Pytorch张量操作
Posted cxq1126
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Pytorch张量操作相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
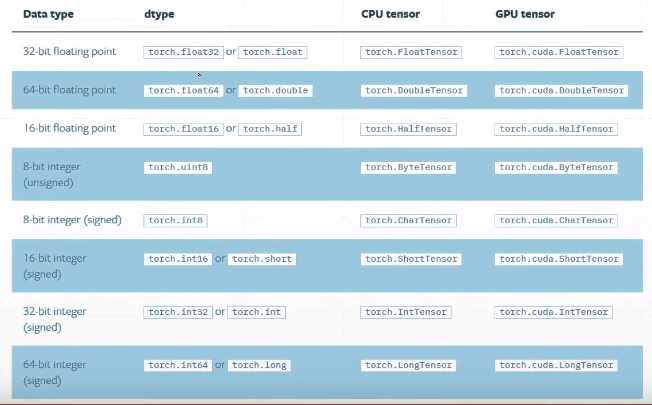
1.数据类型
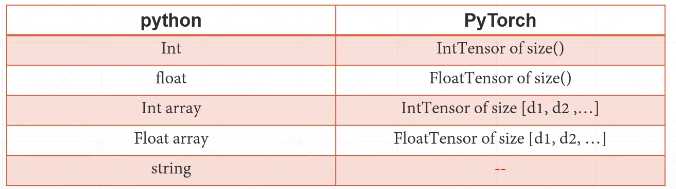
如何表示string?
- One-hot [0,1,0,0,...]
- Embedding Word2vec,glove
类型推断
1 #type check 2 a=torch.randn(2,3) 3 print(a.type()) #torch.FloatTensor 4 print(type(a)) #<class ‘torch.Tensor‘> 这种情况比较少 5 print(isinstance(a, torch.FloatTensor)) #True
标量
1 #标量 dimension 0/rank 0(常用于loss) 2 b=torch.tensor(1.3) 3 print(b) #tensor(1.3000) 4 print(b.shape) #torch.Size([]) 成员 5 print(len(b.shape)) #0 6 print(b.size()) #torch.Size([]) 成员函数
张量
1 #张量 dimension 1(常用于bias) 2 print(torch.tensor([1.1])) #tensor([1.1000]) 指定具体数据,可以是N维 3 print(torch.FloatTensor(1)) #tensor([9.6429e-39]) 指定具体维度,随机初始化 4 data=np.ones(2) 5 print(torch.from_numpy(data)) #tensor([1., 1.], dtype=torch.float64) 从numpy引入 6 7 c=torch.ones(2) 8 print(c.shape) #torch.Size([2]) 9 10 #张量 dimension 2 11 d=torch.randn(2,3) 12 print(d) 13 #tensor([[-1.8543, -0.7280, 0.6671], 14 # [ 1.1492, -0.6379, -0.4835]]) 15 print(d.shape) #torch.Size([2, 3]) 16 print(d.shape[0]) #2 17 print(d.size(1)) #3 18 19 #张量 dimension 3 20 f=torch.rand(1,2,3) 21 print(f) 22 #tensor([[[0.3690, 0.5702, 0.2382], 23 # [0.3130, 0.5591, 0.3829]]]) 24 print(f.shape) #torch.Size([1, 2, 3]) 25 print(f[0]) #取第一个维度 26 #tensor([[0.4535, 0.4307, 0.6469], 27 # [0.1591, 0.0778, 0.4489]]) 28 print(f[0][1]) #tensor([0.1591, 0.0778, 0.4489])
四维适合表示图片类型
eg:a=torch.rand(b,c,h,w)表示b张c通道、h*w的图片
1 a=torch.rand(2,3,28,28) 2 print(a.numel()) #4704 全部元素个数 3 print(a.dim()) #4 维度数量
2.创建Tensor
1 #方法一:import from numpy 2 a=np.ones([2,3]) 3 print(torch.from_numpy(a)) 4 #tensor([[1., 1., 1.], 5 # [1., 1., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64) 6 7 #方法二:import from List 8 print(torch.tensor([[2.,3.2],[1.,22.3]])) 9 #tensor([[ 2.0000, 3.2000], 10 # [ 1.0000, 22.3000]])
Tip:torch.tensor接受现成的数据
torch.Tensor/torch.FloatTensor接受shape或者现成的数据
未初始化的方法(作为容器,要用其他类型把数据覆盖掉):
- torch.empty()
- torch.FlostTensor(d1,d2,d3)
- torch.IntTensor(d1,d2,d3)
1 #设置默认类型 2 print(torch.tensor([1.2,3]).type()) #torch.FloatTensor(不设定的话,默认值) 3 torch.set_default_tensor_type(torch.DoubleTensor) 4 print(torch.tensor([1.2,3]).type()) #torch.DoubleTensor
随机初始化
1 #rand [0,1] 2 a=torch.rand(2,2) 3 print(a) 4 print(torch.rand_like(a)) #根据a的形状生成,也可用dtype指定新类型 5 6 #randint [min,max)不包含max 7 print(torch.randint(1,10,[3,3])) #第1个参数是min,第二个参数是max,第三个参数是shape
正态分布
1 #正态分布 2 print(torch.randn(3,3)) #N(0,1) 3 print(torch.normal(mean=torch.full([10],0),std=torch.arange(1,0,-0.1))) #normal得到的维度为1 4 #tensor([ 0.1445, -0.5133, -0.5565, 0.0831, 0.1350, 0.1023, -0.6264, -0.1651, 0.2856, 0.0187])
其他
1 #ones全1,zeros全0,eye对角,ones_like 2 print(torch.full([2,3],7)) #第一个参数是shape,第二个参数是value 3 #tensor([[7., 7., 7.], 4 # [7., 7., 7.]]) 5 print(torch.full([], 7)) #tensor(7.) 生成标量 6 7 #生成 [0,n-1]的等差数列 8 print(torch.arange(0,10,2)) #tensor([0, 2, 4, 6, 8]) 9 10 #[0,10]等间距切割成steps份 11 print(torch.linspace(0, 10, steps=6)) #tensor([ 0., 2., 4., 6., 8., 10.]) 12 print(torch.logspace(0, 1, steps=5)) #tensor([ 1.0000, 1.7783, 3.1623, 5.6234, 10.0000]) 13 14 15 #randperm 16 print(torch.randperm(10)) #tensor([8, 5, 2, 4, 7, 1, 3, 9, 6, 0]) 17 18 a=torch.rand(2, 3) 19 idx=torch.randperm(2) 20 print(idx) #tensor([1, 0]) 21 print(a[idx]) 22 #tensor([[0.6159, 0.9362, 0.5502], 23 # [0.9774, 0.6772, 0.2909]])
3.索引与切片
1 #切片与索引 2 a=torch.rand(4,3,28,28) 3 print(a[0].shape) #torch.Size([3, 28, 28]) 4 print(a[0,0].shape) #torch.Size([28, 28]) 5 print(a[0,0,2,4]) #tensor(0.7309) 6 7 print(a[:2,:1].shape) #torch.Size([2, 1, 28, 28]) 等价于a[:2,:1,:,:].shape 8 print(a[:,:,::2,::2].shape) #torch.Size([4, 3, 14, 14])
使用特定索引index_select
1 #select by specific index 2 print(a.index_select(2, torch.arange(8)).shape) #torch.Size([4, 3, 8, 28]) 第1个参数表示维度,第2个参数表示索引号(Tensor类型) 3 #...表示任意多的维度 4 print(a[0,...].shape) #torch.Size([3, 28, 28]) 5 print(a[:,1,...].shape) #torch.Size([4, 28, 28])
使用掩码索引masked_select
1 #select by mask 2 x=torch.randn(3,4) 3 mask=x.ge(0.5) #greater equal大于等于 4 print(mask) 5 #tensor([[False, True, False, False], 6 # [ True, False, False, True], 7 # [ True, False, True, False]]) 8 torch.masked_select(x, mask) #tensor([1.1361, 0.5963, 0.6286, 0.5664, 0.5152]) 维度为1
take索引(在原来Tensor的shape基础上打平,然后在打平后的Tensor上进行索引)
1 #select by flatten index 2 src=torch.tensor([[4, 3, 5],[6, 7, 8]]) 3 print(torch.take(src,torch.tensor([0, 2, 5]))) #tensor([4, 5, 8])
4.维度变换
reshape/view可以调整Tensor的shape,返回一个新shape的Tensor
1 a=torch.rand(4,1,28,28) 2 print(a.view(4,28*28).shape) #torch.Size([4, 784]) 3 print(a.reshape(4*28,28).shape) #torch.Size([112, 28])
unsqueeze(index)增加维度
index的范围[-a.dim()-1,a.dim()+1) eg.a的维度=4,范围是[-5,5)
新增加的这一个维度不会改变数据本身,只是为数据新增加了一个组别,这个组别是什么由我们自己定义。
1 a=torch.rand(4,1,28,28) 2 print(a.unsqueeze(0).shape) #torch.Size([1, 4, 1, 28, 28] 3 4 b=torch.tensor([1.2, 2.3]) #torch.Size([2]) 5 print(b.unsqueeze(0)) #tensor([[1.2000, 2.3000]]) torch.Size([2, 1]) 6 print(b.unsqueeze(-1)) 7 #tensor([[1.2000], 8 # [2.3000]]) 9 10 x=torch.rand(32) 11 y=torch.rand(4,32,14,14) 12 x=x.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(0) #[32]->[32,1]->[32,1,1]->[1,32,1,1] 13 print(x.shape) #torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1])) 再进行扩展即可计算x+y
squeeze(index)删减维度,删除size=1的维度
1 a=torch.rand(1,32,1,1) 2 print(a.squeeze().shape) #torch.Size([32]) 不指定维度就挤压全部 3 print(a.squeeze(0).shape) #torch.Size([32, 1, 1]) 4 print(a.squeeze(-1).shape) #torch.Size([1, 32, 1]) 5 print(a.squeeze(1).shape) #torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1]) size不等于1,删减不了
expand维度扩展:broadcasting(只是改变了理解方式,并没有增加数据)
某个size=1的维度上扩展size
1 x=torch.rand(32) 2 y=torch.rand(4,32,14,14) 3 x=x.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(0) #[32]->[32,1]->[32,1,1]->[1,32,1,1] 4 print(x.shape) # torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1]) 5 6 print(x.expand(4,32,14,14).shape) #torch.Size([4, 32, 14, 14]) 7 print(x.expand(-1,32,3,-1).shape) #torch.Size([1, 32, 3, 1]) -1指该维度不变 8 9 print((x.expand(4,32,14,14)+y).shape) #torch.Size([4, 32, 14, 14])
repeat维度重复:memory copied(增加了数据)
repeat会重新申请内存空间,repeat()参数表示各个维度指定的重复次数。
1 a=torch.rand(1,32,1,1) 2 print(a.repeat(4,32,1,1).shape) #torch.Size([4, 1024, 1, 1]) 3 print(a.repeat(4,1,1,1).shape) #torch.Size([4, 32, 1, 1])
转置操作
.t操作指适用于矩阵
1 a=torch.rand(3, 4) 2 print(a.t().shape) #torch.Size([4, 3])
transpose维度交换
1 a=torch.rand(4,3,32,32) 2 b=a.transpose(1, 3).contiguous().view(4,3*32*32).view(4,32,32,3).transpose(1, 3) 3 #[b,c,h,w]->[b,w,h,c]->[b,whc]->[b,w,h,c]->[b,c,h,w] 展开时按原来的顺序展开whc对应32,32,3 4 print(torch.all(torch.eq(a,b))) #tensor(True)
permute
四个维度表示的[batch,channel,h,w] ,如果想把channel放到最后去,形成[batch,h,w,channel],那么如果使用前面的维度交换,至少要交换两次(先13交换再12交换)。而使用permute可以直接指定维度新的所处位置,更加方便。
1 b=torch.rand(4,3,28,32) 2 print(b.transpose(1, 3).shape) #torch.Size([4, 32, 28, 3]) 3 print(b.transpose(1, 3).transpose(1, 2).shape) #torch.Size([4, 28, 32, 3]) 4 5 print(b.permute(0,2,3,1).shape) #torch.Size([4, 28, 32, 3]
以上是关于Pytorch张量操作的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章