30 双向链表的实现
Posted lh03061238
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了30 双向链表的实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/wanmeishenghuo/p/9655599.html 参考狄泰软件相关教程



由上图可以看出来,插入和遍历的时间复杂度是不一样的。
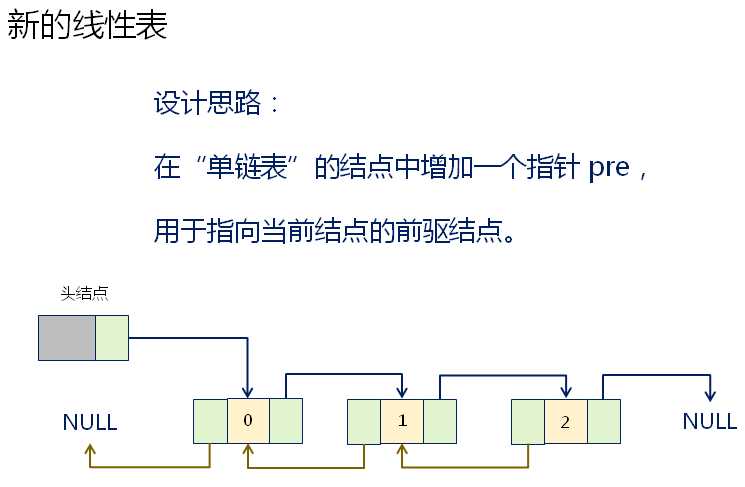
这样不管游标在哪一个位置上,都可以通过后继或者前驱指针任意访问。
双向链表的继承层次:
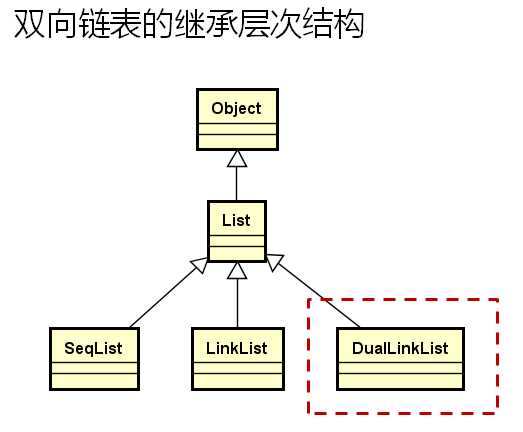
单链表和双向链表应该是兄弟关系,而不应该是继承关系,因为它们的内部机制是完全不同的了。

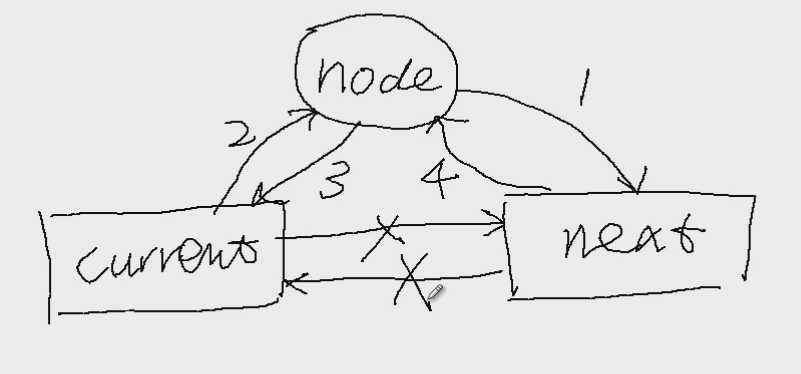
插入新节点图解:
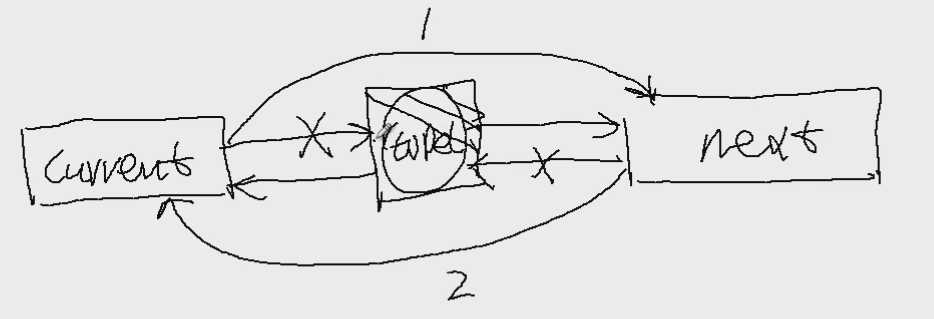
删除节点的步骤:
添加DualLinkList.h文件:
#ifndef DUALLINKLIST_H
#define DUALLINKLIST_H
#include "List.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace DTLib
{
template < typename T >
class DualLinkList : public List<T>
{
protected:
struct Node : public Object
{
T value;
Node* next;
Node* pre;
};
mutable struct : public Object
{
char reserved[sizeof(T)];
Node* next;
Node* pre;
}m_header;
int m_length;
int m_step;
Node* m_current;
Node* position(int i) const // O(n)
{
Node* ret = reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header);
for(int p = 0; p < i; p++)
{
ret = ret->next;
}
return ret;
}
virtual Node* create()
{
return new Node();
}
virtual void destroy(Node* pn)
{
delete pn;
}
public:
DualLinkList()
{
m_header.next = NULL;
m_header.pre = NULL;
m_length = 0;
m_step = 1;
m_current = NULL;
}
bool insert(const T& e)
{
return insert(m_length, e);
}
bool insert(int i, const T& e) // O(n)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i <= m_length));
if( ret )
{
Node* node = create();
if( node != NULL )
{
Node* current = position(i);
Node* next = current->next; //即将插入的节点的后继节点
node->value = e;
node->next = next; //第1步
current->next = node; //第2步
if( current != reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header)) //判断是否是头结点
{
node->pre = current; // 第3步
}
else
{
node->pre = NULL;
}
if( next != NULL )
{
next->pre = node; //第4步
}
m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memery to insert new element...");
}
}
return ret;
}
bool remove(int i) // O(n)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
Node* current = position(i);
Node* toDel = current->next;
Node* next = toDel->next;
if( m_current == toDel )
{
m_current = next;
}
current->next = next; //第1步
if( next != NULL )
{
next->pre = toDel->pre; //第2步
}
m_length--;
destroy(toDel);
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int i, const T& e) // O(n)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
position(i)->next->value = e;
}
return ret;
}
virtual T get(int i) const // O(n)
{
T ret;
if( get(i, ret) )
{
return ret;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Invalid parameter i to get element ...");
}
return ret;
}
bool get(int i, T& e) const // O(n)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
e = position(i)->next->value;
}
return ret;
}
int find(const T& e) const // O(n)
{
int ret = -1;
int i = 0;
Node* node = m_header.next;
while( node )
{
if( node->value == e )
{
ret = i;
break;
}
else
{
node = node->next;
i++;
}
}
return ret;
}
int length() const // O(1)
{
return m_length;
}
void clear() // O(n)
{
while( m_length > 0 )
{
remove(0);
}
}
virtual bool move(int i, int step = 1)
{
bool ret = (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) && (step > 0);
if( ret )
{
m_current = position(i)->next;
m_step = step;
}
return ret;
}
virtual bool end()
{
return (m_current == NULL);
}
virtual T current()
{
if( !end() )
{
return m_current->value;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No value at current position ...");
}
}
virtual bool next() //每次移动step步
{
int i = 0;
while((i < m_step) && !end())
{
m_current = m_current->next;
i++;
}
return (i == m_step);
}
virtual bool pre()
{
int i = 0;
while((i < m_step) && !end())
{
m_current = m_current->pre;
i++;
}
return (i == m_step);
}
~DualLinkList() // O(n)
{
clear();
}
};
}
#endif // DUALLINKLIST_H
和LinkList的不同只在于Node的元素,我们新添加了pre成员。
insert函数和remove函数是改动最大的。
新增加了pre函数。
测试程序如下:
#include <iostream> #include "DualLinkList.h" using namespace std; using namespace DTLib; int main() { DualLinkList<int> dl; for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { dl.insert(0, i); } for(int i = 0; i < dl.length(); i++) { cout << dl.get(i) << endl; } cout << "begin" << endl; for(dl.move(dl.length() - 1); !dl.end(); dl.pre()) { cout << dl.current() << endl; } cout << "end" << endl; return 0; }
第一个for循环时间复杂度是O(n*n),第二个for循环的时间复杂度是O(n)。
结果如下:
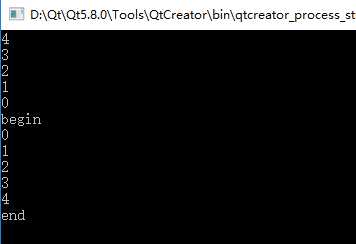
测试程序2:
#include <iostream>
#include "DualLinkList.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
int main()
{
DualLinkList<int> dl;
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
dl.insert(0, i);
dl.insert(0, 5);
}
for(dl.move(0); !dl.end(); dl.next())
{
cout << dl.current() << endl;
}
cout << "begin" << endl;
dl.move(dl.length() - 1);
while(!dl.end())
{
if( dl.current() == 5 )
{
cout << dl.current() << endl;
dl.remove(dl.find(dl.current()));
}
else
{
dl.pre();
}
}
cout << "end" << endl;
for(dl.move(0); !dl.end(); dl.next())
{
cout << dl.current() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
结果如下:
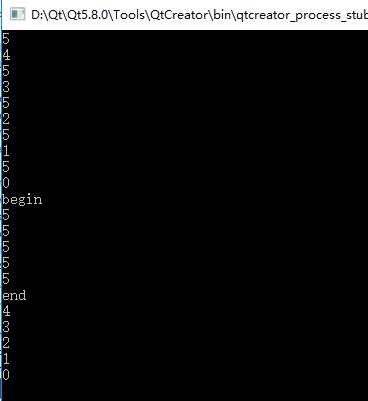
小结:


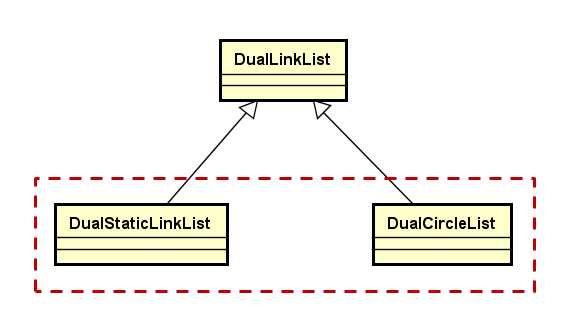
双向链表的子类:
以上是关于30 双向链表的实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章