sql 基础详细(持续更新)
Posted 佟大帅
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了sql 基础详细(持续更新)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
 sql 基础详细(持续更新)
sql 基础详细(持续更新)
SQL基础
一、查询基础语句
查询语句的语法格式
Select * from 表名 where 条件;
具体演示
//创建一个学生成绩表
create table Student_grade(
St_Num int,
St_Class varchar(200),
St_Name varchar(64),
St_Grade float
);
//添加数据
insert into Student_grade values(1,1.3,\'tom\',85);
insert into Student_grade values(2,1.2,\'bob\',64);
insert into Student_grade values(3,1.1,\'tds\',59);
insert into Student_grade values(4,1.1,\'tnw\',90);
insert into Student_grade values(5,1.3,\'rose\',89);
insert into Student_grade values(6,1.2,\'nic\',42);
查询表中数据
select * from Student_grade;
| St_Num | St_Class | St_Name | St_Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.3 | tom | 85 |
| 2 | 1.2 | bob | 64 |
| 3 | 1.1 | tds | 59 |
| 4 | 1.1 | tnw | 90 |
| 5 | 1.3 | rose | 89 |
| 6 | 1.2 | nic | 42 |
常用的比较函数
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| > | 大于 |
| < | 小于 |
| = | 等于 |
| >= | 大于等于 |
| <= | 小于等于 |
| !=/<> | 不等于 |
where后加条件对表中的书局进行筛选。
//找到不及格的同学
select * from Student_Grade where St_Grade<60;
//找到成绩大于80的同学
select * from Student_Grade where St_Grade>80;
//找到班级为\'1.2\'的同学
select * from Student_Grade where St_Class=1.2;
//找到班级是1.1或1.2且成绩在60和90之间的同学
select *from Student_Grade where (St_Class=\'1.1\' or St_Class = \'1.2\') and St_Grade between 60 and 90;
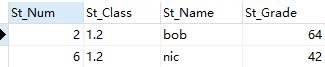
逻辑函数
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| All | 所有运算符用于比较的值到另一个值组中的所有值 |
| AND | AND运算符允许多个条件的存在,在一个SQL语句中的WHERE子句 |
| ANY | ANY运算符用于比较的值在列表中根据任何适用的条件 |
| BETWEEN | BETWEEN 运算符用于搜索一组值的范围内的值,给定的最小值和最大值 |
| IN | IN操作符用来比较的文字值已指定一个值的列表 |
| LIKE | LIKE运算符用于比较相似的值,使用通配符的值 |
| NOT | NOT运算符的含义相反的逻辑运算符,它被使用如 NOT EXISTS, NOT BETWEEN, NOT IN 等,这是一个相反的运算符 |
| OR | 使用OR运算符结合SQL语句的WHERE子句中的多个条件 |
| IS NULL | NULL操作符用来比较NULL的值 |
//找到成绩大于80并且班级为1。3的同学
select * from Student_Grade where St_Grade>80 and St_Class=\'1.3\';
//找到成绩在90-60之间班级为1.1或1.2的同学
select *from Student_Grade where (St_Class=\'1.1\' or St_Class = \'1.2\') and St_Grade between 60 and 90;
//找到名字中含有o的同学
select * from Student_Grade where St_Name like \'%o%\';
//注意在like的使用中的‘%’表示多个字符‘_’表示单个字符
子查询
将已经查询到的数据作为表来进行查询
语法格式
//写法1
select * from (select * from 表名)
//写法2
with
temp1 as (select * from 表名 where 条件)
temp2 as (select * from 表名 where 条件)
temp3 as (select * from 表名 where 条件)
//将temp1的数据作为子查询的对象,其他的各项同理
select * from temp1
//推荐写法2看起来比较清晰也高大上不少
举例
导入数据
数据来自tableau 的示例数据
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1juefKxxgZHAA3dS8eW_3Nw
提取码:tdsc
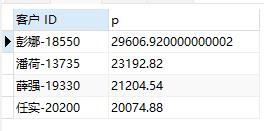
查找类别为办公用品地区是华东销售额>20000的消费者
with
temp1 as (select * from `订单` where 类别=\'办公用品\' and `区域`=\'华东\')
select `客户 ID`,sum(`销售额`) as p from temp1 group by `订单 ID` HAVING sum(`销售额`)>20000
//注意having与where的区别 having的执行顺序在where之后,且having中可以执行聚合函数,where不可以 having是对where的再次筛选
以上是关于sql 基础详细(持续更新)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章