服务端寻路实现总结
Posted leothzhang
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了服务端寻路实现总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
整体思路:
- 通过客户端(Unity)导出地图信息
- 将地图信息放到服务端解析
- 服务端通过A*寻路算法计算路径点,然后服务端将这些路径点返回给客户端
说明:
- 此方案只在场景障碍物都是静态且不考虑高度的条件下有效
- 如果场景障碍物是动态且需要考虑高度的话,则服务端要非常强大的寻路库实现,这部分可以使用recastnavigation(https://github.com/recastnavigation/recastnavigation),同时这也是Unity内部源码使用的方案。
操作步骤:
Unity导出地图信息:
- 设置游戏场景里物体障碍物属性为Navigation Static,并按照物体属性设置物体是否可行走(Walkable)和不可行走(Not Walkable),因为不考虑高度,Generate OffMeshLinks可不勾选。
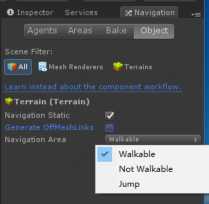
设置Object属性
- 当设置好所有障碍物信息后,执行地图网络烘焙(Bake)。
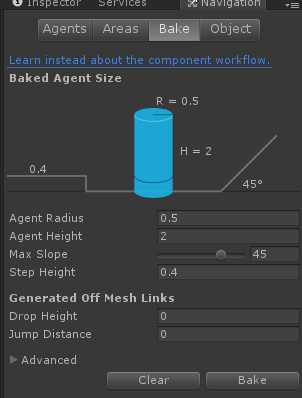

a)点击Bake烘焙出地图网络信息 b)烘焙后的网络信息图 - 如果服务端是通过顶点和索引导入地图信息的,则通过UnityEngine.AI.NavMesh.CalculateTriangulation() 导出顶点和索引信息。
如果服务端是通过二维坐标导入地图信息的,则通过UnityEngine.AI.NavMesh.SamplePosition()逐一顶点采样,如果hit中障碍物,则对应点设为1,否则设为0。
导出顶点和索引代码:
 NavMeshExport
NavMeshExport1 using System.IO; 2 using UnityEditor; 3 using UnityEngine.SceneManagement; 4 using UnityEngine; 5 6 namespace AStar 7 { 8 //navmesh导出数据 9 public class NavMeshExport : MonoBehaviour 10 { 11 [MenuItem("NavMesh/Export")] 12 static void Export() 13 { 14 Debug.Log("NavMesh Export Start"); 15 16 UnityEngine.AI.NavMeshTriangulation navMeshTriangulation = UnityEngine.AI.NavMesh.CalculateTriangulation(); 17 18 //文件路径 19 string path = Application.dataPath /*+ "/AStar/obj/"*/ + SceneManager.GetActiveScene().name + ".obj"; 20 21 //新建文件 22 StreamWriter streamWriter = new StreamWriter(path); 23 24 //顶点 25 for (int i = 0; i < navMeshTriangulation.vertices.Length; i++) 26 { 27 streamWriter.WriteLine("v " + navMeshTriangulation.vertices[i].x + " " + navMeshTriangulation.vertices[i].y + " " + navMeshTriangulation.vertices[i].z); 28 } 29 30 streamWriter.WriteLine("g pPlane1"); 31 32 //索引 33 for (int i = 0; i < navMeshTriangulation.indices.Length;) 34 { 35 streamWriter.WriteLine("f " + (navMeshTriangulation.indices[i] + 1) + " " + (navMeshTriangulation.indices[i + 1] + 1) + " " + (navMeshTriangulation.indices[i + 2] + 1)); 36 i = i + 3; 37 } 38 39 streamWriter.Flush(); 40 streamWriter.Close(); 41 42 43 AssetDatabase.Refresh(); 44 45 Debug.Log("NavMesh Export Success"); 46 } 47 } 48 }
导出后的obj图
导出二维坐标代码:
 NavArrayExport
NavArrayExport1 using UnityEngine; 2 using System.Collections; 3 using System.IO; 4 using System.Text; 5 using UnityEditor; 6 using UnityEngine.SceneManagement; 7 using UnityEngine; 8 9 public class NavArrayExport: MonoBehaviour 10 { 11 #region Public Attributes 12 public Vector3 leftUpStart = Vector3.zero; 13 public float accuracy = 1; 14 public int height = 30; 15 public int wide = 30; 16 public float maxdistance = 0.2f; 17 public float kmin = -10; 18 public float kmax = 20; 19 #endregion 20 21 22 #region Public Methods 23 24 public void Exp() 25 { 26 exportPoint(leftUpStart, wide, height, accuracy); 27 } 28 29 public float ConvertToNearestHalfNum(float num) 30 { 31 float numFloor = Mathf.Floor(num); 32 float half = 0.5f; 33 float d1 = num - numFloor; 34 float d2 = Mathf.Abs(num - (numFloor + half)); 35 float d3 = numFloor + 1 - num; 36 float d = Mathf.Min(d1, d2, d3); 37 if(d == d1) 38 { 39 return numFloor; 40 } 41 else if(d == d2) 42 { 43 return numFloor + 0.5f; 44 } 45 else 46 { 47 return numFloor + 1f; 48 } 49 } 50 51 public void exportPoint(Vector3 startPos, int x, int y, float accuracy) 52 { 53 StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(); 54 int[,] list = new int[x, y]; 55 str.Append("[MAP_DESC] "); 56 str.Append("startpos=").Append(startPos).Append(" "); 57 str.Append("height=").Append(y).Append(" wide=").Append(x).Append(" accuracy=").Append(accuracy).Append(" "); 58 for (int j = 0; j < y; ++j) 59 { 60 for (int i = 0; i < x; ++i) 61 { 62 UnityEngine.AI.NavMeshHit hit; 63 for (float k = kmin; k < kmax; k+=0.5f) 64 { 65 Vector3 p = startPos + new Vector3(i * accuracy, k, -j * accuracy); 66 if (UnityEngine.AI.NavMesh.SamplePosition(p, out hit, maxdistance, UnityEngine.AI.NavMesh.AllAreas)) 67 { 68 //Debug.DrawRay(new Vector3(ConvertToNearestHalfNum(hit.position.x), hit.position.y, ConvertToNearestHalfNum(hit.position.z)), Vector3.up, Color.green); 69 list[(int)(ConvertToNearestHalfNum(hit.position.x) * 2), (int)(ConvertToNearestHalfNum(hit.position.z) * 2)] = 1; 70 break; 71 } 72 } 73 } 74 } 75 str.Append("map="); 76 for (int j = 0; j < y; ++j) 77 { 78 str.Append("["); 79 for (int i = 0; i < x; ++i) 80 { 81 str.Append(Mathf.Abs(1 - list[i, j])).Append(","); 82 } 83 str.Append("],"); 84 } 85 //文件路径 86 string path = Application.dataPath + SceneManager.GetActiveScene().name + ".ini"; 87 88 //新建文件 89 StreamWriter streamWriter = new StreamWriter(path); 90 streamWriter.Write(str.ToString()); 91 streamWriter.Flush(); 92 streamWriter.Close(); 93 94 95 AssetDatabase.Refresh(); 96 } 97 #endregion 98 99 } 100 101 [CustomEditor(typeof(NavArrayExport))] 102 public class NavArrayExportHelper: Editor 103 { 104 public override void OnInspectorGUI() 105 { 106 base.OnInspectorGUI(); 107 if (GUILayout.Button("Export")) 108 { 109 var exp = target as NavExport; 110 exp.Exp(); 111 } 112 } 113 }
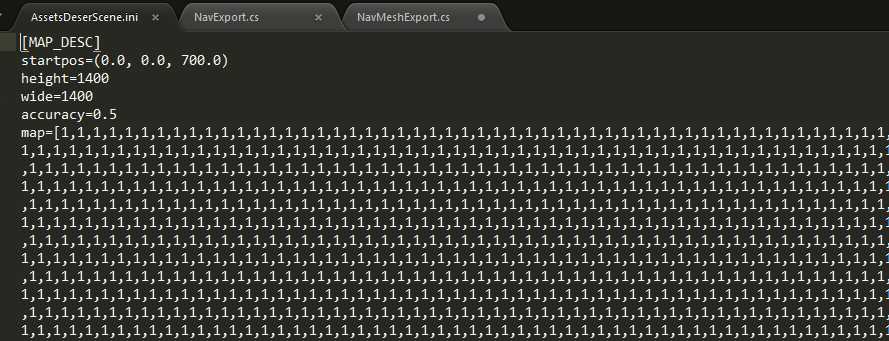 导出的二维坐标表
导出的二维坐标表
服务端实现:
解决了客户端导出的地图信息后,服务端只需要通过获取客户端发送过来的start_pos和end_pos,并通过这两个点执行寻路逻辑,然后得到一串路径点,然后将这些路径点返回给客户端,客户端通过路径点执行对应人物的方向行走即可。不过要注意的是,这里客户端之所以是通过方向行走而不是直接走到那个路径点是因为我们是忽略了高度的因素)
- 服务端load地图信息,具体代码见navmesh的load()和load_map_array()
- 服务端寻路算法实现:
如果是通过顶点索引方案的方式寻路,则记录所有三角形的重心,将重心抽象成地图上的网络点,然后计算寻路时,以这些网络点当成作用对象来进行寻路,具体代码见navmesh的calulate_path()
如果是通过数组的方式,那就更容易了,直接走传统的A*即可,具体代码见navmesh的calulate_path_array()
navmesh代码如下:
 navmesh
navmesh1 #!/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf8 -*- 3 import os 4 import ConfigParser 5 import numpy 6 from heapq import * 7 from vector3 import Vector3 8 from triangle import Triangle 9 from math_tools import MathTools 10 from common.singleton import Singleton 11 from common.logger import Logger 12 class Navmesh(Singleton): 13 ‘‘‘ 14 服务端寻路组件 15 ‘‘‘ 16 def __init__(self): 17 self.vertices = [] 18 self.indices = [] 19 self.all_triangles = [] # 所有三角形 20 self.all_center_o = [] # 所有三角形的重心 21 self.point_2_triangles = {} # 点包含的三角形列表集合 22 23 # obj_file 24 dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__)) 25 #self.map_obj_file_name = ‘{}/{}‘.format(dir,‘test.obj‘) 26 self.map_obj_file_name = ‘{}/{}‘.format(dir,‘AssetsDeserScene.obj‘) 27 28 29 def load(self): 30 with open(self.map_obj_file_name, ‘r+‘) as f: 31 Logger().I(‘loading map data({})...‘.format(self.map_obj_file_name)) 32 lines = f.readlines() 33 for line in lines: 34 for kv in [line.strip().split(‘ ‘)]: 35 if kv[0] == ‘v‘: 36 self.vertices.append(Vector3(float(kv[1]),float(kv[2]),float(kv[3]))) 37 elif kv[0] == ‘f‘: 38 a = int(kv[1])-1 39 b = int(kv[2])-1 40 c = int(kv[3])-1 41 t = Triangle(self.vertices[a], self.vertices[b], self.vertices[c]) 42 self.indices.append(Vector3(a,b,c)) 43 self.all_triangles.append(t) 44 self.all_center_o.append(t.o) 45 46 if t.a not in self.point_2_triangles: 47 self.point_2_triangles[t.a] = [t] 48 elif t not in self.point_2_triangles[t.a]: 49 self.point_2_triangles[t.a].append(t) 50 51 if t.b not in self.point_2_triangles: 52 self.point_2_triangles[t.b] = [t] 53 elif t not in self.point_2_triangles[t.b]: 54 self.point_2_triangles[t.b].append(t) 55 56 if t.c not in self.point_2_triangles: 57 self.point_2_triangles[t.c] = [t] 58 elif t not in self.point_2_triangles[t.c]: 59 self.point_2_triangles[t.c].append(t) 60 61 return True 62 63 def load_map_array(self): 64 conf = ConfigParser.ConfigParser() 65 conf.read(‘map/AssetsDeserScene.ini‘) 66 map_data = conf.get(‘MAP_DESC‘,‘map‘) 67 self.h = conf.getint(‘MAP_DESC‘,‘height‘) 68 self.w = conf.getint(‘MAP_DESC‘,‘wide‘) 69 self.accuracy = conf.getfloat(‘MAP_DESC‘,‘accuracy‘) 70 self.nmap = numpy.array(eval(map_data)) 71 72 def convert_pos_to_arr_idx(self, v_pos): 73 #(0,0,700)->(0,0) 74 #(100,0,700)->(0,199) 75 #(100,0,600)->(199,199) 76 x = (self.h - MathTools.convert_to_half_num(v_pos.z)) * self.accuracy - 1 77 z = MathTools.convert_to_half_num(v_pos.x) * self.accuracy - 1 78 return (int(x), int(z)) 79 80 def convert_arr_idx_to_pos(self, idx): 81 return Vector3((idx[1] + 1) / self.accuracy, 0, self.h - (idx[0] + 1)/self.accuracy) 82 83 def calulate_path_array(self, start_pos, end_pos): 84 ‘‘‘ 85 通过二维数组的地图数据寻路 86 @paramIn: [Vector3] start_pos 87 @paramIn: [Vector3] end_pos 88 ‘‘‘ 89 start = self.convert_pos_to_arr_idx(start_pos) 90 end = self.convert_pos_to_arr_idx(end_pos) 91 res = MathTools.astar(self.nmap, start, end) 92 93 paths = [] 94 95 if res is False or len(res) == 0: 96 # 找不到就直接走向end 97 paths.append(end_pos) 98 return paths 99 100 # 将点路径转化为线段路径 101 res.reverse() 102 paths.append(self.convert_arr_idx_to_pos(res[0])) 103 if len(res) > 1: 104 for i in xrange(1,len(res)): 105 if MathTools.check_points_in_line(start,res[i-1],res[i]): 106 paths[-1] = self.convert_arr_idx_to_pos(res[i]) 107 else: 108 # 斜率开始不一样,则添加最新的点 109 paths.append(self.convert_arr_idx_to_pos(res[i])) 110 start = res[i-1] 111 return paths 112 113 114 115 116 def calulate_path(self, start_pos, end_pos): 117 open_list = [] 118 close_list = [] 119 start_pos_triangle = Triangle(start_pos, start_pos, start_pos) 120 end_pos_triangle = Triangle(end_pos, end_pos, end_pos) 121 122 start_triangle, start_pos = MathTools.fix_border_point_if_needed(start_pos, self.all_triangles) 123 end_triangle, start_pos = MathTools.fix_border_point_if_needed(end_pos, self.all_triangles) 124 rv_path = {} 125 if start_triangle is None: 126 #Logger().W(‘start_pos is not in the navmesh‘) 127 return None 128 if end_triangle is None: 129 #Logger().W(‘end_pos is not in the navmesh‘) 130 return None 131 132 f = {} 133 g = {} 134 h = {} 135 136 open_list.append(start_pos_triangle) 137 138 while end_pos_triangle not in open_list and len(open_list) != 0: 139 # step 1. get the min triangle in open_list 140 t = open_list[0] 141 for i in xrange(0, len(open_list)): 142 if open_list[i] not in f: 143 f[open_list[i]] = 0 144 if f[t] > f[open_list[i]]: 145 t = open_list[i] 146 147 # step 2. remove the triangle from the open_list 148 open_list.remove(t) 149 150 # step 3. append the triangle to the close_list 151 close_list.append(t) 152 153 # step 4. explore 154 155 # step 4.1. get round triangles 156 current = t 157 if current == start_pos_triangle: 158 current = start_triangle 159 round_triangles = [] 160 161 if current.a in self.point_2_triangles: 162 round_triangles = round_triangles + self.point_2_triangles[current.a] 163 if current.b in self.point_2_triangles: 164 round_triangles = round_triangles + self.point_2_triangles[current.b] 165 if current.c in self.point_2_triangles: 166 round_triangles = round_triangles + self.point_2_triangles[current.c] 167 168 # remove dulplicate triangles 169 round_triangles = sorted(set(round_triangles),key=round_triangles.index) 170 if end_triangle in round_triangles: 171 round_triangles.append(end_pos_triangle) 172 173 # step 4.2 174 for i in xrange(0, len(round_triangles)): 175 round_triangle = round_triangles[i] 176 177 if round_triangle is t: 178 continue 179 180 if round_triangle in close_list: 181 continue 182 183 if round_triangle not in open_list: 184 rv_path[round_triangle] = t 185 if t not in g: 186 g[t] = 0 187 g[round_triangle] = g[t] + MathTools.distance(t.o,round_triangle.o) 188 h[round_triangle] = MathTools.distance(round_triangle.o, end_pos) 189 open_list.append(round_triangle) 190 else: 191 if round_triangle not in g: 192 g[round_triangle] = 0 193 if round_triangle not in h: 194 h[round_triangle] = 0 195 G = g[round_triangle] 196 H = h[round_triangle] 197 F = g[round_triangle] + MathTools.distance(round_triangle.o, t.o) + MathTools.distance(round_triangle.o, end_pos) 198 if G + H > F: 199 rv_path[round_triangle] = t 200 g[round_triangle] = g[t] + MathTools.distance(t.o,round_triangle.o) 201 h[round_triangle] = MathTools.distance(round_triangle.o, end_pos) 202 open_list.remove(round_triangle) 203 204 path_list = [] 205 t = end_pos_triangle 206 while t in rv_path and rv_path[t] is not None: 207 path_list.append(t.o) 208 t = rv_path[t] 209 210 path_list.reverse() 211 212 return path_list 213 214 215 # start_pos =Vector3(315.976135254,11.0661716461,360.217041016) 216 # end_pos = Vector3(315.970001221,11.86622715,350.790008545) 217 # nav = Navmesh() 218 # nav.load_map_array() 219 # print nav.calulate_path_array(start_pos,end_pos) 220 221 # start_pos = Vector3(-2.3, 0.3, -2.8) 222 # end_pos = Vector3(3.2, 0.0, -2.8) 223 # print nav.calulate_path(start_pos, end_pos) 224 225 # (-0.3, 0.1, -3.9) 226 # (1.7, 0.1, -4.2) 227 # (3.2, 0.1, -2.8)
- 路径点返回给客户端
感受与体会:
- 当三角形非常大的时候,如下图,使用上述代码的calculate_path()方法会导致人物会出现“绕路”的情况,这是因为三角形太大导致重心已失去位置的“代表性”。如果想要使用三角网络寻路的同时并且解决这个问题,建议用recastnavigation库实现,因为这里的核心原理牵涉到很多复杂的图论问题
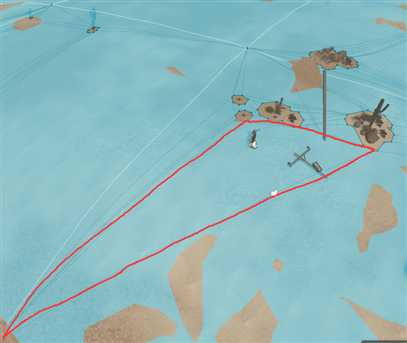
三角网络很大的情况
- 使用二维数组方案最高效且简单
- 当地图比较大时,需要对地图进行分块划分,以节省服务端内存压力,以及省去不必要的寻路计算
以上是关于服务端寻路实现总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
