Java中的异常处理try catch(第八周课堂示例总结)
Posted dongao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java中的异常处理try catch(第八周课堂示例总结)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
异常处理

使用Java异常处理机制:
把可能会发生错误的代码放进try语句块中。
当程序检测到出现了一个错误时会抛出一个异常对象。
异常处理代码会捕获并处理这个错误。
catch语句块中的代码用于处理错误。
当异常发生时,程序控制流程由try语句块跳转到catch语句块。
不管是否有异常发生,finally语句块中的语句始终保证被执行。
如果没有提供合适的异常处理代码,JVM将会结束掉整个应用程序。

异常分类:
Throwable类有两个直接子类:
Exception:出现的问题是可以被捕获的;
Error:系统错误,通常由JVM处理。
可捕获的异常又可以分为两类:
(1)Check异常:直接派生自Exception的异常类,必须被捕获或再次声明抛出
(2)Runtime异常:派生自RuntimeException的异常类。使用throw语句可以随时抛出这种异常对象: throw new ArithmeticException(…);
JDK1.4 以上提供了assert语句,允许程序在运行期间判断某个条件是否满足,不满足时,抛出AssertionError,例如:

异常的“多态”特性
可以有多个catch语句块,每个代码块捕获一种异常。在某个try块后有两个不同的catch 块捕获两个相同类型的异常是语法错误。
使用catch语句,只能捕获Exception类及其子类的对象。因此,一个捕获Exception对象的catch语句块可以捕获所有“可捕获”的异常。
将catch(Exception e)放在别的catch块前面会使这些catch块都不执行,因为Java不会编译这些catch块。
“finally”的功用
资源泄露:当一个资源不再被某应用程序使用,但此程序并未向系统声明不再使用此资源时发生这种情况
finally语句块主要用于解决资源泄露问题,它位于catch语句块之后,JVM保证它们一定执行。
注意:finally语句块中也可能发生异常,如果这种情况发生,先前的异常被放弃。
动手动脑:多层的异常捕获
比较两个代码的区别:
CatchWho1.java
1 public class CatchWho { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 try { 4 try { 5 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); 6 } 7 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { 8 System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); 9 } 10 throw new ArithmeticException(); 11 } 12 catch(ArithmeticException e) { 13 System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); 14 } 15 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { 16 System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); 17 } 18 } 19 }
结果:
catchwho2.java
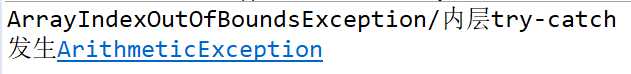
1 public class CatchWho2 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 try { 4 try { 5 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); 6 } 7 catch(ArithmeticException e) { 8 System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); 9 } 10 throw new ArithmeticException(); 11 } 12 catch(ArithmeticException e) { 13 System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); 14 } 15 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { 16 System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); 17 } 18 } 19 }
结果:

分析:catchwho1按照内外层的try catch代码块一步一步执行
catchwho2结果的原因是内存try里的异常并没有被catch(ArithmeticException e)捕获到,故该字段异常,不执行此try catch块下的其他内容,而是此异常的ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException()对象被外层的catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)捕获,打印出相应结果。
辨析:finally语句块一定会执行吗?
1 public class SystemExitAndFinally { 2 public static void main(String[] args) 3 { 4 try{ 5 System.out.println("in main"); 6 throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main"); 7 //System.exit(0); 8 } 9 catch(Exception e){ 10 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); 11 System.exit(0); 12 } 13 finally{ 14 System.out.println("in finally"); 15 } 16 } 17 }
结果:

结论:在exit(0)下, finally里的语句块不会执行。
特别注意: 当有多层嵌套的finally时,异常在不同的层次抛出 ,在不同的位置抛出,可能会导致不同的finally语句块执行顺序。
如何跟踪异常的传播路径?
当程序中出现异常时,JVM会依据方法调用顺序依次查找有关的错误处理程序。
可使用printStackTrace 和 getMessage方法了解异常发生的情况: printStackTrace:打印方法调用堆栈。
每个Throwable类的对象都有一个getMessage方法,它返回一个字串,这个字串是在Exception构造函数中传入的,通常让这一字串包含特定异常的相关信息。
1 // UsingExceptions.java 2 // Demonstrating the getMessage and printStackTrace 3 // methods inherited into all exception classes. 4 public class PrintExceptionStack { 5 public static void main( String args[] ){ 6 try { 7 method1(); 8 } 9 catch ( Exception e ) { 10 System.err.println( e.getMessage() + " " ); 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } 13 } 14 public static void method1() throws Exception { 15 method2(); 16 } 17 public static void method2() throws Exception{ 18 method3(); 19 } 20 public static void method3() throws Exception{ 21 throw new Exception( "Exception thrown in method3" ); 22 } 23 }
输出结果:

受控与不受控的异常
throws语句:throws语句表明某方法中可能出现某种(或多种)异常,但它自己不能处理这些异常,而需要由调用者来处理。 当一个方法包含throws子句时,需要在调用此方法的代码中使用try/catch/finally进行捕获,或者是重新对其进行声明,否则编译时报错。
throws语句中声明的异常称为受控(checked)的异常,通常直接派生自Exception类。
RuntimeException(其基类为Exception) 和Error(基类为Throwable)称为非受控的异常。这种异常不用在throws语句中声明。
1 import java.io.*; 2 3 public class CheckedExceptionDemo { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 try { 6 BufferedReader buf = new BufferedReader( 7 new InputStreamReader(System.in)); //抛出受控的异常 8 System.out.print("请输入整数: "); 9 int input = Integer.parseInt(buf.readLine()); //有可能引发运行时异常 10 System.out.println("input x 10 = " + (input*10)); 11 } 12 //以下异常处理语句块是必须的,否则无法通过编译 13 catch(IOException e) { 14 System.out.println("I/O错误"); 15 } 16 //以下异常处理语句块可以省略,不影响编译,但在运行时出错 17 catch(NumberFormatException e) { 18 System.out.println("输入必须为整数"); 19 } 20 } 21 }
一个方法可以声明抛出多个异常: int g(float h) throws OneException,TwoException { …… }
1 import java.io.*; 2 public class ThrowMultiExceptionsDemo { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 try { 5 throwsTest(); 6 } 7 catch(IOException e) { 8 System.out.println("捕捉异常"); 9 } 10 } 11 private static void throwsTest() throws ArithmeticException,IOException { 12 System.out.println("这只是一个测试"); 13 // 程序处理过程假设发生异常 14 throw new IOException(); 15 //throw new ArithmeticException(); 16 } 17 }

在有继承关系中,一个子类的throws子句抛出的异常,不能是其基类同名方法抛出的异常对象的父类。
自定义异常与异常处理链
介绍一种被广泛使用的异常处理方法——通过自定义异常类捕获并处理业务逻辑错误 。

1 class MyException extends Exception{ 2 public MyException(String Message) { 3 super(Message); 4 } 5 public MyException(String message, Throwable cause) { 6 super(message, cause); 7 } 8 public MyException(Throwable cause) { 9 super(cause); 10 } 11 } 12 public class ExceptionLinkInRealWorld { 13 public static void main(String args[]){ 14 try { 15 throwExceptionMethod(); //有可能抛出异常的方法调用 16 } 17 catch ( MyException e ){ 18 System.err.println( e.getMessage() +"--1"); 19 System.err.println(e.getCause().getMessage()+"--2"); 20 } 21 catch ( Exception e ){ 22 System.err.println("Exception handled in main--3" ); 23 } 24 doesNotThrowException(); //不抛出异常的方法调用 25 } 26 public static void throwExceptionMethod() throws MyException{ 27 try { 28 System.out.println( "Method throwException--4" ); 29 throw new Exception("系统运行时引发的特定的异--W"); // 产生了一个特定的异常 30 } 31 catch( Exception e ){ 32 System.err.println("Exception handled in method throwException--5" ); 33 //转换为一个自定义异常,再抛出 34 throw new MyException("在方法执行时出现异常-W",e); 35 } 36 finally { 37 System.err.println("Finally executed in throwException--6" ); 38 } 39 // any code here would not be reached 40 } 41 public static void doesNotThrowException() 42 { 43 try { 44 System.out.println( "Method doesNotThrowException--7" ); 45 } 46 catch( Exception e ){ 47 System.err.println( e.toString() ); 48 } 49 finally { 50 System.err.println("Finally executed in doesNotThrowException--8" ); 51 } 52 System.out.println("End of method doesNotThrowException--9" ); 53 } 54 } 55 56 //45
结果:

在实际开发中,可以参照ExceptionLinkInRealWorld.java 示例的做法,定义一些与业务逻辑相关的自定义异常类,供上层代码进行捕获,从而能更精确地反映系统真实运行情况并及时进行处理。
关于开发中异常处理的建议
在中间层组件中抛出异常,在界面层组件中捕获异常,在底层组件中捕获JVM抛出的“只有程序员能看懂的”异常,转换为中间层的业务逻辑异常,再由界面层捕获以提供有意义的信息。
自身能够处理的异常,不要再向外界抛出。
尽可能地在靠近异常发生的地方捕获并处理异常。
尽可能地捕获最具体的异常类型,不要在中间层用 catch(Exception)“吃掉”所有异常。
在开发阶段捕获并显示所有异常信息,发布阶段要移除部分代码,以避免“过于专业”的异常信息困扰用户,特别地,系统发布之后,不要将服务端异常的详细信息发给客户端,以免被黑客利用。
以上是关于Java中的异常处理try catch(第八周课堂示例总结)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
