Python开发第二篇:Python基本数据类型
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python开发第二篇:Python基本数据类型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
运算符
1、算数运算:
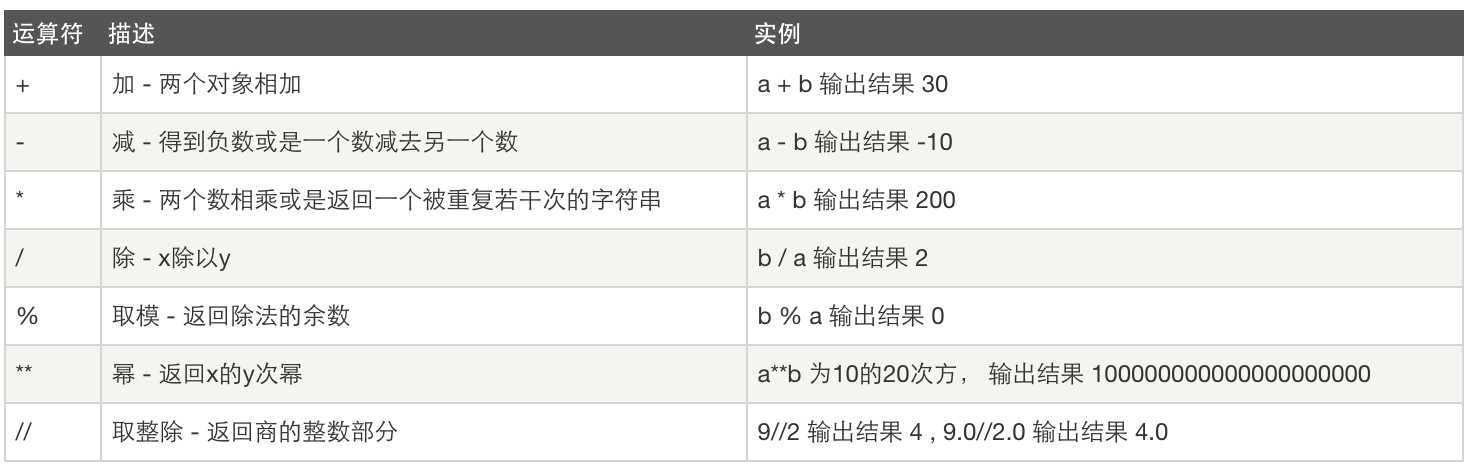
2、比较运算:
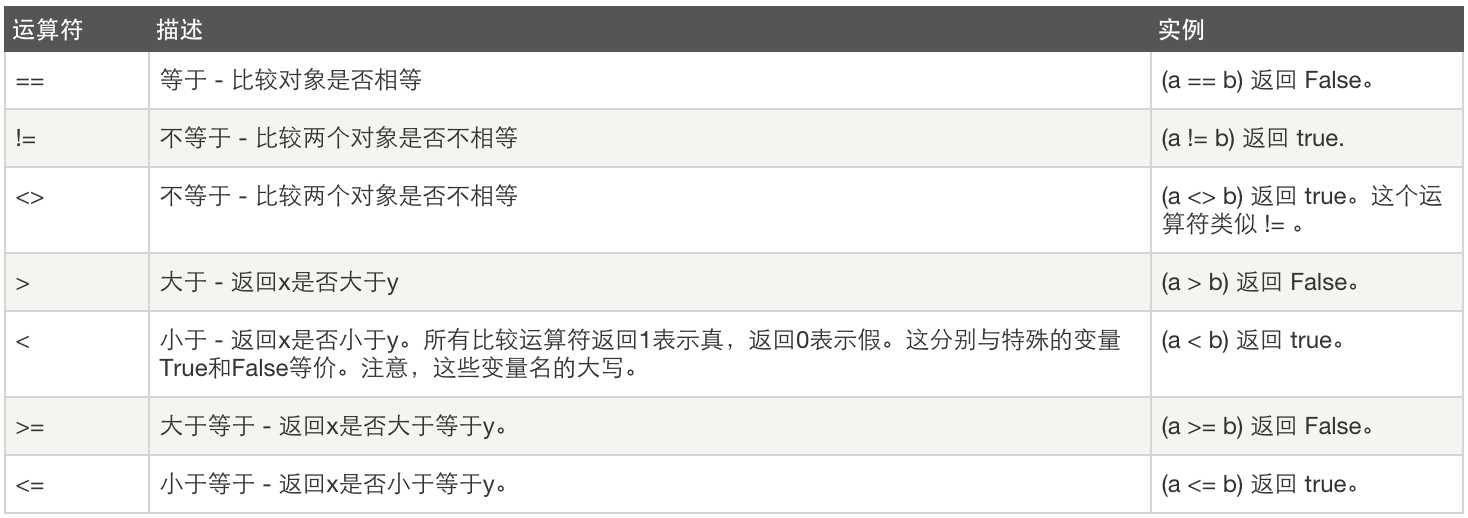
3、赋值运算:
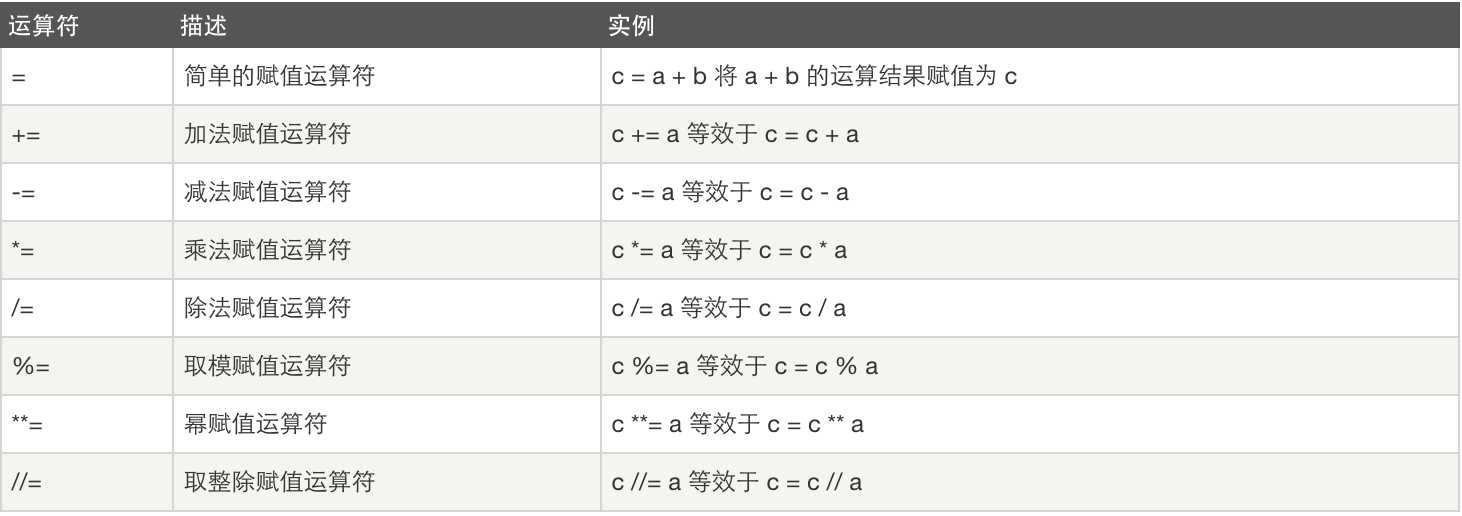
4、逻辑运算:
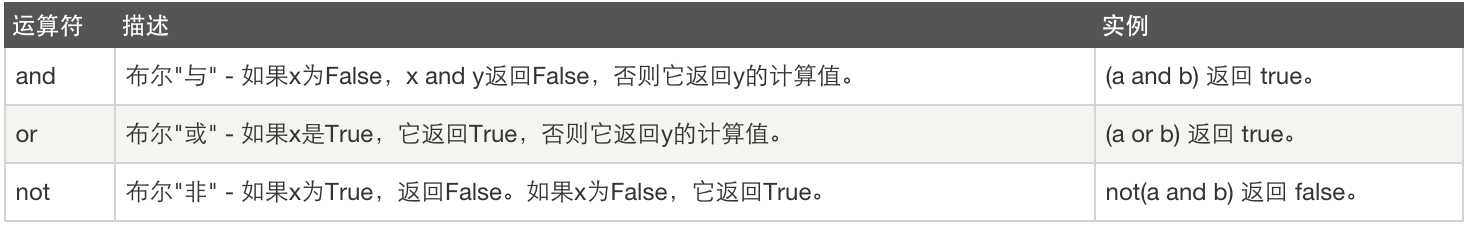
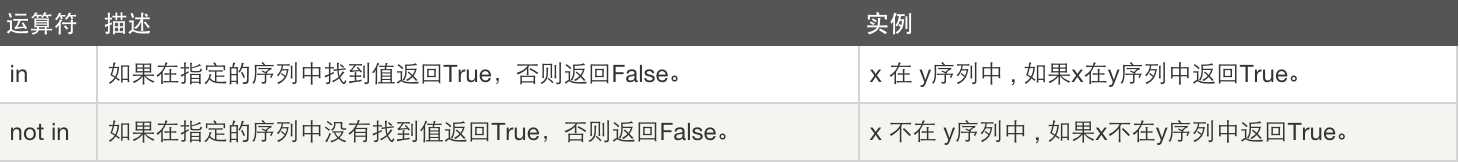
5、成员运算:
基本数据类型
数字:
定义:a =1
特性:
只能存放一个值
一旦定义,不可改变
直接访问
分类:
整形、长整型、布尔、浮点、复数
整型:
Python的整型相当于C中的long型,Python中的整数可以用十进制,八进制,十六进制表示。
>>> 10 10 --------->默认十进制 >>> oct(10) ‘012‘ --------->八进制表示整数时,数值前面要加上一个前缀“0” >>> hex(10) ‘0xa‘ --------->十六进制表示整数时,数字前面要加上前缀0X或0x
python2.*与python3.*关于整型的区别
python2.*
在32位机器上,整数的位数为32位,取值范围为-2**31~2**31-1,即-2147483648~2147483647
在64位系统上,整数的位数为64位,取值范围为-2**63~2**63-1,即-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807
python3.*整形长度无限制
整型工厂函数int()

class int(object): """ int(x=0) -> int or long int(x, base=10) -> int or long Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero. If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead. If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The literal can be preceded by ‘+‘ or ‘-‘ and be surrounded by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. >>> int(‘0b100‘, base=0) """ def bit_length(self): """ 返回表示该数字的时占用的最少位数 """ """ int.bit_length() -> int Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary. >>> bin(37) ‘0b100101‘ >>> (37).bit_length() """ return 0 def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 返回该复数的共轭复数 """ """ Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int. """ pass def __abs__(self): """ 返回绝对值 """ """ x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """ pass def __add__(self, y): """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ pass def __and__(self, y): """ x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """ pass def __cmp__(self, y): """ 比较两个数大小 """ """ x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """ pass def __coerce__(self, y): """ 强制生成一个元组 """ """ x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """ pass def __divmod__(self, y): """ 相除,得到商和余数组成的元组 """ """ x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """ pass def __div__(self, y): """ x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """ pass def __float__(self): """ 转换为浮点类型 """ """ x.__float__() <==> float(x) """ pass def __floordiv__(self, y): """ x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """ pass def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def __getattribute__(self, name): """ x.__getattribute__(‘name‘) <==> x.name """ pass def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 内部调用 __new__方法或创建对象时传入参数使用 """ pass def __hash__(self): """如果对象object为哈希表类型,返回对象object的哈希值。哈希值为整数。在字典查找中,哈希值用于快速比较字典的键。两个数值如果相等,则哈希值也相等。""" """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """ pass def __hex__(self): """ 返回当前数的 十六进制 表示 """ """ x.__hex__() <==> hex(x) """ pass def __index__(self): """ 用于切片,数字无意义 """ """ x[y:z] <==> x[y.__index__():z.__index__()] """ pass def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__ """ 构造方法,执行 x = 123 或 x = int(10) 时,自动调用,暂时忽略 """ """ int(x=0) -> int or long int(x, base=10) -> int or long Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero. If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead. If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The literal can be preceded by ‘+‘ or ‘-‘ and be surrounded by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. >>> int(‘0b100‘, base=0) # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __int__(self): """ 转换为整数 """ """ x.__int__() <==> int(x) """ pass def __invert__(self): """ x.__invert__() <==> ~x """ pass def __long__(self): """ 转换为长整数 """ """ x.__long__() <==> long(x) """ pass def __lshift__(self, y): """ x.__lshift__(y) <==> x<<y """ pass def __mod__(self, y): """ x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """ pass def __mul__(self, y): """ x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """ pass def __neg__(self): """ x.__neg__() <==> -x """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(S, *more): """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ pass def __nonzero__(self): """ x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """ pass def __oct__(self): """ 返回改值的 八进制 表示 """ """ x.__oct__() <==> oct(x) """ pass def __or__(self, y): """ x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """ pass def __pos__(self): """ x.__pos__() <==> +x """ pass def __pow__(self, y, z=None): """ 幂,次方 """ """ x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ pass def __radd__(self, y): """ x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """ pass def __rand__(self, y): """ x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """ pass def __rdivmod__(self, y): """ x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """ pass def __rdiv__(self, y): """ x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """ pass def __repr__(self): """转化为解释器可读取的形式 """ """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass def __str__(self): """转换为人阅读的形式,如果没有适于人阅读的解释形式的话,则返回解释器课阅读的形式""" """ x.__str__() <==> str(x) """ pass def __rfloordiv__(self, y): """ x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """ pass def __rlshift__(self, y): """ x.__rlshift__(y) <==> y<<x """ pass def __rmod__(self, y): """ x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """ pass def __rmul__(self, y): """ x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """ pass def __ror__(self, y): """ x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """ pass def __rpow__(self, x, z=None): """ y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ pass def __rrshift__(self, y): """ x.__rrshift__(y) <==> y>>x """ pass def __rshift__(self, y): """ x.__rshift__(y) <==> x>>y """ pass def __rsub__(self, y): """ x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """ pass def __rtruediv__(self, y): """ x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """ pass def __rxor__(self, y): """ x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """ pass def __sub__(self, y): """ x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """ pass def __truediv__(self, y): """ x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """ pass def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): """ 返回数值被截取为整形的值,在整形中无意义 """ pass def __xor__(self, y): """ x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """ pass denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """ 分母 = 1 """ """the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms""" imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """ 虚数,无意义 """ """the imaginary part of a complex number""" numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """ 分子 = 数字大小 """ """the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms""" real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """ 实属,无意义 """ """the real part of a complex number""" int python2.7

class int(object): """ int(x=0) -> integer int(x, base=10) -> integer Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point numbers, this truncates towards zero. If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string, bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the given base. The literal can be preceded by ‘+‘ or ‘-‘ and be surrounded by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. >>> int(‘0b100‘, base=0) """ def bit_length(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 返回表示该数字的时占用的最少位数 """ """ int.bit_length() -> int Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary. >>> bin(37) ‘0b100101‘ >>> (37).bit_length() """ return 0 def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 返回该复数的共轭复数 """ """ Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int. """ pass @classmethod # known case def from_bytes(cls, bytes, byteorder, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown; NOTE: unreliably restored from __doc__ """ int.from_bytes(bytes, byteorder, *, signed=False) -> int Return the integer represented by the given array of bytes. The bytes argument must be a bytes-like object (e.g. bytes or bytearray). The byteorder argument determines the byte order used to represent the integer. If byteorder is ‘big‘, the most significant byte is at the beginning of the byte array. If byteorder is ‘little‘, the most significant byte is at the end of the byte array. To request the native byte order of the host system, use `sys.byteorder‘ as the byte order value. The signed keyword-only argument indicates whether two‘s complement is used to represent the integer. """ pass def to_bytes(self, length, byteorder, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown; NOTE: unreliably restored from __doc__ """ int.to_bytes(length, byteorder, *, signed=False) -> bytes Return an array of bytes representing an integer. The integer is represented using length bytes. An OverflowError is raised if the integer is not representable with the given number of bytes. The byteorder argument determines the byte order used to represent the integer. If byteorder is ‘big‘, the most significant byte is at the beginning of the byte array. If byteorder is ‘little‘, the most significant byte is at the end of the byte array. To request the native byte order of the host system, use `sys.byteorder‘ as the byte order value. The signed keyword-only argument determines whether two‘s complement is used to represent the integer. If signed is False and a negative integer is given, an OverflowError is raised. """ pass def __abs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ abs(self) """ pass def __add__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self+value. """ pass def __and__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self&value. """ pass def __bool__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ self != 0 """ pass def __ceil__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 整数返回自己 如果是小数 math.ceil(3.1)返回4 """ """ Ceiling of an Integral returns itself. """ pass def __divmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 相除,得到商和余数组成的元组 """ """ Return divmod(self, value). """ pass def __eq__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self==value. """ pass def __float__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ float(self) """ pass def __floordiv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self//value. """ pass def __floor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Flooring an Integral returns itself. """ pass def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return getattr(self, name). """ pass def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def __ge__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self>=value. """ pass def __gt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self>value. """ pass def __hash__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return hash(self). """ pass def __index__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 用于切片,数字无意义 """ """ Return self converted to an integer, if self is suitable for use as an index into a list. """ pass def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__ """ 构造方法,执行 x = 123 或 x = int(10) 时,自动调用,暂时忽略 """ """ int(x=0) -> integer int(x, base=10) -> integer Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point numbers, this truncates towards zero. If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string, bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the given base. The literal can be preceded by ‘+‘ or ‘-‘ and be surrounded by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. >>> int(‘0b100‘, base=0) # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __int__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ int(self) """ pass def __invert__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ ~self """ pass def __le__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self<=value. """ pass def __lshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self<<value. """ pass def __lt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self<value. """ pass def __mod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self%value. """ pass def __mul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self*value. """ pass def __neg__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ -self """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """ pass def __ne__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self!=value. """ pass def __or__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self|value. """ pass def __pos__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ +self """ pass def __pow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return pow(self, value, mod). """ pass def __radd__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value+self. """ pass def __rand__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value&self. """ pass def __rdivmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return divmod(value, self). """ pass def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return repr(self). """ pass def __rfloordiv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value//self. """ pass def __rlshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value<<self. """ pass def __rmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value%self. """ pass def __rmul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value*self. """ pass def __ror__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value|self. """ pass def __round__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Rounding an Integral returns itself. Rounding with an ndigits argument also returns an integer. """ pass def __rpow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return pow(value, self, mod). """ pass def __rrshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value>>self. """ pass def __rshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self>>value. """ pass def __rsub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value-self. """ pass def __rtruediv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value/self. """ pass def __rxor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value^self. """ pass def __sizeof__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Returns size in memory, in bytes """ pass def __str__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return str(self). """ pass def __sub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self-value. """ pass def __truediv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self/value. """ pass def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Truncating an Integral returns itself. """ pass def __xor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self^value. """ pass denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms""" imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """the imaginary part of a complex number""" numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms""" real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """the real part of a complex number""" python3.5
长整型long:
python3.*
长整型,整型统一归为整型

python3.5 >>> a=9223372036854775807 >>> a 9223372036854775807 >>> a+=1 >>> a 9223372036854775808
布尔bool:
真True 或 假False | 1 或 0
浮点数float:
Python的浮点数就是数学中的小数,类似C语言中的double。
在运算中,整数与浮点数运算的结果是浮点数
浮点数也就是小数,之所以称为浮点数,是因为按照科学记数法表示时,
一个浮点数的小数点位置是可变的,比如,1.23*109和12.3*108是相等的。
浮点数可以用数学写法,如1.23,3.14,-9.01,等等。但是对于很大或很小的浮点数,
就必须用科学计数法表示,把10用e替代,1.23*109就是1.23e9,或者12.3e8,0.000012
可以写成1.2e-5,等等。
整数和浮点数在计算机内部存储的方式是不同的,整数运算永远是精确的而浮点数运算则可能会有
四舍五入的误差。
复数complex:
复数由实数部分和虚数部分组成,一般形式为x+yj,其中的x是复数的实数部分,y是复数的虚数部分,这里的x和y都是实数。
注意,虚数部分的字母j大小写都可以,
>>> 1.3 + 2.5j == 1.3 + 2.5J
True
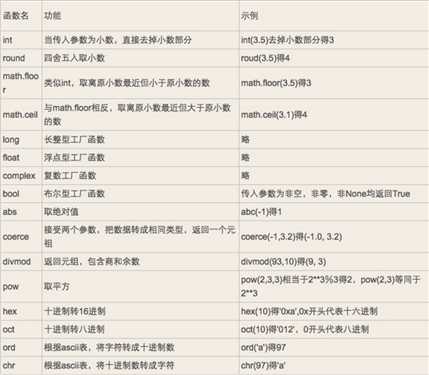
数字相关内建函数
以上是关于Python开发第二篇:Python基本数据类型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
