vue-toy: 200行代码模拟Vue实现
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了vue-toy: 200行代码模拟Vue实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
vue-toy
200行左右代码模拟vue实现,视图渲染部分使用React来代替Snabbdom,欢迎Star。
项目地址:https://github.com/bplok20010/vue-toy
已实现的参数:
interface Options {
el: htmlElement | string;
propsData?: Record<string, any>;
props?: string[];
name?: string;
data?: () => Record<string, any>;
methods?: Record<string, (e: Event) => void>;
computed?: Record<string, () => any>;
watch?: Record<string, (newValue: any, oldValue: any) => any>;
render: (h: typeof React.createElement) => React.ReactNode;
renderError?: (h: typeof React.createElement, error: Error) => React.ReactNode;
mounted?: () => void;
updated?: () => void;
destroyed?: () => void;
errorCaptured?: (e: Error, vm: React.ReactInstance) => void;
}示例:
import Vue from "vue-toy";
const Hello = Vue.component({
render(h){
return h(‘span‘, null, ‘vue-toy‘) ;
}
})
new Vue({
el: document.getElementById("root"),
data() {
return {
msg: "hello vue toy"
};
},
render(h) {
return h("h1", null, this.msg, h(Hello));
}
});基本原理
官方原理图: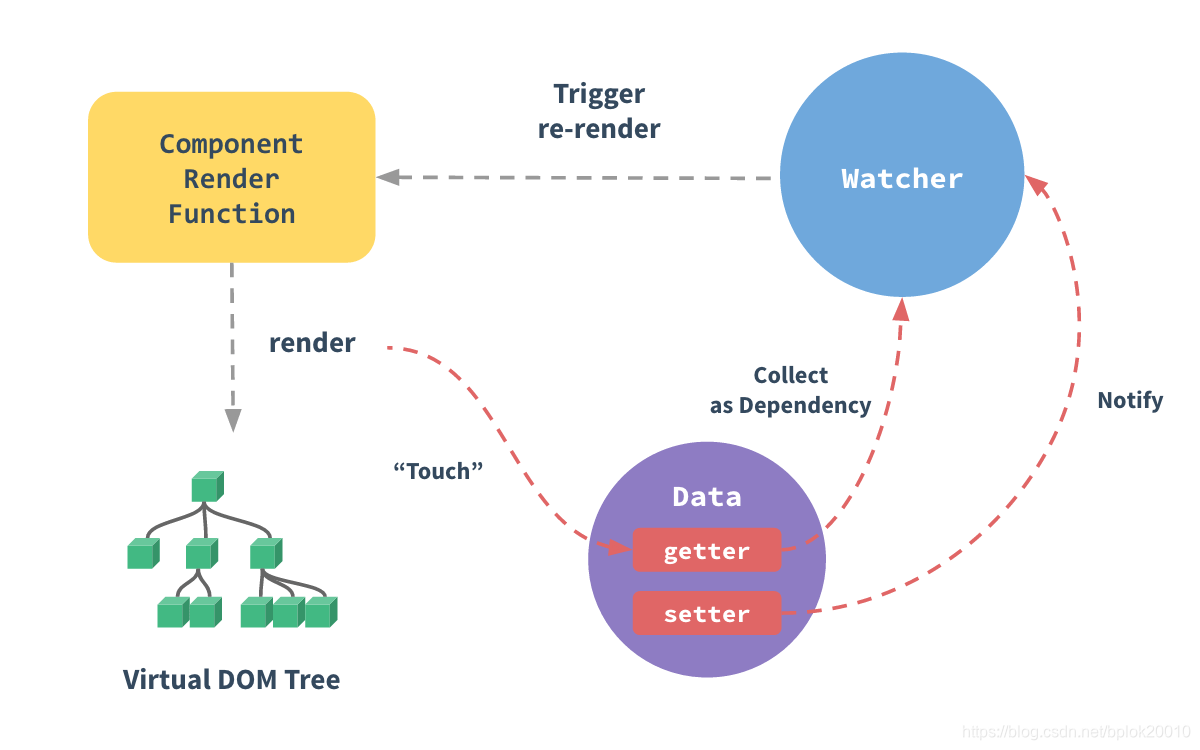
实现基本步骤:
- 使用Observable创建观察对象
- 定义好视图既render函数
- 收集视图依赖,并监听依赖属性
- 渲染视图
- 重复3-4
// 创建观察对象
// 观察对象主要使用的是Object.defineProperty或Proxy来实现,
const data = observable({
name: ‘vue-toy‘,
});
// 渲染模版
const render = function(){
return <h1>{data.name}</h1>
}
// 计算render的依赖属性,
// 依赖属性改变时,会重新计算computedFn,并执行监控函数watchFn,
// 属性依赖计算使用栈及可以了。
// watch(computedFn, watchFn);
watch(render, function(newVNode, oldVNode){
update(newVNode, mountNode);
});
//初始渲染
mount(render(), mountNode);
// 改变观察对象属性,如果render依赖了该属性,则会重新渲染
data.name = ‘hello vue toy‘;视图渲染部分(既render)使用的是vdom技术,vue使用
Snabbdom库,vue-toy使用的是react来进行渲染,所以在render函数里你可以直接使用React的JSX语法,不过别忘记import React from ‘react‘,当然也可以使用preactinferno等 vdom库。由于vue的template的最终也是解析并生成render函数,模版的解析可用
htmleParser库来生成AST,剩下就是解析指令并生产代码,由于工作量大,这里就不具体实现,直接使用jsx。
响应式实现
一个响应式示例代码:
const data = Observable({
name: "none",
});
const watcher =new Watch(
data,
function computed() {
return "hello " + this.name;
},
function listener(newValue, oldValue) {
console.log("changed:", newValue, oldValue);
}
);
// changed vue-toy none
data.name = "vue-toy";Observable实现
源码
观察对象创建这里使用Proxy实现,示例:
function Observable(data) {
return new Proxy(data, {
get(target, key) {
return target[key];
},
set(target, key, value) {
target[key] = value;
return true;
},
});
}这就完成了一个对象的观察,但以上示例代码虽然能观察对象,但无法实现对象属性改动后通知观察者,这时还缺少Watch对象来计算观察函数的属性依赖及Notify来实现属性变更时的通知。
Watch实现
定义如下:
Watch(data, computedFn, watchFn);- data 为 computedFn 的 上下文 既
this非必须 - computedFn 为观察函数并返回观察的数据,Watch会计算出里面的依赖属性。
- watchFn 当computedFn 返回内容发生改变时,watchFn会被调用,同时接收到新、旧值
大概实现如下:
// Watch.js
// 当前正在收集依赖的Watch
const CurrentWatchDep = {
current: null,
};
class Watch {
constructor(data, exp, fn) {
this.deps = [];
this.watchFn = fn;
this.exp = () => {
return exp.call(data);
};
// 保存上一个依赖收集对象
const lastWatchDep = CurrentWatchDep.current;
// 设置当前依赖收集对象
CurrentWatchDep.current = this;
// 开始收集依赖,并获取观察函数返回的值
this.last = this.exp();
// 还原
CurrentWatchDep.current = lastWatchDep;
}
clearDeps() {
this.deps.forEach((cb) => cb());
this.deps = [];
}
// 监听依赖属性的改动,并保存取消回调
addDep(notify) {
// 当依赖属性改变时,重新触发依赖计算
this.deps.push(notify.sub(() => {
this.check();
}));
}
// 重新执行依赖计算
check() {
// 清空所有依赖,重新计算
this.clearDeps();
// 作用同构造函数
const lastWatchDep = CurrentWatchDep.current;
CurrentWatchDep.current = this;
const newValue = this.exp();
CurrentWatchDep.current = lastWatchDep;
const oldValue = this.last;
// 对比新旧值是否改变
if (!shallowequal(oldValue, newValue)) {
this.last = newValue;
// 调用监听函数
this.watchFn(newValue, oldValue);
}
}
}
Notify实现
观察对象发生改变后需要通知监听者,所以还需要实现通知者Notify:
class Notify {
constructor() {
this.listeners = [];
}
sub(fn) {
this.listeners.push(fn);
return () => {
const idx = this.listeners.indexOf(fn);
if (idx === -1)
return;
this.listeners.splice(idx, 1);
};
}
pub() {
this.listeners.forEach((fn) => fn());
}
}调整Observable
前面的Observable太简单了,无法完成属性计算的需求,结合上面Watch Notify的来调整下Observable。
function Observable(data) {
const protoListeners = Object.create(null);
// 给观察数据的所有属性创建一个Notify
each(data, (_, key) => {
protoListeners[key] = new Notify();
});
return new Proxy(data, {
get(target, key) {
// 属性依赖计算
if (CurrentWatchDep.current) {
const watcher = CurrentWatchDep.current;
watcher.addDep(protoListener[key]);
}
return target[key];
},
set(target, key, value) {
target[key] = value;
if (protoListeners[key]) {
// 通知所有监听者
protoListeners[key].pub();
}
return true;
},
});
}好了,观察者的创建和订阅都完成了,开始模拟Vue。
模拟Vue
vue-toy 使用React来实现视图的渲染,所以render函数里如果使用JSX则需要引入React
准备
既然已经实现了Observable和Watch,那我们就来实现基本原理的示例:
import Observable from "vue-toy/cjs/Observable";
import Watch from "vue-toy/cjs/Watch";
function mount(vnode) {
console.log(vnode);
}
function update(vnode) {
console.log(vnode);
}
const data = Observable({
msg: "hello vue toy!",
counter: 1
});
function render() {
return `render: ${this.counter} | ${this.msg}`;
}
new Watch(data, render, update);
mount(render.call(data));
setInterval(() => data.counter++, 1000);
// 在控制台可看到每秒的输出信息这时将mount update的实现换成vdom就可以完成一个基本的渲染。
但这还不够,我们需要抽象并封装成组件来用。
Component
这里的Component像是React的高阶函数HOC,使用示例:
const Hello = Component({
props: ["msg"],
data() {
return {
counter: 1,
};
},
render(h) {
return h("h1", null, this.msg, this.counter);
},
});大概实现如下,options 参考文章开头
function Component(options) {
return class extends React.Component {
// 省略若干...
constructor(props) {
super(props);
// 省略若干...
// 创建观察对象
this.$data = Observable({ ...propsData, ...methods, ...data }, computed);
// 省略若干...
// 计算render依赖并监听
this.$watcher = new Watch(
this.$data,
() => {
return options.render.call(this, React.createElement);
},
debounce((children) => {
this.$children = children;
this.forceUpdate();
})
);
this.$children = options.render.call(this, React.createElement);
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps) {
if (
!shallowequal(
pick(this.props, options.props || []),
pick(nextProps, options.props || [])
)
) {
this.updateProps(nextProps);
this.$children = options.render.call(this, React.createElement);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 生命周期关联
componentDidMount() {
options.mounted?.call(this);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.$watcher.clearDeps();
options.destroyed?.call(this);
}
componentDidUpdate() {
options.updated?.call(this);
}
render() {
return this.$children;
}
};
}创建主函数 Vue
最后创建入口函数Vue,实现代码如下:
export default function Vue(options) {
const RootComponent = Component(options);
let el;
if (typeof el === "string") {
el = document.querySelector(el);
}
const props = {
...options.propsData,
$el: el,
};
return ReactDOM.render(React.createElement(RootComponent, props), el);
}
Vue.component = Component;好了,Vue的基本实现完成了。
感谢阅读。
最后,欢迎Star:https://github.com/bplok20010/vue-toy
以上是关于vue-toy: 200行代码模拟Vue实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章