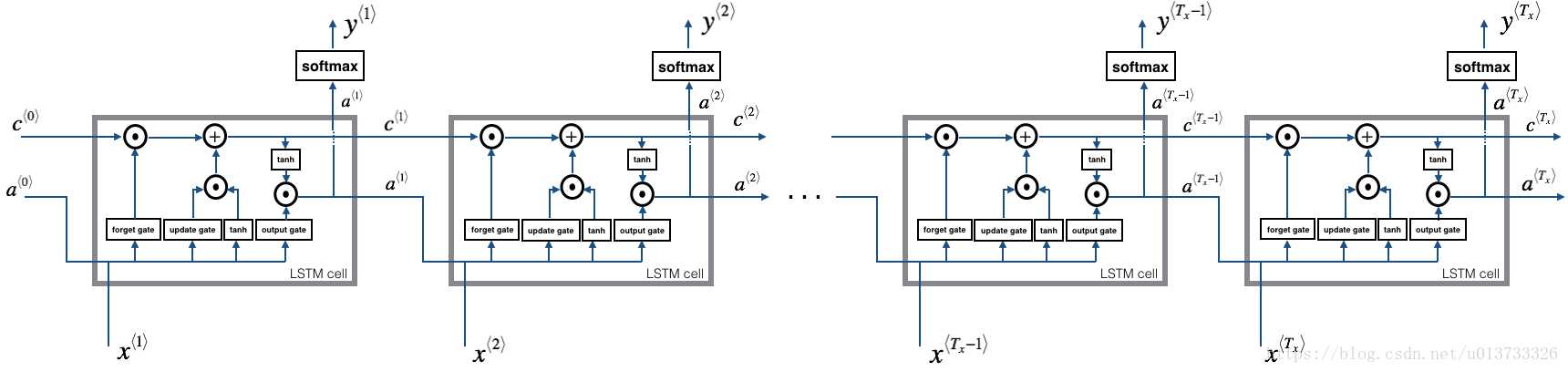
1 def lstm_forward(x, a0, parameters): 2 """ 3 Implement the forward propagation of the recurrent neural network using an LSTM-cell described in Figure (3). 4 5 Arguments: 6 x -- Input data for every time-step, of shape (n_x, m, T_x). 7 a0 -- Initial hidden state, of shape (n_a, m) 8 parameters -- python dictionary containing: 9 Wf -- Weight matrix of the forget gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 10 bf -- Bias of the forget gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1) 11 Wi -- Weight matrix of the update gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 12 bi -- Bias of the update gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1) 13 Wc -- Weight matrix of the first "tanh", numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 14 bc -- Bias of the first "tanh", numpy array of shape (n_a, 1) 15 Wo -- Weight matrix of the output gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 16 bo -- Bias of the output gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1) 17 Wy -- Weight matrix relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, n_a) 18 by -- Bias relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, 1) 19 20 Returns: 21 a -- Hidden states for every time-step, numpy array of shape (n_a, m, T_x) 22 y -- Predictions for every time-step, numpy array of shape (n_y, m, T_x) 23 caches -- tuple of values needed for the backward pass, contains (list of all the caches, x) 24 """ 25 # Initialize "caches", which will track the list of all the caches 26 caches = [] 27 28 ### START CODE HERE ### 29 # Retrieve dimensions from shapes of x and Wy (≈2 lines) 30 n_x,m,T_x = x.shape 31 n_y,n_a = parameters[‘Wy‘].shape 32 33 # initialize "a", "c" and "y" with zeros (≈3 lines) 34 a = np.zeros((n_a, m, T_x)) 35 c = np.zeros((n_a, m, T_x)) 36 y = np.zeros((n_y, m, T_x)) 37 38 # Initialize a_next and c_next (≈2 lines) 39 a_next = a0 40 c_next = np.zeros((n_a, m)) 41 42 # loop over all time-steps 43 for t in range(T_x): 44 # Update next hidden state, next memory state, compute the prediction, get the cache (≈1 line) 45 a_next, c_next, yt_pred, cache = lstm_cell_forward(x[:,:,t], a_next, c_next, parameters) 46 # Save the value of the new "next" hidden state in a (≈1 line) 47 a[:,:,t] = a_next 48 # Save the value of the prediction in y (≈1 line) 49 y[:,:,t] = yt_pred 50 # Save the value of the next cell state (≈1 line) 51 c[:,:,t] = c_next 52 # Append the cache into caches (≈1 line) 53 caches.append(cache) 54 ### END CODE HERE ### 55 56 # store values needed for backward propagation in cache 57 caches = (caches, x) 58 return a, y, c, caches
3.基本的RNN的反向传播
3.1RNN单元的反向传播

1 def rnn_cell_backward(da_next, cache): 2 """ 3 Implements the backward pass for the RNN-cell (single time-step). 4 5 Arguments: 6 da_next -- Gradient of loss with respect to next hidden state 7 cache -- python dictionary containing useful values (output of rnn_cell_forward()) 8 9 Returns: 10 gradients -- python dictionary containing: 11 dx -- Gradients of input data, of shape (n_x, m) 12 da_prev -- Gradients of previous hidden state, of shape (n_a, m) 13 dWax -- Gradients of input-to-hidden weights, of shape (n_a, n_x) 14 dWaa -- Gradients of hidden-to-hidden weights, of shape (n_a, n_a) 15 dba -- Gradients of bias vector, of shape (n_a, 1) 16 """ 17 # Retrieve values from cache 18 (a_next, a_prev, xt, parameters) = cache 19 20 # Retrieve values from parameters 21 Wax = parameters["Wax"] 22 Waa = parameters["Waa"] 23 Wya = parameters["Wya"] 24 ba = parameters["ba"] 25 by = parameters["by"] 26 27 ### START CODE HERE ### 28 # compute the gradient of tanh with respect to a_next (≈1 line) 29 dtanh = (1 - np.square(a_next)) * da_next 30 31 # compute the gradient of the loss with respect to Wax (≈2 lines) 32 dxt = np.dot(Wax.T, dtanh) 33 dWax= np.dot(dtanh, xt.T) 34 35 # compute the gradient with respect to Waa (≈2 lines) 36 da_prev = np.dot(Waa.T, dtanh) 37 dWaa = np.dot(dtanh, a_prev.T) 38 39 # compute the gradient with respect to b (≈1 line) 40 dba = np.sum(dtanh, keepdims=True, axis=-1) 41 ### END CODE HERE ### 42 43 # Store the gradients in a python dictionary 44 gradients = {"dxt": dxt, "da_prev": da_prev, "dWax": dWax, "dWaa": dWaa, "dba": dba} 45 return gradients
3.2整个循环神经网络的反向传播
1 def rnn_backward(da, caches): 2 """ 3 Implement the backward pass for a RNN over an entire sequence of input data. 4 5 Arguments: 6 da -- Upstream gradients of all hidden states, of shape (n_a, m, T_x) 7 caches -- tuple containing information from the forward pass (rnn_forward) 8 9 Returns: 10 gradients -- python dictionary containing: 11 dx -- Gradient w.r.t. the input data, numpy-array of shape (n_x, m, T_x) 12 da0 -- Gradient w.r.t the initial hidden state, numpy-array of shape (n_a, m) 13 dWax -- Gradient w.r.t the input‘s weight matrix, numpy-array of shape (n_a, n_x) 14 dWaa -- Gradient w.r.t the hidden state‘s weight matrix, numpy-arrayof shape (n_a, n_a) 15 dba -- Gradient w.r.t the bias, of shape (n_a, 1) 16 """ 17 ### START CODE HERE ### 18 # Retrieve values from the first cache (t=1) of caches (≈2 lines) 19 caches, x = caches 20 a1, a0, x1, parameters = caches[0] 21 22 # Retrieve dimensions from da‘s and x1‘s shapes (≈2 lines) 23 n_a, m, T_x = da.shape 24 n_x, m = x1.shape 25 26 # initialize the gradients with the right sizes (≈6 lines) 27 dx = np.zeros([n_x, m, T_x]) 28 da0 = np.zeros([n_a, m]) 29 dWax = np.zeros([n_a, n_x]) 30 dWaa = np.zeros([n_a, n_a]) 31 dba = np.zeros([n_a, 1]) 32 da_prevt = np.zeros([n_a, m]) 33 34 # Loop through all the time steps 35 for t in reversed(range(T_x)): 36 # Compute gradients at time step t. Choose wisely the "da_next" and the "cache" to use in the backward propagation step. (≈1 line) 37 gradients = rnn_cell_backward(da[:,:,t] + da_prevt, caches[t]) 38 # Retrieve derivatives from gradients (≈ 1 line) 39 dxt, da_prevt, dWaxt, dWaat, dbat = gradients["dxt"], gradients["da_prev"], gradients["dWax"], gradients["dWaa"], gradients["dba"] 40 # Increment global derivatives w.r.t parameters by adding their derivative at time-step t (≈4 lines) 41 dx[:, :, t] = dxt 42 dWax += dWaxt 43 dWaa += dWaat 44 dba += dbat 45 46 # Set da0 to the gradient of a which has been backpropagated through all time-steps (≈1 line) 47 da0 = da_prevt 48 ### END CODE HERE ### 49 50 # Store the gradients in a python dictionary 51 gradients = {"dx": dx, "da0": da0, "dWax": dWax, "dWaa": dWaa,"dba": dba} 52 return gradients
4.LSTM反向传播
4.1LSTM单元的反向传播

1 def lstm_cell_backward(da_next, dc_next, cache): 2 """ 3 Implement the backward pass for the LSTM-cell (single time-step). 4 5 Arguments: 6 da_next -- Gradients of next hidden state, of shape (n_a, m) 7 dc_next -- Gradients of next cell state, of shape (n_a, m) 8 cache -- cache storing information from the forward pass 9 10 Returns: 11 gradients -- python dictionary containing: 12 dxt -- Gradient of input data at time-step t, of shape (n_x, m) 13 da_prev -- Gradient w.r.t. the previous hidden state, numpy array of shape (n_a, m) 14 dc_prev -- Gradient w.r.t. the previous memory state, of shape (n_a, m, T_x) 15 dWf -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the forget gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 16 dWi -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the update gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 17 dWc -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the memory gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 18 dWo -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the output gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 19 dbf -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the forget gate, of shape (n_a, 1) 20 dbi -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the update gate, of shape (n_a, 1) 21 dbc -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the memory gate, of shape (n_a, 1) 22 dbo -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the output gate, of shape (n_a, 1) 23 """ 24 # Retrieve information from "cache" 25 (a_next, c_next, a_prev, c_prev, ft, it, cct, ot, xt, parameters) = cache 26 27 ### START CODE HERE ### 28 # Retrieve dimensions from xt‘s and a_next‘s shape (≈2 lines) 29 n_x,m = xt.shape 30 n_a, m = a_next.shape 31 32 # Compute gates related derivatives, you can find their values can be found by looking carefully at equations (7) to (10) (≈4 lines) 33 dot = da_next * np.tanh(c_next) * ot * (1-ot) 34 dcct = (dc_next * it + ot * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * it * da_next) * (1 - np.square(cct)) 35 dit = (dc_next * cct + ot * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * cct * da_next) * it * (1 - it) 36 dft = (dc_next * c_prev + ot * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * c_prev * da_next) * ft * (1 - ft) 37 38 # Compute parameters related derivatives. Use equations (11)-(14) (≈8 lines) 39 concat = np.concatenate((a_prev, xt), axis=0).T 40 dWf = np.dot(dft, concat) 41 dWi = np.dot(dit, concat) 42 dWc = np.dot(dcct, concat) 43 dWo = np.dot(dot, concat) 44 dbf = np.sum(dft, axis=1, keepdims=True) 45 dbi = np.sum(dit, axis=1, keepdims=True) 46 dbc = np.sum(dcct, axis=1, keepdims=True) 47 dbo = np.sum(dot, axis=1, keepdims=True) 48 49 # Compute derivatives w.r.t previous hidden state, previous memory state and input. Use equations (15)-(17). (≈3 lines) 50 da_prev = np.dot(parameters[‘Wf‘][:,:n_a].T, dft) + np.dot(parameters["Wi"][:, :n_a].T, dit) + np.dot(parameters[‘Wc‘][:,:n_a].T, dcct) + np.dot(parameters[‘Wo‘][:,:n_a].T, dot) 51 dc_prev = dc_next * ft + ot * (1-np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * ft * da_next 52 dxt = np.dot(parameters[‘Wf‘][:, n_a:].T, dft) + np.dot(parameters["Wi"][:, n_a:].T, dit)+ np.dot(parameters[‘Wc‘][:,n_a:].T,dcct) + np.dot(parameters[‘Wo‘][:,n_a:].T, dot) 53 ### END CODE HERE ### 54 55 # Save gradients in dictionary 56 gradients = {"dxt": dxt, "da_prev": da_prev, "dc_prev": dc_prev, "dWf": dWf,"dbf": dbf, "dWi": dWi,"dbi": dbi, 57 "dWc": dWc,"dbc": dbc, "dWo": dWo,"dbo": dbo} 58 return gradients
4.2整个LSTM网络的反向传播
1 def lstm_backward(da, caches): 2 """ 3 Implement the backward pass for the RNN with LSTM-cell (over a whole sequence). 4 5 Arguments: 6 da -- Gradients w.r.t the hidden states, numpy-array of shape (n_a, m, T_x) 7 dc -- Gradients w.r.t the memory states, numpy-array of shape (n_a, m, T_x) 8 caches -- cache storing information from the forward pass (lstm_forward) 9 10 Returns: 11 gradients -- python dictionary containing: 12 dx -- Gradient of inputs, of shape (n_x, m, T_x) 13 da0 -- Gradient w.r.t. the previous hidden state, numpy array of shape (n_a, m) 14 dWf -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the forget gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 15 dWi -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the update gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 16 dWc -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the memory gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 17 dWo -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the save gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x) 18 dbf -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the forget gate, of shape (n_a, 1) 19 dbi -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the update gate, of shape (n_a, 1) 20 dbc -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the memory gate, of shape (n_a, 1) 21 dbo -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the save gate, of shape (n_a, 1) 22 """ 23 # Retrieve values from the first cache (t=1) of caches. 24 (caches, x) = caches 25 (a1, c1, a0, c0, f1, i1, cc1, o1, x1, parameters) = caches[0] 26 27 ### START CODE HERE ### 28 # Retrieve dimensions from da‘s and x1‘s shapes (≈2 lines) 29 n_a, m, T_x = da.shape 30 n_x, m = x1.shape 31 32 # initialize the gradients with the right sizes (≈12 lines) 33 dx = np.zeros((n_x, m, T_x)) 34 da0 = np.zeros((n_a, m)) 35 da_prevt = np.zeros(da0.shape) 36 dc_prevt = np.zeros(da0.shape) 37 dWf = np.zeros((n_a, n_a + n_x)) 38 dWi = np.zeros(dWf.shape) 39 dWc = np.zeros(dWf.shape) 40 dWo = np.zeros(dWf.shape) 41 dbf = np.zeros((n_a, 1)) 42 dbi = np.zeros(dbf.shape) 43 dbc = np.zeros(dbf.shape) 44 dbo = np.zeros(dbf.shape) 45 46 # loop back over the whole sequence 47 for t in reversed(range(T_x)): 48 # Compute all gradients using lstm_cell_backward 49 gradients = lstm_cell_backward(da[:, :, t], dc_prevt, caches[t]) 50 # Store or add the gradient to the parameters‘ previous step‘s gradient 51 dx[:,:,t] = gradients["dxt"] 52 dWf += gradients["dWf"] 53 dWi += gradients["dWi"] 54 dWc += gradients["dWc"] 55 dWo += gradients["dWo"] 56 dbf += gradients["dbf"] 57 dbi += gradients["dbi"] 58 dbc += gradients["dbc"] 59 dbo += gradients["dbo"] 60 # Set the first activation‘s gradient to the backpropagated gradient da_prev. 61 da0 = gradients["da_prev"] 62 ### END CODE HERE ### 63 64 # Store the gradients in a python dictionary 65 gradients = {"dx": dx, "da0": da0, "dWf": dWf,"dbf": dbf, "dWi": dWi,"dbi": dbi, 66 "dWc": dWc,"dbc": dbc, "dWo": dWo,"dbo": dbo} 67 return gradients
以上是关于循环序列模型-week1编程题1(一步步搭建循环神经网络)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章