面试-HashMap原理与源码分析(JDK1.8)
Posted wangymd
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了面试-HashMap原理与源码分析(JDK1.8)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、HashMap介绍
HashMap为Map接口的一个实现类,实现了Map所有的操作。
HashMap除了允许key、value为null值和非线程安全外,其他实现几乎和HashTable一致。
HashMap使用散列存储的方式保存kay-value键值对,因此其不支持数据保存的顺序。如果想要使用有序容器可以使用LinkedHashMap。
在性能上当HashMap中保存的key的哈希算法能够均匀的分布在每个bucket中的时候,HashMap在基本的get和set操作的的时间复杂度都是O(n)。
在遍历HashMap的时候,其遍历节点的个数为bucket(位桶)的个数+HashMap中保存的节点个数。因此当遍历操作比较频繁的时候需要注意HashMap的初始化容量不应该太大。 这一点其实比较好理解:当保存的节点个数一致的时候,bucket越少,遍历次数越少。
另外HashMap在resize的时候会有很大的性能消耗,因此当需要在HashMap中保存大量数据的时候,传入适当的默认容量以避免resize,可以很大的提高性能。 具体的resize操作请参考下面对此方法的分析。
HashMap采用位桶+链表+红黑树(自平衡二叉查找树)实现,当链表长度超过阈值(8)时,将链表转换为红黑树,这样大大减少了查找时间.
2、默认设置
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; //默认初始化容量 static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; //最大容量 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; //默认加载因子 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; //当put一个元素到某个位桶,如果其链表长度达到8时将链表转换为红黑树 static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; // static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; // transient Node<K,V>[] table; //存储元素数组 transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; // transient int size; //元素个数 transient int modCount; // int threshold; //扩容阈值 final float loadFactor; //加载因子
3、构造方法
/** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity * (16) and the default load factor (0.75). */ public HashMap() { //无参数构造方法;默认初始容量16;加载因子0.75f; this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted//loadFactor = 0.75f:加载因子。其他成员默认。 }
/** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial * capacity and the default load factor (0.75). * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative. */ public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { //初始容量initialCapacity;默认加载因子0.75f this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); }
/** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial * capacity and load factor. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity * @param loadFactor the load factor * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative * or the load factor is nonpositive */ public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { //初始容量initialCapacity;初始加载因子:loadFactor if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity); }
/** * Returns a power of two size for the given target capacity.
* 计算初始化容量, */ static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) { int n = cap - 1; n |= n >>> 1; //n右移1;按位或赋值给n n |= n >>> 2; //n右移2;按位或赋值给n n |= n >>> 4; //n右移4;按位或赋值给n n |= n >>> 8; //n右移8;按位或赋值给n n |= n >>> 16; //n右移16;按位或赋值给n return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1; }
4、数据存与取
存数据:
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods. * * @param hash hash for key * @param key the key * @param value the value to put * @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don‘t change existing value * @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode. * @return previous value, or null if none */ final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) //判断添加第一个元素 n = (tab = resize()).length; //添加一地个元素 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) //判断table的在(n-1)&hash索引值是否空,如果空创建一个节点插入次位置 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); //创建新的节点 else { //发生冲突时处理 Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //判断第一个Node是否是要找的值 e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) //红黑树处理 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); // else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { //累积hash冲突数量 if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); // if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); //treeifyBin首先判断HashMap长度,如果小于64进行resize扩容,如果大于64存储结构转换为红黑树 break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //如果key已经存在,停止遍历 break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key //查到key已存在,更新对应value值 V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; //节点赋值新值 afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; //返回旧值 } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) //判断当前元素容量是否大于阈值,如果是需要进行扩容 resize(); //扩容 afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
/** * Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in * accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold. * Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the * elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move * with a power of two offset in the new table. * * @return the table */ final Node<K,V>[] resize() { //扩容 Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; int oldThr = threshold; int newCap, newThr = 0; if (oldCap > 0) { if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { //容量大于等于最大容量 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; //阈值等于int最大值 return oldTab; } else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold //容量扩容一倍 } else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold //使用阈值初始化容量 newCap = oldThr; else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; //初始化默认容量:16 newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); //初始化默认阈值:加载因子(0.75f) * 初始化容量(16) } if (newThr == 0) { //如果阈值=0,初始化大小 float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; //创建新的节点数组,数组长度为扩容后的长度 table = newTab; if (oldTab != null) { for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { //根据旧数组长度,进行遍历 Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { oldTab[j] = null; if (e.next == null) newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; //将就数组元素赋值给新数组 else if (e instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); else { // preserve order // Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; Node<K,V> next; do { //遍历链表 next = e.next; if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { if (loTail == null) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e; loTail = e; } else { if (hiTail == null) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null); if (loTail != null) { // loTail.next = null; newTab[j] = loHead; } if (hiTail != null) { // hiTail.next = null; newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; } } } } } return newTab; }
/**
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { //链表数据结构
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
//判断两个Node节点是否相同
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
/** * Entry for Tree bins. Extends LinkedHashMap.Entry (which in turn * extends Node) so can be used as extension of either regular or * linked node. */ static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> { TreeNode<K,V> parent; //父节点 TreeNode<K,V> left; //左子树 TreeNode<K,V> right; //右子树 TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion boolean red; //颜色属性 TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, val, next); } /** * Returns root of tree containing this node.
* 返回根节点 */ final TreeNode<K,V> root() { for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) { if ((p = r.parent) == null) return r; r = p; } } 。。。省略。。。 }
取数据:
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return first; if ((e = first.next) != null) { if (first instanceof TreeNode) return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); //红黑树查询结果 do { //遍历链表查询结果 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } return null; }
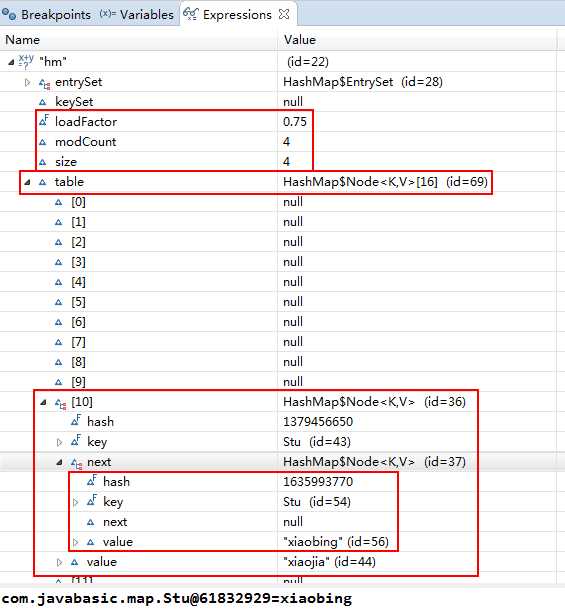
5、demo程序,查看数据结构(散列数组+链表)
package com.javabasic.map; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Set; /** * 源码分析 * * * 允许使用null键和null值; * 线程不同步,效率高; * * * @author wangymd * */ public class HashMapTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Stu stu1 = new Stu(1,"xiaojia"); Stu stu2 = new Stu(1,"xiaoyi"); Stu stu3 = new Stu(1,"xiaobing"); Stu stu4 = new Stu(1,"xiaoding"); Map<Stu, String> hm = new HashMap<Stu, String>(); hm.put(stu1, "xiaojia"); hm.put(stu2, "xiaoyi"); hm.put(stu3, "xiaobing"); hm.put(stu4, "xiaoding"); Set<Entry<Stu, String>> entrySet = hm.entrySet(); //断点,查看数据结构;如下图 for (Entry<Stu, String> entry : entrySet) { Stu key = entry.getKey(); String value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key.getName() + "----" + value); } } } class Stu{ Integer id; String name; public Stu() {} public Stu(Integer id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
以上是关于面试-HashMap原理与源码分析(JDK1.8)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章