python结合shell脚本实现简单的日常集中巡检
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python结合shell脚本实现简单的日常集中巡检相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、环境配置
1.说明
下面的安装过程适合开发、调试Python脚本,如果是直接使用的话没有这么复杂。为了防止由于版本问题导致安装问题,请到http://pan.baidu.com/s/1nt1NKSh 下载所需软件(本人上传,链接不会失效)。
2.安装过程(如果不是下载的安装包,除了python之外,其他都可以采用pip安装,更方便)
1)安装python
因为Python 本身不大,并且属于解释型语言,所以建议采用默认安装,即安装到C盘。 需要注意的是到下图步骤后点开标识的下拉箭头选择第一个,否则还需要手动配置环境变量。
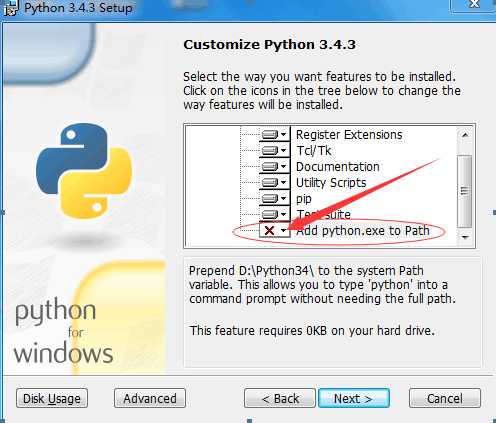
2)安装pycrypto,过程如图所示
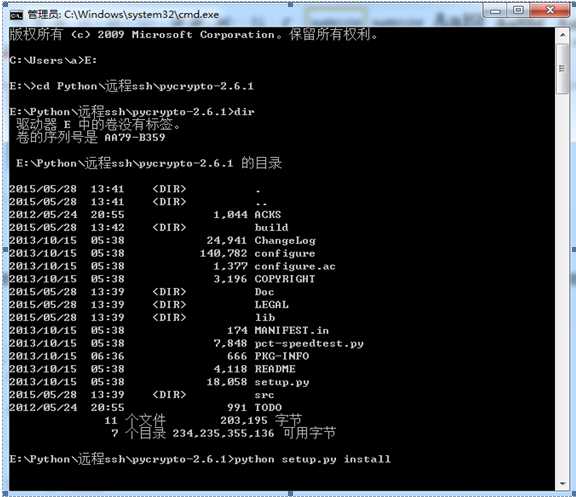
3)安装ecdsa,步骤同上
4)安装paramiko,步骤同上
5)修改文件
Python安装目录下:/Crypto/Random/OSRNG/nt.py 文件中找到
import winrandom
改成
from Crypto.Random.OSRNG import winrandom
二、所需文件及其内容
1.IP地址及口令文件
创建一个名字为ip.txt的文本文件(只要跟python脚本中文件名字一致即可),内容格式:
IP,username,password
参数说明:
IP:远程服务器的IP地址
username:oracle用户,即能登录sqlplus的用户
password:oracle用户密码

2.数据库巡检文件,代码如下
#!/bin/bash . $HOME/.profile sqlplus -S "/ as sysdba" <<EOF host echo "**************** check Instance status************" select status,database_status from v\\$instance; host echo "****************check database status************" select log_mode,open_mode from v\\$database; EOF echo "*********************check alter log file ***********" dump=$(sqlplus -s "/ as sysdba" <<EOF set head off select value from v\\$parameter where name=‘background_dump_dest‘; exit EOF) startline=$(cat $dump/alert*.log |grep -n "$(date +‘%a %b %e‘)"|head -1| awk -F: ‘{print $1}‘) echo "Contains the ORA- line in the file:" if [ "$startline" = "" ] then echo "There is no information today." else awk -v line=$startline ‘BEGIN{ORS="\\n"}NR>line{print $0}‘ $dump/alert*.log |grep ORA- |wc -l fi echo echo "****************check listening status****************" ##startline=$(lsnrctl status|grep -n "Listening Endpoints Summary"| head -1 |awk -F: ‘{print $1}‘) ##lsnrctl status |awk -v line=$startline ‘BEGIN{ORS="\\n"}NR>=line{print $0}‘ line=$(lsnrctl status |grep -n "The command completed successfully"| head -1 |awk -F: ‘{print $1}‘) ##echo $line if [ "$line" = "" ] then echo "can not get Listening info." else echo "Listening normal" fi echo echo "****************check disk space (above 90%)****************" df |sed -e ‘s/%//‘|awk ‘$5>90{print $0}‘
3.数据库服务器状态文件
echo "********** memory ***********************" free echo " " echo "********** disk space *******************" df -Th echo " " echo "********** vm state ********************" vmstat 2 3 echo " " echo "********** load state ********************" w echo " "
4.python脚本文件
import paramiko import datetime import os ##读取的脚本功能 1:巡检内容 2:负载状态 func=1 ##读取当前路径 base_dir=os.getcwd() ##命令开始执行时间 starttime=datetime.datetime.now() print(" -------------------------------------------------------------") print("| |") print(" startime: ",starttime) print("| |") print(" -------------------------------------------------------------") ##注意路径前面的r,否则有些文件会当作转义字符处理 ##读取命令脚本 if func==1: cmd_filepath=base_dir+r"\\xunjian.txt" else : cmd_filepath=base_dir+r"\\fuzai.txt" cmd_file=open(cmd_filepath,"r") cmd=cmd_file.read() ##读取IP地址列表 ip_filepath=base_dir+r"\\ip.txt" ip_file=open(ip_filepath,"r") while 1: ipinfo=ip_file.readline() if not ipinfo : break else : ##读取IP,用户名,密码 infos=ipinfo.split(‘,‘) host=infos[0] username=infos[1] pwd=infos[2].strip() pwd=pwd.strip(‘\\n‘) ##远程连接服务器 client = paramiko.SSHClient() client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy()) client.connect(host, 22, username, pwd) stdin, stdout, stderr = client.exec_command(cmd) print(" -------------------------------------------------------------") print("| |") print(" ",host) print("| |") print(" -------------------------------------------------------------") for line in stdout: print(line.strip(‘\\n‘)) client.close() print("") print(‘check complete................................‘) ##命令执行完成时间 endtime=datetime.datetime.now() print(" -------------------------------------------------------------") print("| |") print(" endtime: ",endtime) print("| |") print(" -------------------------------------------------------------") print(" -------------------------------------------------------------") print("| |") print(" startime: ",starttime) print(" endtime: ",endtime) print(" cost: ",endtime-starttime) print("| |") print(" -------------------------------------------------------------")
三、效果展示
1.数据库状态

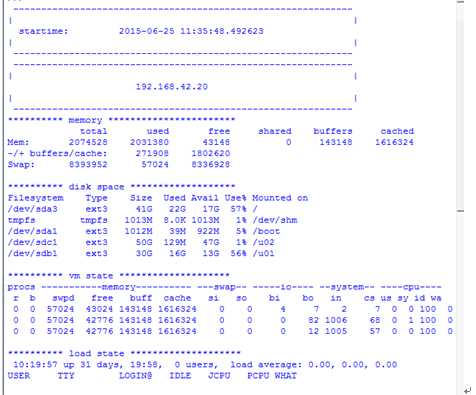
2.服务器状态
以上是关于python结合shell脚本实现简单的日常集中巡检的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章