openpcdet之pointpillar代码阅读——第三篇:损失函数的计算
Posted 非晚非晚
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了openpcdet之pointpillar代码阅读——第三篇:损失函数的计算相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
pointpillar相关的其它文章链接如下:
0. 检测头的设计
检测头流程的设计如下:

1. 损失计算的理论
Pointpillars使用了和SECOND相同的损失函数。每个三维目标检测框可以用7个变量来描述,
(
x
,
y
,
z
,
w
,
l
,
h
,
θ
)
\\left( x,y,z,w,l,h,\\theta\\right)
(x,y,z,w,l,h,θ),其中
(
x
,
y
,
z
)
\\left( x,y,z\\right)
(x,y,z)表示中心,
(
w
,
l
,
h
)
\\left(w,l,h\\right)
(w,l,h)表示三维框的尺度,
(
θ
)
\\left(\\theta\\right)
(θ) 表示框的朝向信息。那么检测框回归任务中要学习的参数为这7个变量的偏移量。
总共有三个loss:定位Loss,分类Loss和角度Loss。其中权重比例分别是
β
l
o
c
=
2
,
β
c
l
s
=
1
,
β
d
i
r
=
0.2
\\beta_loc=2,\\beta_cls=1,\\beta_dir=0.2
βloc=2,βcls=1,βdir=0.2。

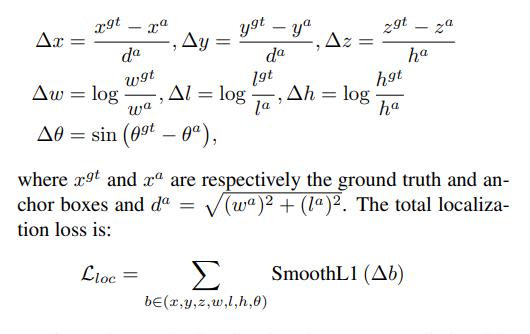
定位Loss
定位loss,也就是的box的loss,总共有7个值 ( x , y , z , w , l , h , θ ) \\left( x,y,z,w,l,h,\\theta\\right) (x,y,z,w,l,h,θ),也就是说定位loss也包含了方向loss。
后面要讲的方向分类损失,是为了避免车辆难以区分正负朝向做的分类。
方向分类Loss
方向分类损失,是为了避免目标180度错误判断而引进的。
和SECOND中相同,为了避免方向判别错误,作者引入了个Softmax损失学习物体的方向分类(softmax classification loss)。该损失记做
L
d
i
r
L_dir
Ldir 。
分类Loss
有关分类损失,作者也是采用了Focal Loss,定义如下,其中
α
=
0.25
,
γ
=
2
\\alpha=0.25,\\gamma=2
α=0.25,γ=2,

2. 生成anchors
功能:根据类别,生成不同的anchors
pointpillars针对每个类别独自生成了anchors,生成anchors是一次性操作,每个anchors的位置和尺度的单位为米,这部分在x_shifts部分体现。
这部分代码在:pcdet/models/dense_heads/target_assigner/anchor_generator.py,具体的注释代码如下:
import torch
class AnchorGenerator(object):
def __init__(self, anchor_range, anchor_generator_config):
super().__init__()
self.anchor_generator_cfg = anchor_generator_config
self.anchor_range = anchor_range# [0, -39.68, -3, 69.12, 39.68, 1]
self.anchor_sizes = [config['anchor_sizes'] for config in anchor_generator_config] #anchor的大小
self.anchor_rotations = [config['anchor_rotations'] for config in anchor_generator_config] #0和90度
self.anchor_heights = [config['anchor_bottom_heights'] for config in anchor_generator_config]
self.align_center = [config.get('align_center', False) for config in anchor_generator_config] #list:3 --> [False, False, False]
assert len(self.anchor_sizes) == len(self.anchor_rotations) == len(self.anchor_heights)
self.num_of_anchor_sets = len(self.anchor_sizes)
def generate_anchors(self, grid_sizes):
#grid_size为list,它的大小为3个[216, 248]
assert len(grid_sizes) == self.num_of_anchor_sets
all_anchors = []
num_anchors_per_location = []
for grid_size, anchor_size, anchor_rotation, anchor_height, align_center in zip(
grid_sizes, self.anchor_sizes, self.anchor_rotations, self.anchor_heights, self.align_center):
#2 * 3 * 1,每个点返回6个anchor
num_anchors_per_location.append(len(anchor_rotation) * len(anchor_size) * len(anchor_height))
if align_center:
x_stride = (self.anchor_range[3] - self.anchor_range[0]) / grid_size[0]
y_stride = (self.anchor_range[4] - self.anchor_range[1]) / grid_size[1]
x_offset, y_offset = x_stride / 2, y_stride / 2
else:
#计算每个网格的在点云空间中的实际大小
# 用于将每个anchor映射回实际点云中的大小
# (69.12 - 0) / (216 - 1) = 0.3214883848678234 单位:米
x_stride = (self.anchor_range[3] - self.anchor_range[0]) / (grid_size[0] - 1)
# (39.68 - (-39.68.)) / (248 - 1) = 0.3212955490297634 单位:米
y_stride = (self.anchor_range[4] - self.anchor_range[1]) / (grid_size[1] - 1)
# 由于没有进行中心对齐,所有每个点相对于左上角坐标的偏移量都是0
x_offset, y_offset = 0, 0
#生成anchor的位置,这里使用的实际尺寸,单位米
# 产生x坐标 --> 216个点 [0, 69.12]
x_shifts = torch.arange(
self.anchor_range[0] + x_offset, self.anchor_range[3] + 1e-5, step=x_stride, dtype=torch.float32,
).cuda()
# 产生y坐标 --> 248个点 [0, 79.36]
y_shifts = torch.arange(
self.anchor_range[1] + y_offset, self.anchor_range[4] + 1e-5, step=y_stride, dtype=torch.float32,
).cuda()
z_shifts = x_shifts.new_tensor(anchor_height)
num_anchor_size, num_anchor_rotation = anchor_size.__len__(), anchor_rotation.__len__()
anchor_rotation = x_shifts.new_tensor(anchor_rotation)
anchor_size = x_shifts.new_tensor(anchor_size)
x_shifts, y_shifts, z_shifts = torch.meshgrid([
x_shifts, y_shifts, z_shifts
]) # [x_grid, y_grid, z_grid]
anchors = torch.stack((x_shifts, y_shifts, z_shifts), dim=-1) # [x, y, z, 3],([216, 248, 1, 3])
anchors = anchors[:, :, :, None, :].repeat(1, 1, 1, anchor_size.shape[0], 1) #([216, 248, 1, 1, 3])
anchor_size = anchor_size.view(1, 1, 1, -1, 3).repeat([*anchors.shape[0:3], 1, 1])
#加入尺寸
anchors = torch.cat((anchors, anchor_size), dim=-1)
anchors = anchors[:, :, :, :, None, :].repeat(1, 1, 1, 1, num_anchor_rotation, 1)
#加入旋转
anchor_rotation = anchor_rotation.view(1, 1, 1, 1, -1, 1).repeat([*anchors.shape[0:3], num_anchor_size, 1, 1])
anchors = torch.cat((anchors, anchor_rotation), dim=-1) # [x, y, z, num_size, num_rot, 7]
anchors = anchors.permute(2, 1, 0, 3, 4, 5).contiguous()
#anchors = anchors.view(-1, anchors.shape[-1])
# anchors 的大小([1, 248, 216, 1, 2, 7]),(z, y, x, l, w, h, theta)
anchors[..., 2] += anchors[..., 5] / 2 # shift to box centers
all_anchors.append(anchors)
#all_anchors按照类别组成anchors
return all_anchors, num_anchors_per_location
if __name__ == '__main__':
from easydict import EasyDict
config = [
EasyDict(
'anchor_sizes': [[2.1, 4.7, 1.7], [0.86, 0.91, 1.73], [0.84, 1.78, 1.78]],
'anchor_rotations': [0, 1.57],
'anchor_heights': [0, 0.5]
)
]
A = AnchorGenerator(
anchor_range=[-75.2, -75.2, -2, 75.2, 75.2, 4],
anchor_generator_config=config
)
import pdb
pdb.set_trace()
A.generate_anchors([[188, 188]])
3. GT与anchor的匹配
在PointPillars中指定正负样本的时候由BEV视角计算GT和先验框的iou,不需要进行z轴上的高度的匹配。就像上一篇文章介绍的,代码中按照匹配的阈值正负样本的分类。一个Batch样本中anchor与GT的匹配是逐帧逐类别进行的。
这部分代码在:pcdet/models/dense_heads/target_assigner/axis_aligned_target_assigner.py,具体的注释代码如下:
import numpy as np
import torch
from ....ops.iou3d_nms import iou3d_nms_utils
from ....utils import box_utils
class AxisAlignedTargetAssigner(object):
def __init__(self, model_cfg, class_names, box_coder, match_height=False):
super().__init__()
anchor_generator_cfg = model_cfg.ANCHOR_GENERATOR_CONFIG
anchor_target_cfg = model_cfg.TARGET_ASSIGNER_CONFIG
# 编码box的7个残差参数(x, y, z, w, l, h, θ) --> pcdet.utils.box_coder_utils.ResidualCode
self.box_coder = box_coder
self.match_height = match_height #False,不匹配高度
self.class_names = np.array(class_names)
self.anchor_class_names = [config['class_name'] for config in anchor_generator_cfg]
# 前景、背景采样系数 ,None
self.pos_fraction = anchor_target_cfg.POS_FRACTION if anchor_target_cfg.POS_FRACTION >= 0 else None
#总采样数,512
self.sample_size = anchor_target_cfg.SAMPLE_SIZE
#False
self.norm_by_num_examples = anchor_target_cfg.NORM_BY_NUM_EXAMPLES
self.matched_thresholds =
self.unmatched_thresholds =
for config in anchor_generator_cfg:
self.matched_thresholds[config['class_name']] = config['matched_threshold']
self.unmatched_thresholds[config['class_name']] = config['unmatched_threshold']
self.use_multihead = model_cfg.get('USE_MULTIHEAD', False)
# self.separate_multihead = model_cfg.get('SEPARATE_MULTIHEAD', False)
# if self.seperate_multihead:
# rpn_head_cfgs = model_cfg.RPN_HEAD_CFGS
# self.gt_remapping =
# for rpn_head_cfg in rpn_head_cfgs:
# for idx, name in enumerate(rpn_head_cfg['HEAD_CLS_NAME']):
# self.gt_remapping[name] = idx + 1
def assign_targets(self, all_anchors, gt_boxes_with_classes):
"""
Args:
all_anchors: [(N, 7), ...]
gt_boxes: (B, M, 8)
Returns:
"""
"""
处理一批数据中所有点云的anchors和gt_boxes,
计算每个anchor属于前景还是背景,
为每个前景的anchor分配类别和计算box的回归残差和回归权重
Args:
all_anchors: [(N, 7), ...]
gt_boxes_with_classes: (B, M, 8) # 最后维度数据为 (x, y, z, w, l, h, θ,class)
Returns:
all_targets_dict =
# 每个anchor的类别
'box_cls_labels': cls_labels, # (batch_size,num_of_anchors)
# 每个anchor的回归残差 -->(∆x, ∆y, ∆z, ∆l, ∆w, ∆h, ∆θ)
'box_reg_targets': bbox_targets, # (batch_size,num_of_anchors,7)
# 每个box的回归权重
'reg_weights': reg_weights # (batch_size,num_of_anchors)
"""
bbox_targets = []
cls_labels = []
reg_weights = []
batch_size = gt_boxes_with_classes.shape[0]
gt_classes = gt_boxes_with_classes[:, :, -1] #gt的类别
gt_boxes = gt_boxes_with_classes[:, :, :-1] # gt的7个参数
for k in range(batch_size):
cur_gt = gt_boxes[k] # 取出当前帧中的 gt_boxes (num_of_gt,7)
cnt = cur_gt.__len__() - 1 #最后面的一个gt
"""
由于在OpenPCDet的数据预处理时,以一批数据中拥有GT数量最多的帧为基准,
其他帧中GT数量不足,则会进行补0操作,使其成为一个矩阵,例:
[
[1,1,2,2,3,2],
[2,2,3,1,0,0],
[3,1,2,0,0,0]
]
因此这里从每一行的倒数第二个类别开始判断,
截取最后一个非零元素的索引,来取出当前帧中真实的GT数据
"""
while cnt > 0 and cur_gt[cnt].sum() == 0:
cnt -= 1
cur_gt = cur_gt[:cnt + 1] #取出当前帧中的所有gt
cur_gt_classes = gt_classes[k][:cnt + 1].int() #取出当前帧中的类别
target_list = []
#按照类别遍历所有的anchors
# # anchors 的大小([1, 248, 216, 1, 2, 7]),(z, y, x, l, w, h, theta)
for anchor_class_name, anchors in zip(self.anchor_class_names, all_anchors):
#取出gt中当前的类别
if cur_gt_classes.shape[0] > 1:
mask = torch.from_numpy(self.class_names[cur_gt_classes.cpu() - 1] == anchor_class_name)
else:
mask = torch.tensor([self.class_names[c - 1] == anchor_class_name
for c in cur_gt_classes], dtype=torch.bool)
if self.use_multihead:
anchors = anchors.permute(3, 4, 0, 1, 2, 5).contiguous().view(-1, anchors.shape[-1])
# if self.seperate_multihead:
# selected_classes = cur_gt_classes[mask].clone()
# if len(selected_classes) > 0:
# new_cls_id = self.gt_remapping[anchor_class_name]
# selected_classes[:] = new_cls_id
# else:
# selected_classes = cur_gt_classes[mask]
selected_classes = cur_gt_classes[mask]
else:
feature_map_size = anchors.shape[:3]
#将anchors展开
anchors = anchors.view(-1, anchors.shape[-1])
selected_classes = cur_gt_classes[mask]
single_target = self.assign_targets以上是关于openpcdet之pointpillar代码阅读——第三篇:损失函数的计算的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章