整理树形结构数据
Posted xiaozhengyu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了整理树形结构数据相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
整理树形结构数据
树形结构是一种常见的数据组织结构:

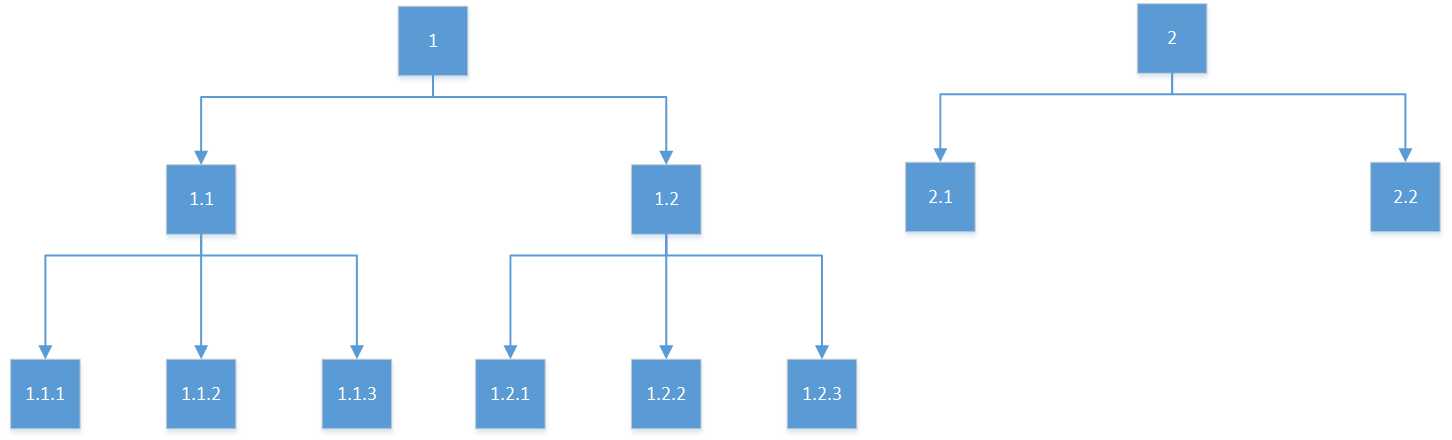
今天恰好需要完成一个接口,将数据组织长树形结构,下面是简化的代码:
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.List;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Node {
/**
* 当前节点ID
*/
private String id;
/**
* 当前节点名称
*/
private String name;
/**
* 父节点ID
*/
private String parentId;
/**
* 子节点列表
*/
private List<Node> childNodeList;
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author xzy
* @date 2020-06-30 10:39
* 说明:
*/
public class TreeBuilder {
/**
* 构造森林
*
* @param nodeList - 森林中的所有节点
* @return - 使用给定节点构造出来的森林
*/
public List<Node> buildForest(List<Node> nodeList) {
//所有树的根节点
List<Node> rootNodeList = new LinkedList<>();
// 遍历所有节点,找出所有树根节点,然后构建每棵树。
nodeList.forEach(node -> {
if (isRootNode(node)) {
node.setChildNodeList(buildTree(node.getId(), nodeList));
rootNodeList.add(node);
}
});
return rootNodeList;
}
/**
* 判断给定节点是否为树根节点
*
* @param node - 待判断的节点
* @return true:是 false:否
*/
private boolean isRootNode(Node node) {
//若父节点ID的值为null或者“”,则认为节点没有父节点,即节点是树根节点
return "".equals(node.getParentId()) || node.getParentId() == null;
}
/**
* 构建树
*
* @param rootNodeId - 根节点ID
* @param nodeList - 森林中的所有节点
* @return - 以给定节点为根的一棵树
*/
List<Node> buildTree(String rootNodeId, List<Node> nodeList) {
List<Node> subTree = new LinkedList<>();
nodeList.forEach(node -> {
if (rootNodeId.equals(node.getParentId())) {
node.setChildNodeList(buildTree(node.getId(), nodeList));
subTree.add(node);
}
});
return subTree;
}
/**
* 构造森林
*
* @param rootNodeId - 树节点ID
* @param nodeList - 树节点列表
*/
public List<Node> buildForest(String rootNodeId, List<Node> nodeList) {
//所有树的根节点
List<Node> rootNodeList = new LinkedList<>();
// 遍历所有节点,找出所有树根节点,然后构建每棵树。
if ("".equals(rootNodeId) || rootNodeId == null) {
nodeList.forEach(node -> {
if (isRootNode(node)) {
node.setChildNodeList(buildForest(node.getId(), nodeList));
rootNodeList.add(node);
}
});
} else {
nodeList.forEach(node -> {
if (rootNodeId.equals(node.getParentId())) {
node.setChildNodeList(buildForest(node.getId(), nodeList));
rootNodeList.add(node);
}
});
}
return rootNodeList;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node node1 = new Node("1", "node1", "", null);
Node node11 = new Node("11", "node11", "1", null);
Node node111 = new Node("111", "node111", "11", null);
Node node112 = new Node("112", "node112", "11", null);
Node node113 = new Node("113", "node113", "11", null);
Node node12 = new Node("12", "node12", "1", null);
Node node121 = new Node("121", "node121", "12", null);
Node node122 = new Node("122", "node122", "12", null);
Node node123 = new Node("123", "node123", "12", null);
Node node2 = new Node("2", "node2", "", null);
Node node21 = new Node("21", "node21", "2", null);
Node node22 = new Node("22", "node22", "2", null);
List<Node> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
nodeList.add(node1);
nodeList.add(node11);
nodeList.add(node111);
nodeList.add(node112);
nodeList.add(node113);
nodeList.add(node12);
nodeList.add(node121);
nodeList.add(node122);
nodeList.add(node123);
nodeList.add(node2);
nodeList.add(node21);
nodeList.add(node22);
TreeBuilder treeBuilder = new TreeBuilder();
nodeList = treeBuilder.buildForest(nodeList);
nodeList = treeBuilder.buildForest("", nodeList);
}
}
以上是关于整理树形结构数据的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章