python基础----内置函数
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python基础----内置函数相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一 内置函数
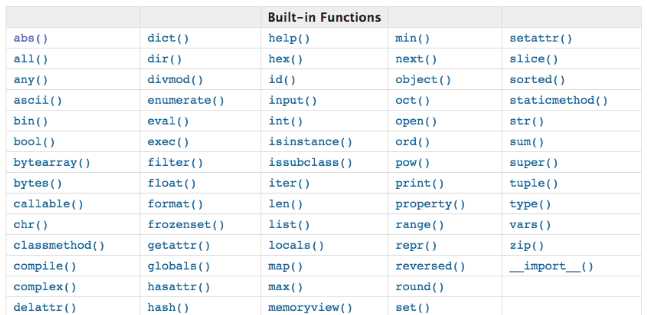
这里全是用print打印来查看输出结果
1)abs() 绝对值
1 print(abs(-1)) #1 2 print(abs(0)) #0 3 a = abs(True) 4 print(a) #1 5 print(abs(False)) #0
2)all() 可迭代对象为空,返回True,有任何一个值为假,则为False
1 print(all(" ")) #True 2 print(all((1,2,3,None))) #Flase 3 print(all((1,2,3,))) #True 4 print(all(i for i in range(1,10))) #True
3)any() 可迭代对象为空,发挥False 有任何一个值为真,则为True
1 print(any("")) #Flase 2 print(all((1,2,3,None))) #Flase 3 print(all((1,2,3,))) #True 4 print(all(i for i in range(1,10))) #True
4)bin() 十进制转2进制 ,0b代表2进制
1 print(bin(3)) #0b11 2 print(bin(10)) #0b1010
5)hex() 十进制转16进制,0x代表16进制
1 print(hex(10)) #0xa 2 print(hex(100)) #0x64
6)bool() 判断布尔值, 为空和None,0 为False 其他都是True
1 print(bool(0)) #False 2 print(bool([])) #False 3 print(bool("")) #False 4 print(bool(())) #False 5 print(bool({})) #False 6 print(bool(None)) #False 7 print(bool("hello world")) #True
7)bytes() 把字符串转成字节形式,需要指定字符编码“utf-8”
1 print(bytes("hello",encoding="utf-8")) 2 #输出结果是:b‘hello‘ b就是字节
8)callable() 查看可不可以被调用,为True,代表可以调用
1 print(callable(sum)) #True 2 print(callable(max)) #True
9)
# chr() 把数字转为对应的ascll码print(chr(100)) #dprint(chr(67)) #C # old() 把ascll字符转成对应的数字 0-65535
print(ord("c")) #97
10)
1 # set 集合 2 s ={1,2,3,4,5} 3 print(s) 4 # 5 # # frozenset() 不可变集合 6 f = frozenset({1,2,3,4,5}) 7 print(type(f)) 8 #输出结果:<class ‘frozenset‘> 9 10 # dir() 查看对象的调用方法 11 # print(dir(sum)) 12 # print(dir(max)) 13 14 # help() 查看帮助信息 15 # print(help(sum)) 16 # print(help(max)) 17 18 19 # divmod() 整除, 取余,传两个参数 20 print(divmod(10,3)) 21 print(divmod(100,7)) 22 #输出结果:(3, 1) 23 # (14, 2) 24 25 # enumerate() 把索引 跟元素一一对应 放到元组里 26 d = enumerate([1,2,3]) 27 print(list(d)) #[(0, 1), (1, 2), (2, 3)] 28 for i in enumerate([1,2,3,4,5,]): 29 print(i) 30 #输出结果 (0, 1) 31 #(1, 2) 32 #(2, 3) 33 #(3, 4) 34 #(4, 5) 35 36 37 38 # hash() 哈希算法 相同的字符串,得到的哈希值一定是一样的 39 print(hash("hello world")) #-7815794705108155137 40 print(hash("hello world")) #-7815794705108155137 41 42 # id() 查看唯一标示身份编号 相当于身份证 43 a = 1 44 b = 2 45 print(id(a)) #1422046272 46 print(id(b)) #1422046304 47 print(a is b) #False 48 # 49 x = "a" 50 y = "a" 51 print(id(x)) #40510776 52 print(id(y)) #40510776 53 print(x is y) #True 54 55 #iter() 把一个可迭代对象变成迭代器 56 57 # # max()最大值 58 print(max([1,2,3,4,5,6])) #6 简单玩法 59 salases = { 60 "egon":19999, 61 "alex":29999, 62 "wupiqi":39999, 63 "yuanhao":49999, 64 } 65 #高级玩法 用函数 66 def get_value(k): 67 return salases[k] 68 print(max(salases,key=get_value)) # yuanhao 69 #超高级玩法,匿名函数 70 print(max(salases,key=lambda k:salases[k])) #yuanhao 71 # # min()最小值 72 print(min([1,2,3,4,5,6])) #1 简单玩法 73 #高级玩法 用函数 74 def get_value1(k): 75 return salases[k] 76 print(min(salases,key=get_value1)) #egon 77 78 #超高级玩法,匿名函数 79 print(min(salases,key=lambda k:salases[k])) #egon 80 81 82 83 # zip() 拉链 84 l = [1,2,3,4,5] #迭代器 85 s = "hello" 86 res = zip(l,s) 87 for i in res: 88 print(i) #输出结果 (1,“h”) (2,"e") .......(5,"o") 89 90 91 # sorted() 返回值是列表,默认升序排列 92 l = [2,4,6,7,1,10] 93 print(sorted(l)) 94 print(sorted(l,reverse=True)) #降序排列 95 s = "hello world" 96 print(sorted(s)) #字符串是按ascll码顺序排列的
11)
1 #map 映射 2 l = [1,2,3,45,] #平方 3 m = map(lambda item:item**2,l) 4 #print(list(m)) 5 # for i in m: 6 # print(i) 7 #加扩展Sb 8 l1 = ["alex","egon","wupeiqi","yuanhao"] 9 m1 = map(lambda a:a+"sb",l1) 10 print(list(m1)) 11 12 13 #filter 过滤 14 name =[ 15 {"name":"egon","age":101}, 16 {"name":"alex","age":100}, 17 {"name":"wupeiqi","age":10000}, 18 {"name":"yuanhao","age":2000}, 19 20 ] 21 f = filter(lambda d:d["age"]>100,name) 22 #print(list(f)) 23 for i in f: 24 print(i) 25 26 #reduce 合并 27 from functools import reduce #注意用reduce 需要导入 前面的模块 28 l3 = list(range(100)) 29 print(l3) 30 print(reduce(lambda x,y:x+y,l3,100))
以上是关于python基础----内置函数的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章