微软SMB 3.0文件共享协议新特性介绍
Posted tcicy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了微软SMB 3.0文件共享协议新特性介绍相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
SMB(*nix平台和Win NT4.0又称CIFS)协议是Windows平台标准文件共享协议。Linux平台通过samba来支持。SMB最新版本v3.0,在v2.0基础上针对WAN和分布式有改进。详细内容如下:
透明故障切换:
SMB3.0提供故障切换功能,在一台服务器故障情况下,客户端请求可以平滑切换到另外一台服务器,可以实现0宕机时间,切换过程少量IO会有延迟。该功能要求SMB服务器是一个集群,客户端和服务器都采用SMB3.0,共享开启“Continuous Availability”。SMB3.0以前协议客户可以正常访问SMB3.0共享,但是不支持透明故障切换功能。
切换过程示意图如下:
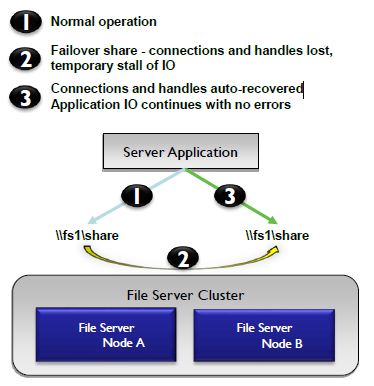
分布式支持:
SMB3.0可以将多台服务器组建成为一个集群,集群里面所有节点对客户端提供文件共享服务。在集群节点故障情况下,共享可以实现0宕机时间;并且可以快速故障恢复。
SMB2.0客户端可以正常访问SMB3.0集群,但是不支持故障切换;SMB1.0客户端不支持。
架构示意图如下:
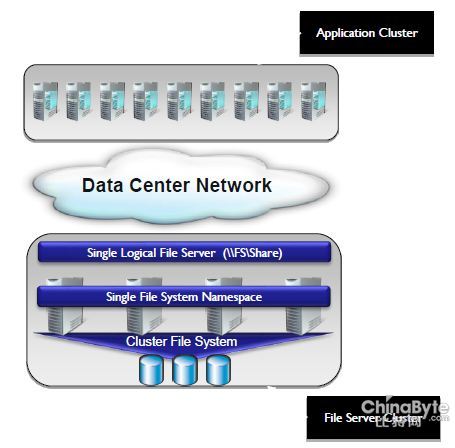
RDMA支持:
SMB3.0支持RDMA功能,客户端和服务器都需要使用支持RDMA功能适配器(iWARP、RoCE、Infiniband)。RDMA功能可以使SMB共享可以获得更高带宽和更低延迟,有效减轻CPU I/O处理负载。结合SMB多通道功能可以实现负载均衡和故障切换功能。
SMB3.0以前客户端可以访问SMB3.0基于RDMA的共享,但不支持RDMA功能。RDMA架构示意图如下:

SMB多通道(Multichannel):
如果SMB客户端或者服务器拥有两块以上网卡,SMB多通道技术可以自动侦测使用多有网络路径,可以合并使用所有网卡带宽,SMB多通道技术可以结合多核处理器的RSS(RSS可以将IO请求均衡分发到不同处理器核心)技术。SMB多通道可以利用操作系统现有网卡绑定技术,但是不依赖。如果一种一块网卡故障,SMB多通道可以自动进行故障切换。
SMB3.0以前客户端无法使用SMB多通道技术,SMB多通道架构示意图如下:

SMB目录租约:
SMB3.0可以将共享的元数据信息缓存在客户端,客户端元数据请求直接从本地读取,这样可以提高查询性能,减少客户端与服务器之间延迟。目录缓存一致性通过租约实现(类似于DNS租约管理机制)。如果目录元数据有更新,服务器主动通知客户端更新。该功能要求SMB3.0客户端:
SMB加密功能:
SMB3.0自身提供端-端数据加密功能,可以在保证数据在复杂网络环境中的安全性。加密功能不需要依赖IPSec、PKI和特定硬件,使用AES CCM 128位加密算法。
VSS服务
VSS全称volume shadowcopy service,是微软为Windows操作系统提供的一个快照机制。SMB3.0共享提供VSS支持,主要服务于备份需求。VSS的影子拷贝由SMB3.0服务器提供,在不影响现有卷访问情况下,备份客户端可以通过影子拷贝完成备份过程,应用主机不参与备份数据传输过程,可以降低应用主机的负载。SMB3.0的VSS支持,原理跟RDMA基本相似。
SMB3.0 VSS架构示意图如下:

==================================================================================
SMB(Server Message Block)通信协议是微软(Microsoft)和英特尔(Intel)在1987年制定的协议,主要是作为Microsoft网络的通讯协议。SMB 是在会话层(session layer)和表示层(presentation layer)以及小部分应用层(application layer)的协议。SMB使用了NetBios的应用程序接口 (Application Program Interface,简称API)。另外,它是一个开放性的协议,允许了协议扩展——使得它变得更大而且复杂;大约有65个最上层的作业,而每个作业都超过120个函数,甚至Windows NT也没有全部支持到,最近微软又把 SMB 改名为 CIFS(Common Internet File System),并且加入了许多新的特色。
SMB3.0新特性
-
SMB透明故障转移:让管理员可执行群集文件服务器中节点的硬件或软件维护,且不会中断将数据存储在这些文件共享上的服务器应用程序。此外,如果群集节点出现硬件或软件故障,SMB 客户端将以透明方式重新连接到其他群集节点,且不会中断将数据存储在这些文件共享上的服务器应用程序。即客户端能够持续、稳定的对远程文件服务器进行通讯,用户不会感受到单点服务器故障所带来的性能影响(不兼容SMB1.0或SMB2.x)。
-
SMB横向扩展:可构建横向扩展文件服务器(Scale-Out File Server),在使用群集共享卷(CSV)版本2时,管理员可以通过文件服务器群集中所有节点,创建可供同时访问含直接I/O的数据文件的文件共享。这可更好地利用文件服务器客户端的网络带宽和负载平衡,以及优化服务器应用程序的性能。
-
SMB多通道:如果在SMB3.0客户端及服务器之间提供多条路径,则支持网络带宽和网络容错的聚合,提升了网络可用性及文件服务器的稳定性,并让服务器应用程序可以充分利用可用网络带宽,以及在发生网络故障时快速恢复。
-
SMB直接访问(SMB over Remote Direct Memory Access[RDMA]):支持使用具有RDMA功能且可全速运行的网络适配器,其中延迟非常低且CPU利用率极少。对于Hyper-V或Microsoft SQL Server等实现工作负载,这让远程服务器如同本地存储一般。
-
用于服务器应用程序的性能计数器:全新 SMB 性能计数器提供有关吞吐量、延迟和 I/O/秒 (IOPS) 的按共享列出的详细信息,从而让管理员可以分析用于存储数据的 SMB 3.0 文件共享的性能。这些计数器专为将文件存储在远程文件共享上的服务器应用程序而设计,如 Hyper-V 和 SQL Server。
-
性能优化:SMB 3.0 客户端和 SMB 3.0 服务器均已针对小型随机读/写 I/O 优化,这种 I/O 在 SQL Server OLTP 等服务器应用程序中很常见。此外,默认情况下打开大型最大传输单元 (MTU),这将大幅提高大型连续传输性能,如 SQL Server 数据仓库、数据库备份或还原、部署或复制虚拟硬盘。
-
SMB加密:提供SMB数据的端对端加密并防止数据在未受信任网络中遭受窃听。无需新部署成本,且无需Internet协议安全性(IPsec)、专用硬件或WAN加速器。它可按共享配置,也可针对整个文件服务器配置,并且可针对数据遍历未受信任网络的各种方案启动。
-
为SMB文件共享所提供的VSS:
-
SMB目录租用:缩短分支机构的应用程序响应时间。使用目录租用后,缩短了从客户端到服务器的往返时间,因为是从保留时间较长的目录缓存中检索元数据。缓存一致性得到保持,因为在服务器上的目录信息更改时将通知客户端。适用于主文件夹(读/写,无共享)和 发布(只读,带共享)。
-
SMB PowerShell:借助于全新的SMB Windows PowerShell cmdlet,管理员可以从命令行以端对端方式管理文件服务器上的文件共享。
SMB 3.0在windows server 2012中是一个非常重要的新特性,未来我们在生产环境字中我们将看到非常多的SMB3.0的应用,它是一个低成本高性能的文件与存储解决方案。
Last September at the //Build Conference, we announced SMB 2.2, an update to our Server Message Block protocol used by default for file sharing in Windows. Since then we have actively engaged with the community through various channels and have spoken in detail about all the great work that has gone into the release and why we think this is truly a game changer. Windows Server 2012 provides a vast set of new SMB features with an updated SMB protocol that greatly enhance the reliability, availability, manageability, and performance of file servers.
Looking back at the amount of changes that have gone into this release – the lines of code written, array of features introduced, new scenarios we have enabled, work we have done with our partners, a minor revision doesn’t do justice the work that has gone in. So moving on, SMB 2.2 is SMB 3.0!
Regular followers of this blog have seen detailed posts on various SMB improvements over the last few months. To summarize, the following are some of the key new functionalities available with Windows Server 2012 SMB 3.0:
- SMB for Server Applications – Many of the new SMB features are specifically designed for server applications that store the data on file shares—for example, database applications such as Microsoft SQL Server or virtualization software such as Hyper-V. This allows applications to take advantage of advances in storage management, performance, reliability, and cost efficiency that come with SMB to deliver an application storage solution that rivals traditional Fibre Channel storage solutions in features and capabilities, but remains easier to provision and less expensive to implement.
- Active file sharing with SMB Scale Out – Enables customers to scale share bandwidth by adding cluster nodes, as the maximum share bandwidth is the aggregate bandwidth of all file server nodes and not restricted to the bandwidth of a single cluster node as in previous versions. Scale-out file shares also makes it much easier to manage a file server cluster, as it is no longer necessary to create multiple clustered file servers, each with separate cluster disks, to take advantage of all nodes in a cluster. Further, the administrator can transparently redirect SMB client connections to a different file server cluster node to better balance the cluster load.
- Scalable, fast, and efficient storage access with SMB Direct – SMB Direct (SMB over Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA)) is a new transport protocol for SMB in Windows Server 2012. It enables direct memory-to-memory data transfers between servers, with minimal CPU utilization and low latency, using standard RDMA-capable network adapters (iWARP, InfiniBand, and RoCE). Any application which accesses files over SMB can transparently benefit from SMB Direct. Minimizing the CPU cost of file I/O means application servers can handle larger compute workloads with the saved CPU cycles (for example, Hyper-V can host more virtual machines).
- Fast data transfers and network fault tolerance with SMB Multichannel – Given that customers can now store server application data on remote SMB file shares, SMB was enhanced to improve network performance and reliability. SMB Multichannel takes advantage of multiple network interfaces to provide both high performance through bandwidth aggregation, and network fault tolerance through the use of multiple network paths to data on an SMB share.
- Transparent Failover and node fault tolerance with SMB – Supporting business critical server application workloads requires the connection to the storage back end to be continuously available. The new SMB server and client cooperate to make failover of file server cluster nodes transparent to applications, for all file operations, and for both planned cluster resource moves and unplanned node failures.
- VSS for SMB file shares – VSS for SMB file shares extends the Windows Volume ShadowCopy Service infrastructure to enable application-consistent shadow copies of server application data stored on SMB file shares, for backup and restore purposes. In addition, VSS for SMB file shares enables backup applications to read the backup data directly from a shadow copy file share rather than involving the application server in the data transfer. Because this feature leverages the existing VSS infrastructure, it is easy to integrate with existing VSS-aware backup software and VSS-aware applications like Hyper-V.
- Secure data transfer with SMB encryption – SMB Encryption protects data in-flight from eavesdropping and tampering attacks. Deployment is as simple as checking a box, with no additional setup requirements. This becomes more critical as mobile workers access data in centralized remote locations from unsecured networks. SMB Encryption is beneficial even within a secured corporate network if the data being accessed is sensitive..
- Faster access to documents over high latency networks with SMB Directory Leasing – SMB Directory Leasing reduces the latency seen by branch office users accessing files over high latency WAN networks. This is accomplished by enabling the client to cache directory and file meta-data in a consistent manner for longer periods, thereby reducing the associated round-trips to fetch the metadata from the server. This results in faster application response times for branch office users
- SMB Ecosystem – A critical aspect of Windows Server 2012 development is the partnership we have established with vendors to ship SMB 3.0 capable systems. We have been working closely with several server vendors and open source partners over the past year, by proactively providing extensive protocol documentation and numerous open “plugfest” events provide opportunities for test and feedback. Finally, and most importantly, the SMB ecosystem now reaches all the way to key server applications such as SQL Server and Hyper-V to ensure that SMB 3.0 capabilities are fully leveraged all the way through the stack, and across the multivendor network.
With so many new features, SMB offers a richer set of capabilities that, when combined, provide organizations with a robust high performance storage alternative to traditional Fibre Channel storage solutions at a much more affordable cost point from both an acquisition and operational perspective.
以上是关于微软SMB 3.0文件共享协议新特性介绍的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章