1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30分)
Posted littlepage
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30分)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
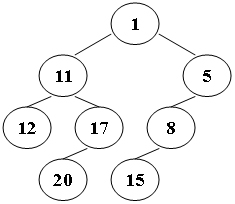
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can be determined by a given pair of postorder and inorder traversal sequences. And it is a simple standard routine to print the numbers in level-order. However, if you think the problem is too simple, then you are too naive. This time you are supposed to print the numbers in "zigzagging order" -- that is, starting from the root, print the numbers level-by-level, alternating between left to right and right to left. For example, for the following tree you must output: 1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the inorder sequence and the third line gives the postorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the zigzagging sequence of the tree in a line. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
8
12 11 20 17 1 15 8 5
12 20 17 11 15 8 5 1
Sample Output:
1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15这题考察建树和层序交错打印一棵树,我们只需要在层序遍历的时候进行赋值属于第N层,紧接着进行顺序或者逆序打印即可
#include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <vector> using namespace std; struct node { int data; node *left, *right; node(int d): data(d), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} }*root; int N, in[99999], post[99999], maxLevel = -1; node* build(int root, int start, int end) { if(start > end) return NULL; int i = start; while(i < end && in[i] != post[root]) i++; node *n = new node(in[i]); n->left = build(root - 1 - (end - i), start, i - 1); n->right = build(root - 1, i + 1, end); return n; } vector<node*> v[99999], ans; void level(node *root) { queue<pair<node*, int>> que; que.push({root, 0}); while(!que.empty()) { pair<node*, int> n = que.front(); v[n.second].push_back(n.first); maxLevel = max(maxLevel, n.second); que.pop(); if(n.first->left) que.push({n.first->left, n.second + 1}); if(n.first->right) que.push({n.first->right, n.second + 1}); } } int main() { scanf("%d", &N); for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) scanf("%d", &in[i]); for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) scanf("%d", &post[i]); root = build(N - 1, 0, N - 1); level(root); for(int i = 0; i <= maxLevel; i++) { if(i % 2 == 0) { for(int j = v[i].size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) ans.push_back(v[i][j]); } else { for(int j = 0; j < v[i].size(); j++) ans.push_back(v[i][j]); } } printf("%d", ans[0]->data); for(int i = 1; i < ans.size(); i++) printf(" %d", ans[i]->data); return 0; }
以上是关于1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30分)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章