Elasticsearch入门和查询语法分析(ik中文分词)
Posted johnson108178
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Elasticsearch入门和查询语法分析(ik中文分词)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
全文搜索现在已经是很常见的功能了,当然你也可以用mysql加Sphinx实现。但开源的Elasticsearch(简称ES)目前是全文搜索引擎的首选。目前像GitHub、维基百科都使用的是ES,它可以快速的存储,搜索和分析数据。
一、安装与启动
ES的运行需要依赖java环境,可以在命令行运行 java --version 。如果出现
说明已经安装了,否则你就需要安装下java环境。
然后我们就可以开始装ES了。1、可以用docker容器安装。2、用压缩包安装。
我是用压缩包安装的。
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-6.3.1.tar.gz tar -xzf elasticsearch-6.3.1.tar.gz cd elasticsearch-6.3.1/
然后输入 ./bin/elasticsearch 就可以启动ES了。在浏览器上输入 localhost:9200 ,如果出现
就说明ES成功跑起来了。
不了解ES的同学可以去看看阮老师的这篇文章http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2017/08/elasticsearch.html。
二、IK分词
ES默认的分词是英文分词,对中文分词支持的并不好。所以我们就需要安装ik中文分词。让我们看看区别。
在这里需要说明的一点时,ES很多API请求都是GET带上了Request Body。所以通过浏览器或者postman等工具发起GET请求时会报错。有两种方法可以解决。
1、通过命令含的curl请求。
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_analyze" -H ‘Content-Type: application/json‘ -d‘ { "analyzer" : "standard", "text" : "this is a test" } ‘
2、在代码中通过curl请求。
// 通过php的guzzle包发起的请求
$client = new Client(); $response = $client->get(‘localhost:9200/_analyze‘, [ ‘json‘ => [ ‘analyzer‘ => ‘standard‘, ‘text‘ => "功能进阶", ] ]); $res = ($response->getBody()->getContents());
然后我们来看看ik中文分词和ES默认的分词区别。同样是上面的请求
ES默认分词结果
{ "tokens": [ { "token": "功", "start_offset": 0, "end_offset": 1, "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>", "position": 0 }, { "token": "能", "start_offset": 1, "end_offset": 2, "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>", "position": 1 }, { "token": "进", "start_offset": 2, "end_offset": 3, "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>", "position": 2 }, { "token": "阶", "start_offset": 3, "end_offset": 4, "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>", "position": 3 } ] }
ik中文分词结果
ik分词也分两种分析器。ik_smart:尽可能少的进行中文分词。ik_max_word:尽可能多的进行中文分词。
$response = $client->get(‘localhost:9200/_analyze‘, [ ‘json‘ => [ ‘analyzer‘ => ‘ik_max_word‘, ‘text‘ => "功能进阶", ] ]);
得到的结果为:
{ "tokens": [ { "token": "功能", "start_offset": 0, "end_offset": 2, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 1 }, { "token": "能进", "start_offset": 1, "end_offset": 3, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 2 }, { "token": "进阶", "start_offset": 2, "end_offset": 4, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 3 } ] }
而ik_smart
$response = $client->get(‘localhost:9200/_analyze‘, [ ‘json‘ => [ ‘analyzer‘ => ‘ik_smart‘, ‘text‘ => "功能进阶", ] ]);
的结果为
{ "tokens": [ { "token": "功能", "start_offset": 0, "end_offset": 2, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 1 }, { "token": "进阶", "start_offset": 2, "end_offset": 4, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 3 } ] }
其实他们的区别通过名字你也可以略知一二。哈哈。。。
假如有人想问,我就想把“功能进阶”当成一个词来搜索,可以吗?
Of course!!
这时候我们就要自定义分词。进入你的ES目录,运行 cd config/analysis-ik/ 进去ik分词的配置。找到IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml文件,然后 vi IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml 。
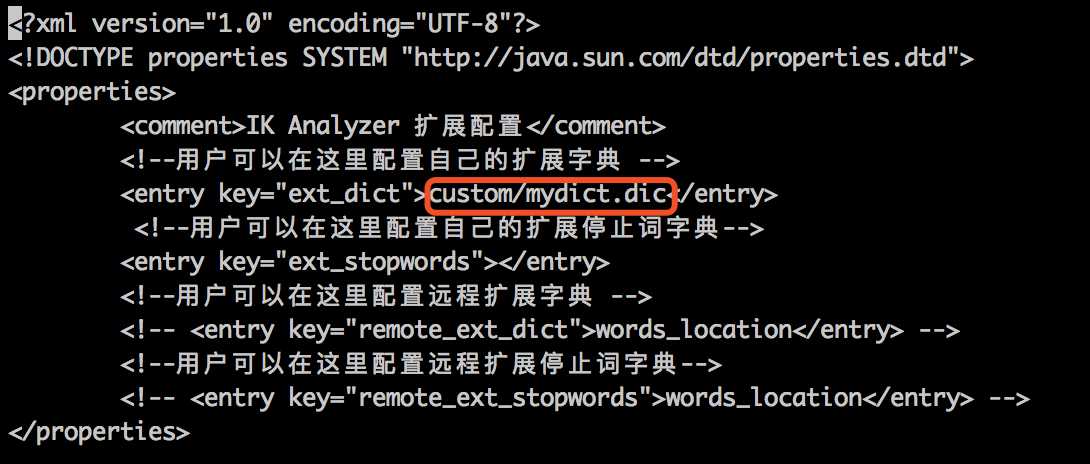
我在 elasticsearch-6.3.0/config/analysis-ik 目录下,创建了 custom/mydict.dic ,然后添加到上图的红色框框中,这就是你自定义分词的文件。如果有多个文件,可以用英文分号(;)隔开。

可以看到,我在自定义中文分词文件中添加了“功能进阶”这个词。这时候用ik_smart分析器的结果是:
{ "tokens": [ { "token": "功能进阶", "start_offset": 0, "end_offset": 4, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 0 } ] }
很好,这就是我们想要的。
三、Query DSL
- match
查询语法如下:title是需要查询的字段名,可以被替换成任何字段。query对应的是所需的查询。比如这里会被拆分成‘php’和‘后台’,应为operator是or,所以ES会去所有数据里的title字段查询包含‘后台’和‘php’的,如果operator为and,这查询的是即包含‘后台’又有‘php’的数据,这应该很好理解。
$response = $client->get(‘localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search‘, [ ‘json‘ => [ ‘query‘ => [ ‘match‘ => [ ‘title‘ => [ ‘query‘ => ‘后台php‘, ‘operator‘ => ‘or‘, ] ] ] ] ]);
- multi_match
如果想在多个字段中查找,那就需要用到multi_match查询,语法如下:
$response = $client->get(‘localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search‘, [ ‘json‘ => [ ‘query‘ => [ ‘multi_match‘ => [ ‘query‘ => ‘张三 php‘, ‘fields‘ => [‘title‘, ‘desc‘, ‘user‘] ] ] ] ]);
- query_string
查询语法如下:类似match查询的operator,在这里需要在query中用OR或AND实现。
$response = $client->get(‘localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search‘, [ ‘json‘ => [ ‘query‘ => [ ‘query_string‘ => [ ‘query‘ => ‘(张三) OR (php)‘, ‘default_field‘ => ‘title‘, ] ] ] ]);
多字段查询如下:
$response = $client->get(‘localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search‘, [ ‘json‘ => [ ‘query‘ => [ ‘query_string‘ => [ ‘query‘ => ‘(张三) OR (php)‘, ‘fields‘ => [‘title‘, ‘user‘], ] ] ] ]);
- range query
这是范围查询,例如查询年龄在10到20岁之间的。查询语法如下:
$response = $client->get(‘localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search‘, [ ‘json‘ => [ ‘query‘ => [ ‘range‘ => [ ‘age‘ => [ ‘gte‘ => 10, ‘lte‘ => 20, ], ] ] ] ]);
gte表示>=,lte表示<=,gt表示>,lt表示<。
- bool查询
bool查询的语法都是一样的。如下:
$response = $client->get(‘localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search‘, [ ‘json‘ => [ ‘query‘ => [ ‘bool‘ => [ ‘must/filter/should/must_not‘ => [ [ ‘query_string‘ => [ ‘query‘ => ‘研发‘, ] ], [ ‘range‘ => [ ‘age‘ => [ ‘gt‘ => 20 ] ] ], ], ] ] ] ]);
1)must:must查询是查询字段中必须满足上面两个条件,并且会计算到score中。
2)filter:filter查询与must一样,都必须满足上面两个条件,只不过查询结果不会计算score,也就是score始终为0.
3)should:should查询只需要满足上面两种查询条件中的一种即可。
4)must_not:must_not查询是必须不满足上面两个查询条件。
以上也是我看文档总结出来的,如有不对的地方,望大神指点。
以上是关于Elasticsearch入门和查询语法分析(ik中文分词)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章