英文电影评论情感分析
Posted 清风紫雪
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了英文电影评论情感分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
分析步骤
数据集
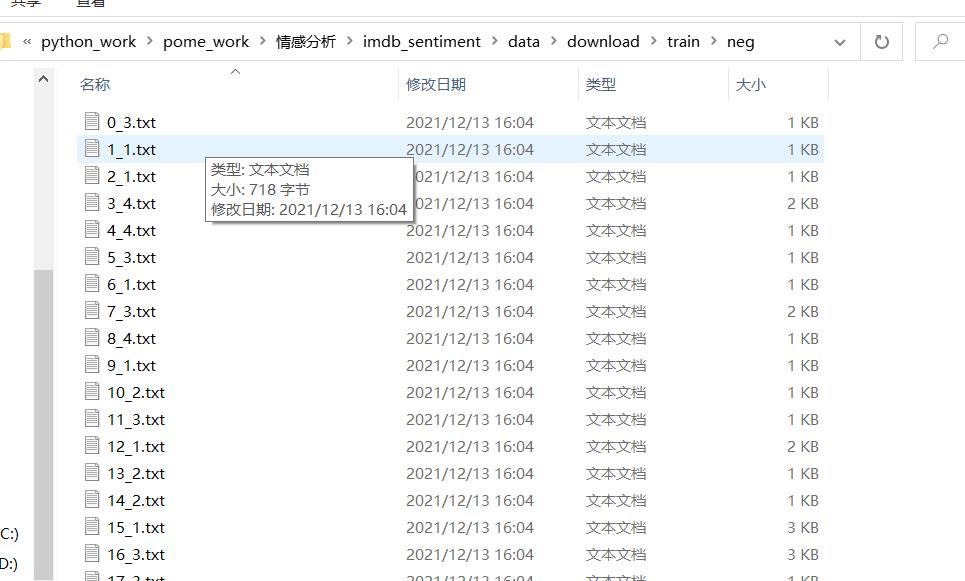
现在我们有一个经典的数据集IMDB数据集,地址:http://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/,这是一份包含了5万条流行电影的评论数据,其中训练集25000条,测试集25000条。数据格式如下:
下图左边为名称,其中名称包含两部分,分别是序号和情感评分,(1-4为neg,5-10为pos),右边为评论内容。
文本预处理
文本是一类序列数据,一篇文章可以看作是字符或单词的序列,本节将介绍文本数据的常见预处理步骤,预处理通常包括四个步骤:
-
读入文本
-
分词
-
建立字典,将每个词映射到一个唯一的索引(index)
-
将文本从词的序列转换为索引的序列,方便输入模型
文本的tokenization
tokenization就是通常所说的分词,分出的每一个词语我们把它称为token。
常见的分词工具很多,比如:
-
jieba分词:https://github.com/fxsjy/jieba -
清华大学的分词工具THULAC:
https://github.com/thunlp/THULAC-Python
构造词典
这里我们可以考虑把文本中的每个词语和其对应的数字,使用字典保存,同时实现方法把句子通过字典映射为包含数字的列表。
实现文本序列化之前,考虑以下几点:
-
如何使用字典把词语和数字进行对应
-
不同的词语出现的次数不尽相同,是否需要对高频或者低频词语进行过滤,以及总的词语数量是否需要进行限制
-
得到词典之后,如何把句子转化为数字序列,如何把数字序列转化为句子
-
不同句子长度不相同,每个batch的句子如何构造成相同的长度(可以对短句子进行填充,填充特殊字符)
-
对于新出现的词语在词典中没有出现怎么办(可以使用特殊字符代理)
思路分析:
-
对所有句子进行分词
-
词语存入字典,根据次数对词语进行过滤,并统计次数
-
实现文本转数字序列的方法
-
实现数字序列转文本方法
# -*-coding:utf-8-*-
import pickle
from tqdm import tqdm
from 情感分析.imdb_sentiment import dataset
# from 情感分析.imdb_sentiment.vocab import Vocab
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
class Vocab:
UNK_TAG = "<UNK>" # 表示未知字符
PAD_TAG = "<PAD>" # 填充符
PAD = 0
UNK = 1
def __init__(self):
self.dict = # 保存词语和对应的数字
self.UNK_TAG: self.UNK,
self.PAD_TAG: self.PAD
self.count = # 统计词频的
def fit(self, sentence):
"""
接受句子,统计词频
:param sentence:[str,str,str]
:return:None
"""
for word in sentence:
self.count[word] = self.count.get(word, 0) + 1 # 所有的句子fit之后,self.count就有了所有词语的词频
def build_vocab(self, min_count=1, max_count=None, max_features=None):
"""
根据条件构造 词典
:param min_count:最小词频
:param max_count: 最大词频
:param max_features: 最大词语数
:return:
"""
if min_count is not None:
self.count = word: count for word, count in self.count.items() if count >= min_count
if max_count is not None:
self.count = word: count for word, count in self.count.items() if count <= max_count
if max_features is not None:
# [(k,v),(k,v)....] --->k:v,k:v
self.count = dict(sorted(self.count.items(), lambda x: x[-1], reverse=True)[:max_features])
for word in self.count:
self.dict[word] = len(self.dict) # 每次word对应一个数字
# 把dict进行翻转
self.inverse_dict = dict(zip(self.dict.values(), self.dict.keys()))
def transform(self, sentence, max_len=None):
"""
把句子转化为数字序列
:param sentence:[str,str,str]
:return: [int,int,int]
"""
if len(sentence) > max_len:
sentence = sentence[:max_len]
else:
sentence = sentence + [self.PAD_TAG] * (max_len - len(sentence)) # 填充PAD
return [self.dict.get(i, 1) for i in sentence]
def inverse_transform(self, incides):
"""
把数字序列转化为字符
:param incides: [int,int,int]
:return: [str,str,str]
"""
return [self.inverse_dict.get(i, "<UNK>") for i in incides]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dict)
def collate_fn(batch):
"""
对batch数据进行处理
:param batch: [一个getitem的结果,getitem的结果,getitem的结果]
:return: 元组
"""
reviews, labels = zip(*batch)
return reviews, labels
def get_dataloader(train=True):
imdb_dataset = dataset.ImdbDataset(train)
my_dataloader = DataLoader(imdb_dataset, batch_size=200, shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn)
return my_dataloader
if __name__ == \'__main__\':
# sentences = [["今天", "天气", "很", "好"],
# ["今天", "去", "吃", "什么"]]
# ws = Vocab()
# for sentence in sentences:
# # 统计词频
# ws.fit(sentence)
# # 构造词典
# ws.build_vocab(min_count=1)
# print(ws.dict)
# # 把句子转换成数字序列
# ret = ws.transform(["好", "好", "好", "好", "好", "好", "好", "热", "呀"], max_len=13)
# print(ret)
# # 把数字序列转换成句子
# ret = ws.inverse_transform(ret)
# print(ret)
# pass
ws = Vocab()
dl_train = get_dataloader(True)
dl_test = get_dataloader(False)
for reviews, label in tqdm(dl_train, total=len(dl_train)):
for sentence in reviews:
ws.fit(sentence)
for reviews, label in tqdm(dl_test, total=len(dl_test)):
for sentence in reviews:
ws.fit(sentence)
ws.build_vocab()
print(len(ws))
pickle.dump(ws, open("./models/vocab.pkl", "wb"))
会生成对应的词典pkl文件
构造Dataset与Dataloader
# -*-coding:utf-8-*-
import os
import pickle
import re
import zipfile
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from tqdm import tqdm
class ImdbDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, train=True):
# super(ImdbDataset,self).__init__()
if not os.path.exists("./data/download"):
unzip_file("./data/test.zip", "./data/download")
unzip_file("./data/train.zip", "./data/download")
data_path = r"./data/download"
data_path += r"/train" if train else r"/test"
self.total_path = [] # 保存所有的文件路径
for temp_path in [r"/pos", r"/neg"]:
cur_path = data_path + temp_path
self.total_path += [os.path.join(cur_path, i) for i in os.listdir(cur_path) if i.endswith(".txt")]
def __getitem__(self, idx):
file = self.total_path[idx]
# 从txt获取评论并分词
review = tokenlize(open(file, "r", encoding="utf-8").read())
# 获取评论对应的label
label = int(file.split("_")[-1].split(".")[0])
label = 0 if label < 5 else 1
return review, label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.total_path)
def tokenlize(sentence):
"""
进行文本分词
:param sentence: str
:return: [str,str,str]
"""
fileters = [\'!\', \'"\', \'#\', \'$\', \'%\', \'&\', \'\\(\', \'\\)\', \'\\*\', \'\\+\', \',\', \'-\', \'\\.\', \'/\', \':\', \';\', \'<\', \'=\', \'>\',
\'\\?\', \'@\', \'\\[\', \'\\\\\', \'\\]\', \'^\', \'_\', \'`\', \'\\\', \'\\|\', \'\\\', \'~\', \'\\t\', \'\\n\', \'\\x97\', \'\\x96\', \'”\',
\'“\', ]
sentence = sentence.lower() # 把大写转化为小写
sentence = re.sub("<br />", " ", sentence)
# sentence = re.sub("I\'m","I am",sentence)
# sentence = re.sub("isn\'t","is not",sentence)
sentence = re.sub("|".join(fileters), " ", sentence)
result = [i for i in sentence.split(" ") if len(i) > 0]
return result
def unzip_file(zip_src, dst_dir):
"""
解压缩
:param zip_src:
:param dst_dir:
:return:
"""
r = zipfile.is_zipfile(zip_src)
if r:
fz = zipfile.ZipFile(zip_src, \'r\')
bar = tqdm(fz.namelist())
bar.set_description("unzip " + zip_src)
for file in bar:
fz.extract(file, dst_dir)
else:
print(\'This is not zip\')
# 以下为调试代码
def collate_fn(batch):
"""
对batch数据进行处理
:param batch: [一个getitem的结果,getitem的结果,getitem的结果]
:return: 元组
"""
reviews, labels = zip(*batch)
return reviews, labels
# def test_file(train=True):
# if not os.path.exists("./data/download"):
# unzip_file("./data/data.zip", "./data/download")
# data_path = r"./data/download"
# data_path += r"/train" if train else r"/test"
# total_path = [] # 保存所有的文件路径
# for temp_path in [r"/pos", r"/neg"]:
# cur_path = data_path + temp_path
# total_path += [os.path.join(cur_path, i) for i in os.listdir(cur_path) if i.endswith(".txt")]
# print(total_path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
from 情感分析.imdb_sentiment.vocab import Vocab
imdb_dataset = ImdbDataset(True)
my_dataloader = DataLoader(imdb_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn)
for review,label in my_dataloader:
vocab_model = pickle.load(open("./models/vocab.pkl", "rb"))
print(review[0])
result = vocab_model.transform(review[0], 100)
print(result)
break
# unzip_file("./data/a.zip", "./data/download")
# if os.path.exists("./data/download"):
# print("T")
# data = open("./data/download/train/pos\\\\10032_10.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8").read()
# result = tokenlize("--or something like that. Who the hell said that theatre stopped at the orchestra pit--or even at the theatre door?")
# result = tokenlize(data)
# print(result)
# test_file()
测试输出:
[\'this\', \'movie\', \'was\', \'kind\', \'of\', \'interesting\', \'i\', \'had\', \'to\', \'watch\', \'it\', \'for\', \'a\', \'college\', \'class\', \'about\', \'india\', \'however\', \'the\', \'synopsis\', \'tells\', \'you\', \'this\', \'movie\', \'is\', \'about\', \'one\', \'thing\', \'when\', \'it\', "doesn\'t", \'really\', \'contain\', \'much\', \'cold\', \'hard\', \'information\', \'on\', \'those\', \'details\', \'it\', \'is\', \'not\', \'really\', \'true\', \'to\', \'the\', \'synopsis\', \'until\', \'the\', \'very\', \'end\', \'where\', \'they\', \'sloppily\', \'try\', \'to\', \'tie\', \'all\', \'the\', \'elements\', \'together\', \'the\', \'gore\', \'factor\', \'is\', \'superb\', \'however\', \'even\', \'right\', \'at\', \'the\', \'very\', \'beginning\', \'you\', \'want\', \'to\', \'look\', \'away\', \'because\', \'the\', \'gore\', \'is\', \'pretty\', \'intense\', \'only\', \'watch\', \'this\', \'movie\', \'if\', \'you\', \'want\', \'to\', \'see\', \'some\', \'cool\', \'gore\', \'because\', \'the\', \'plot\', \'is\', \'thin\', \'and\', \'will\', \'make\', \'you\', \'sad\', \'that\', \'you\', \'wasted\', \'time\', \'listening\', \'to\', \'it\', "i\'ve", \'seen\', \'rumors\', \'on\', \'other\', \'websites\', \'about\', \'this\', \'movie\', \'being\', \'based\', \'on\', \'true\', \'events\', \'however\', \'you\', \'can\', \'not\', \'find\', \'any\', \'information\', \'about\', \'it\', \'online\', \'so\', \'basically\', \'this\', \'movie\', \'was\', \'a\', \'waste\', \'of\', \'time\', \'to\', \'watch\']
[2, 3, 93, 390, 14, 181, 90, 136, 100, 312, 7, 17, 78, 5879, 1056, 80, 17356, 117, 18, 6179, 3176, 12, 2, 3, 4, 80, 16, 187, 128, 7, 642, 483, 1011, 314, 987, 1655, 2011, 122, 48, 1176, 7, 4, 8, 483, 496, 100, 18, 6179, 1636, 18, 52, 458, 429, 329, 46669, 2039, 100, 11337, 36, 18, 1366, 753, 18, 2188, 10851, 4, 14736, 117, 9, 855, 58, 18, 52, 2691, 12, 116, 100, 266, 1061, 223, 18, 2188, 4, 819, 371, 308, 312, 2, 3, 11, 12, 116, 100, 46, 65, 710, 2188, 223, 18, 106]
word embedding
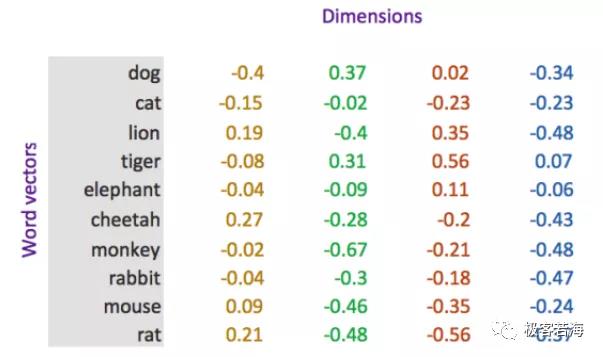
word embedding是深度学习中表示文本常用的一种方法。和one-hot编码不同,word embedding使用了浮点型的稠密矩阵来表示token。根据词典的大小,我们的向量通常使用不同的维度,例如100,256,300等。其中向量中的每一个值是一个参数,其初始值是随机生成的,之后会在训练的过程中进行学习而获得。
如果我们文本中有20000个词语,如果使用one-hot编码,那么我们会有20000*20000的矩阵,其中大多数的位置都为0,但是如果我们使用word embedding来表示的话,只需要20000* 维度,比如20000*300
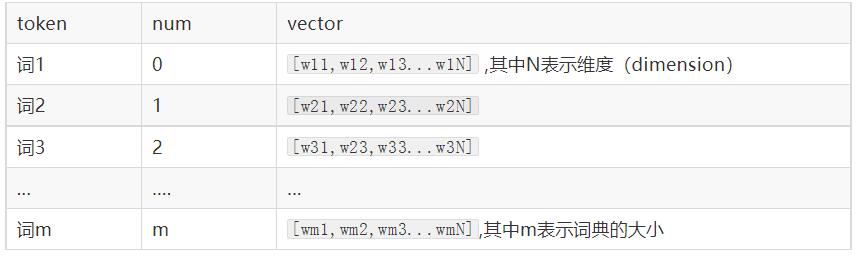
我们会把所有的文本转化为向量,把句子用向量来表示
但是在这中间,我们会先把token使用数字来表示,再把数字使用向量来表示。
即:token---> num ---->vector
word embedding API
torch.nn.Embedding(num_embeddings,embedding_dim)
参数介绍: