算法排序汇总
Posted chaostudy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了算法排序汇总相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
排序算法
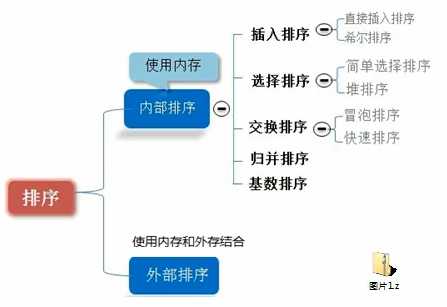
排序的分类:
1)内部排序:
指将需要处理的所有数据都加载到内部存储器中进行排序。
2)外部排序法:
数据量过大,无法全部加载到内存中,需要借助外部存储进行排序。
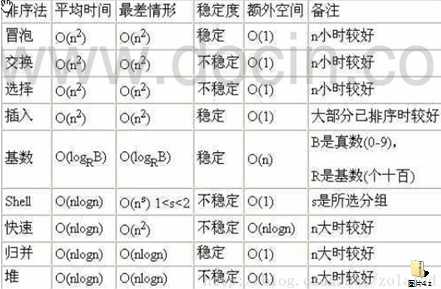
常见的算法时间复杂度由小到大依次为:
O(1)<O(log2n)<O(n)<O(nlog2n)<O(n2)<O(n3)< O(nk) <O(2n)
随着问题规模n的不断增大,上述时间复 杂度不断增大,算法的执行效率越低
测速代码
int[] arr = new int[80000];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random()*8000000);
}
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SSS");
long date1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
String str1 = simpleDateFormat.format(date1);
System.out.println("排序前的时间:"+str1);
//加入要测试的排序方式代码。如:
shellSort(arr);
long date2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
String str2 = simpleDateFormat.format(date2);
System.out.println("排序后的时间:"+str2);
long date3 = date2 - date1;
System.out.println("80000随机数排序花费毫秒数:" + date3);
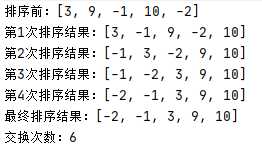
冒泡排序
public class MaoPao {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3,9,-1,10,-2};
int temp = 0;
for (int j = 0;j < arr.length ; j++){
for (int i = 0; i <arr.length-1 ; i++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[i+1]){
temp = arr[i+1];
arr[i+1] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
System.out.println("第"+(j+1)+"次排序结果:"+Arrays.toString(arr));
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
加flag判断优化后
public class MaoPao {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3,9,-1,10,-2};
System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
sort(arr);
}
public static void sort(int[] arr){
int temp = 0;
boolean flag = false;
for (int j = 0;j < arr.length ; j++){
for (int i = 0; i <arr.length-1 ; i++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[i+1]){
flag = true;
temp = arr[i+1];
arr[i+1] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
if (!flag){
break;
}else {
flag = false;
}
System.out.println("第"+(j+1)+"次排序结果:"+Arrays.toString(arr));
}
System.out.println("最终排序结果:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}

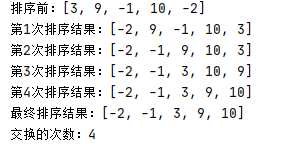
选择排序
可以比作打牌,把牌全摸好后,开始排序
public class SelectSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={3,9,-1,10,-2};
System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
selectSort(arr);
}
//选择排序
public static void selectSort(int[] arr){
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1 ; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
int min = arr[i];
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (min > arr[j]){
min = arr[j];
minIndex = j;
}
}
if (minIndex!=i){
arr[minIndex] = arr[i];
arr[i] = min;
count++;
}
System.out.println("第"+ (i+1) + "次排序结果:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));
}
System.out.println("最终排序结果:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println("交换的次数:"+count);
}
}

插入排序
可以比作打牌,边摸牌,边排序
public class InsertSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3,9,-1,10,-2};
System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
insertSort(arr);
}
public static void insertSort(int[] arr){
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
int insertValue = arr[i];
int insertIndex = i - 1;
while (insertIndex >= 0 && insertValue < arr[insertIndex]) {
arr[insertIndex + 1] = arr[insertIndex];
insertIndex--;
}
arr[insertIndex+1] = insertValue;
System.out.println("第" + i + "轮插入");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
}


希尔排序
希尔排序法介绍.
希尔排序是希尔(DonaldShell) 于1959年提出的一 种排序算法。希尔排序也是一种插入排序, 它是简单插入排序经过改进之后的一-个更高效的版本,也称为缩小增量排序。
希尔排序法基本思想
希尔排序是把记录按下标的一定增量分组,对每组使用直接插入排序算法排序;随着增量逐渐减少,每组包含的关键词越来越多,当增量减至1时,整个文件恰被分成一组,算法便终止
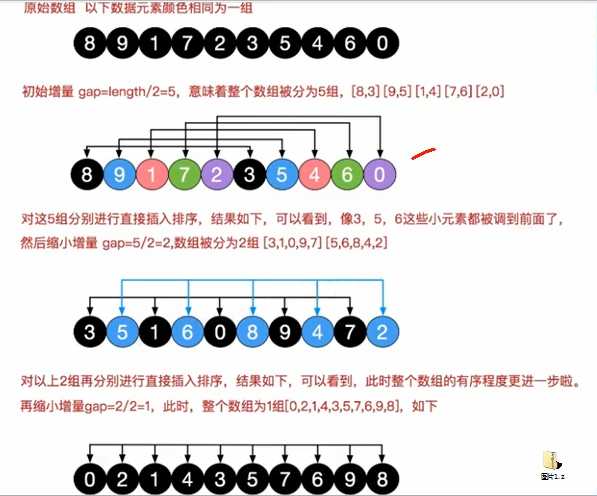
交换法:
public class ShellSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3,9,-1,10,-2};
shellSort(arr);
}
public static void shellSort(int[] arr){
int temp = 0;
int count = 0;
for (int step = arr.length / 2; step > 0 ; step /= 2){
for (int i = step; i <arr.length ; i++) {
//遍历各组中所有的元素(共step组,每组有2个元素),步长step ;
for (int j = i - step; j >= 0 ; j -= step){
if (arr[j] > arr[j + step]){
count++;
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + step];
arr[j + step] = temp;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
}


移位法:
public static void shellSort(int[] arr){
for (int step = arr.length / 2; step > 0 ; step /= 2){
for (int i = step; i <arr.length ; i++) {
//遍历各组中所有的元素(共step组,每组有2个元素),步长step ;
int j = i;
int temp = arr[j];
if (arr[j] < arr[j-step]){
while (j - step >= 0 && temp < arr[j - step]){
arr[j] = arr[j-step];
j -= step;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// System.out.println("第"+(count++)+"轮排序结果" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}



快速排序
public static void quickSort(int[] arr,int left,int right){
int l = left;
int r = right;
int middle = arr[(left + right)/2];
int temp = 0;
while (l < r){
while (arr[l] < middle){
l++;
}
while (arr[r] > middle){
r--;
}
if (l >= r){
break;
}
temp = arr[l];
arr[l] = arr[r];
arr[r] = temp;
if (arr[l] == middle){
r--;
}
if (arr[r] == middle){
l++;
}
}
if (l == r){
l++;
r--;
}
if (left < r){
quickSort(arr, left, r);
}
if (right > l){
quickSort(arr, l , right);
}
}



归并排序
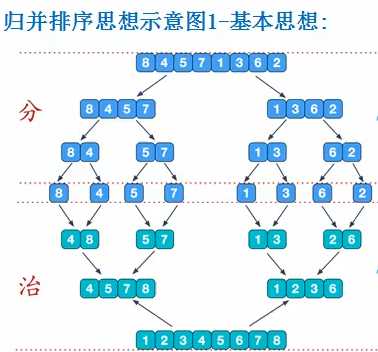
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {8,4,5,7,1,3,6,2};
int[] temp = new int[arr.length];
margeSoft(arr, 0, arr.length-1, temp);
System.out.println("归并排序及结果:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void margeSoft(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp){
if (left < right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
margeSoft(arr, left, mid, temp);
margeSoft(arr, mid + 1, right, temp);
marge(arr, left ,mid ,right ,temp);
}
}
/**
*
* @param arr 排序的原始数组
*@param left 左边有序序列的初始索引
* @param mid 中间索引
* @param right 右边索引
* @param temp 做中转的数组
*/
public static void marge(int[] arr,int left,int mid ,int right,int[] temp){
int i = left;//初始化i,左边有序序列的初始索引
int j = mid + 1;//初始化j,右边有序序列的初始索引
int t = 0;//指向temp数组的当前索引
//(一)
//先把左右两边(有序)的数据按照规则填充到temp数组
//直到左右两边的有序序列,有一边处理完毕为止
while (i <= mid && j <= right){
if (arr[i] <= arr[j]){
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}else {
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
}
//(二)
//把有剩余数据的一边的数据依次全部填充到temp
while (i <= mid){
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}
while (j <= right){
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
//(三)
//将temp数组的元素拷贝到arr,
t = 0;
int tempLeft = left;
while (tempLeft <= right){
arr[tempLeft++] = temp[t++];
}
}
}



基数排序(桶排扩展)
- 基数排序是对传统桶排序的扩展,速度很快.
- 基数排序是经典的空间换时间的方式,占用内存很大,当对海量数据排序时,容易造成OutOfMemoryError。
- 基数排序时稳定的。[注 :假定在待排序的记录序列中,存在多个具有相同的关键字的记录,若经过排序,这些记录的相对次序保持不变,即在原序列中,r[i]=r[j], 且r[i]在r[j]之前, 而在排序后的序列中,r[i]仍在ri]之前, 则称这种排序算法是稳定的;否则称为不稳定的]
将每个元素的个/十/百/千/万/。。。位数取出,然后看这个数应该放在哪个对应的桶(一个一维数组)
按照这个桶的顺序(一维数组的下标依次职出数据,放入原来数组)
以下示例不支持负数排序;
负数排序思想:求绝对值,然后进行反转
public class RadixSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {53,5,542,748,14,214};
radixSort(arr);
}
public static void radixSort(int[] arr){
//定义一个二维数组,表示10个桶,每个桶就是一个一 维数组
//说明.
//1.二维数组包含10个一维数组
//2.为了防止在放入数的时候,数据溢出,则每个一维数组(桶),大小定为arr .1ength
//3.名明确,基数排序是使用空间换时间的经典算法
//得到数组中最大位的个数
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max){
max = arr[i];
}
}
int maxLength = (max + "").length();
int[][] bucket = new int[10][arr.length];
//为了记录每个桶中,实际存放了多少个数据,我们定义一个一维数组来记录各个桶的每次放入的数据个数
//0-9个桶中数的个数
int[] count = new int[10];
for (int i = 0, n = 1; i < maxLength; i++,n *= 10) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
int geValue = arr[j] /n % 10;//个位的值
//比如说53,geValue==3;count[geValue]==(3桶中的数的个数)
bucket[geValue][count[geValue]]= arr[j];
count[geValue]++;
}
int index = 0;
//遍历每一桶,并将桶中的数据,放入到原数组
for (int k = 0; k < bucket.length; k++) {
//第K桶中的数不等于0
if (count[k]!=0){
for (int l = 0; l < count[k]; l++) {
//bucket[k][l]第K个桶中第L个元素
arr[index++] = bucket[k][l];
}
}
//每轮处理后,需要将每个count[k]=0;
count[k] = 0;
}
System.out.println("第"+ i + "轮排序后结果:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
}



以上是关于算法排序汇总的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章