JUnitJUnit 参数化测试
Posted jiangbo44
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JUnitJUnit 参数化测试相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
环境
- JDK 6
- JUnit 4.13
- Spring Tool Suite 4.6.2
- Maven 3.6.3
参数化测试
参数化测试首先需要指定 Runner:org.junit.runners.Parameterized,然后准备测试数据。
有两种注入测试数据的方法,一种是构造函数注入,另一种是字段注入,字段注入必须是 public。
参数化测试
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>jiangbo.java.junit</groupId>
<artifactId>15-java-junit-parameterized</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<description>JUnit 参数化测试示例</description>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.6</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.6</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
CaculatorTest1
package jiangbo.java.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class CaculatorTest1 {
private int number1;
private int number2;
private int addExpected;
public CaculatorTest1(int number1, int number2, int addExpected) {
this.number1 = number1;
this.number2 = number2;
this.addExpected = addExpected;
}
@Test
public void testAdd() {
int actual = Caculator.add(number1, number2);
assertEquals(addExpected, actual);
}
// 指定了测试的名称
@Parameters(name = "第 {index} 个: {0} + {1} = {2}")
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{ 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 2 },
{ 2, 1, 3 },
{ -1, 0, -1 },
{ 0, -1, -1 },
{ 1, -1, 0 },
{ -1, 1, 0 }
});
}
}
CaculatorTest2
package jiangbo.java.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameter;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class CaculatorTest2 {
// 默认 0
@Parameter
public int number1;
@Parameter(1)
public int number2;
@Parameter(2)
public int addExpected;
@Parameter(3)
public int subtractExpected;
@Test
public void testAdd() {
int actual = Caculator.add(number1, number2);
assertEquals(addExpected, actual);
}
@Test
public void testSubtract() throws Exception {
int actual = Caculator.subtract(number1, number2);
assertEquals(subtractExpected, actual);
}
@Parameters
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 2, 0 },
{ 2, 1, 3, 1 },
{ -1, 0, -1, -1 },
{ 0, -1, -1, 1 },
{ 1, -1, 0, 2 },
{ -1, 1, 0, -2 }
});
}
}
CaculatorTest1 输出
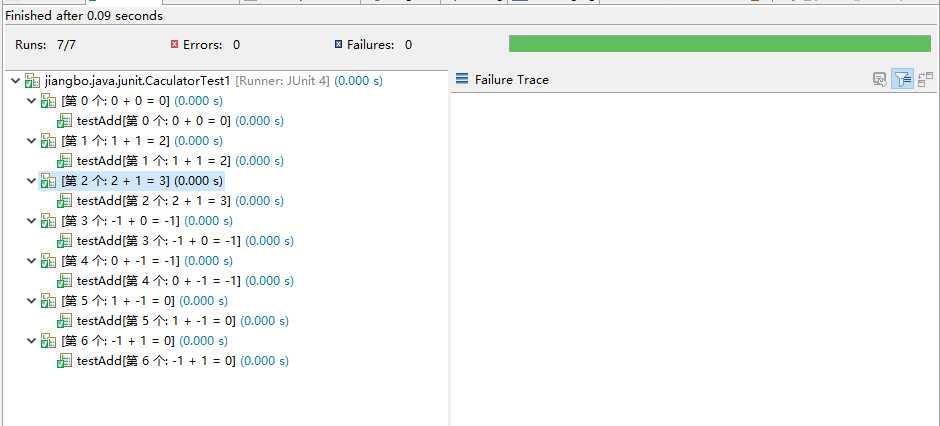
以上是关于JUnitJUnit 参数化测试的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章