卷积神经网络中nn.Conv2d()和nn.MaxPool2d()以及卷积神经网络实现minist数据集分类
Posted GreenOrange
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了卷积神经网络中nn.Conv2d()和nn.MaxPool2d()以及卷积神经网络实现minist数据集分类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
卷积神经网络中nn.Conv2d()和nn.MaxPool2d()
卷积神经网络之Pythorch实现:
nn.Conv2d()就是PyTorch中的卷积模块
参数列表
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| in_channels | 输入数据体的深度 |
| out_channels | 输出数 据体的深度 |
| kernel_size | 滤波器(卷积核)的大小 注1 |
| stride | 滑动的步长 |
| padding | 零填充的圈数 注2 |
| bias | 是否启用偏置,默认是True,代表启用 |
| groups | 输出数据体深度上和输入数 据体深度上的联系 注3 |
| dilation | 卷积对于输入数据体的空间间隔 注4 |
注:1. 可以使用一 个数字来表示高和宽相同的卷积核,比如 kernel_size=3,也可以使用 不同的数字来表示高和宽不同的卷积核,比如 kernel_size=(3, 2);
-
padding=0表示四周不进行零填充,而 padding=1表示四周进行1个像素点的零填充;
-
groups表示输出数据体深度上和输入数 据体深度上的联系,默认 groups=1,也就是所有的输出和输入都是相 关联的,如果 groups=2,这表示输入的深度被分割成两份,输出的深 度也被分割成两份,它们之间分别对应起来,所以要求输出和输入都 必须要能被 groups整除。
-
默认dilation=1详情见 nn.Conv2d()中dilation参数的作用或者CSDN
nn.MaxPool2d()表示网络中的最大值池化
参数列表:
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| kernel_size | 与上面nn.Conv2d()相同 |
| stride | 与上面nn.Conv2d()相同 |
| padding | 与上面nn.Conv2d()相同 |
| dilation | 与上面nn.Conv2d()相同 |
| return_indices | 表示是否返回最大值所处的下标,默认 return_indices=False |
| ceil_mode | 表示使用一些方格代替层结构,默认 ceil_mode=False |
注:一般不会去设置return_indices和ceil_mode参数
import torch.nn as nn
class SimpleCNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SimpleCNN, self).__init__()
layer1 = nn.Sequential()
# 把一个三通道的照片RGB三个使用32组卷积核卷积,每组三个卷积核,组内卷积后相加得出32组输出
layer1.add_module(\'conv1\', nn.Conv2d(3, 32, (3, 3), (1, 1), padding=1))
layer1.add_module(\'relu1\', nn.ReLU(True))
layer1.add_module(\'pool1\', nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2))
self.layer1 = layer1
layer2 = nn.Sequential()
layer2.add_module(\'conv2\', nn.Conv2d(32, 64, (3, 3), (1, 1), padding=1))
layer2.add_module(\'relu2\', nn.ReLU(True))
layer2.add_module(\'pool2\', nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2))
self.layer2 = layer2
layer3 = nn.Sequential()
layer3.add_module(\'conv3\', nn.Conv2d(64, 128, (3, 3), (1, 1), padding=1))
layer3.add_module(\'relu3\', nn.ReLU(True))
layer3.add_module(\'pool3\', nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2))
self.layer3 = layer3
layer4 = nn.Sequential()
layer4.add_module(\'fc1\', nn.Linear(2048, 512))
layer4.add_module(\'fc_relu1\', nn.ReLU(True))
layer4.add_module(\'fc2\', nn.Linear(512, 64))
layer4.add_module(\'fc_relu2\', nn.ReLU(True))
layer4.add_module(\'f3\', nn.Linear(64, 10))
self.layer4 = layer4
def forward(self, x):
conv1 = self.layer1(x)
conv2 = self.layer2(conv1)
conv3 = self.layer3(conv2)
fc_input = conv3.view(conv3.size(0), -1)
fc_out = self.layer4(fc_input)
return fc_out
model = SimpleCNN()
print(model)
输出
SimpleCNN(
(layer1): Sequential(
(conv1): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(pool1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(layer2): Sequential(
(conv2): Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
(relu2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(pool2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(layer3): Sequential(
(conv3): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu3): ReLU(inplace=True)
(pool3): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(layer4): Sequential(
(fc1): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(fc_relu1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=64, bias=True)
(fc_relu2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(f3): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
)
提取模型的层级结构
提取层级结构可以使用以下几个nn.Model的属性,第一个是children()属性,它会返回下一级模块的迭代器,在上面这个模型中,它会返回在self.layer1,self.layer2,self.layer4上的迭代器而不会返回它们内部的东西;modules()
会返回模型中所有的模块的迭代器,这样它就能访问到最内层,比如self.layer1.conv1这个模块;还有一个与它们相对应的是name_children()属性以及named_modules(),这两个不仅会返回模块的迭代器,还会返回网络层的名字。
提取出model中的前两层
nn.Sequential(*list(model.children())[:2])
输出:
Sequential(
(0): Sequential(
(conv1): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(pool1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(1): Sequential(
(conv2): Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(pool2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
)
提取出model中的所有卷积层
conv_model = nn.Sequential()
for layer in model.named_modules():
if isinstance(layer[1], nn.Conv2d):
conv_model.add_module(layer[0].split(\'.\')[1] ,layer[1])
print(conv_model)
输出:
Sequential(
(conv1): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(conv2): Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(conv3): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
)
提取网络参数并对其初始化
nn.Moudel里面有两个特别重要的关于参数的属性,分别是named_parameters()和parameters()。前者会输出网络层的名字和参数的迭代器,后者会给出一个网络的全部参数的迭代器。
for param in model.named_parameters():
print(param[0])
# print(param[1])
输出:
layer1.conv1.weight
layer1.conv1.bias
layer2.conv2.weight
layer2.conv2.bias
layer3.conv3.weight
layer3.conv3.bias
layer4.fc1.weight
layer4.fc1.bias
layer4.fc2.weight
layer4.fc2.bias
layer4.f3.weight
layer4.f3.bias
案例:使用卷积神经网络实现对Minist数据集的预测
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.utils.data
import torchvision.datasets
import os
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import transforms
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=(3, 3)),
nn.BatchNorm2d(16),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3)),
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
)
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3)),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3)),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(128 * 4 * 4, 1024),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(1024, 128),
nn.Linear(128, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"] = "TRUE"
data_tf = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5], [0.5])]
)
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root=\'F:/机器学习/pytorch/书/data/mnist\', train=True,
transform=data_tf, download=True)
test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root=\'F:/机器学习/pytorch/书/data/mnist\', train=False,
transform=data_tf, download=True)
batch_size = 100
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size
)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
dataset=test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size
)
model = CNN()
model = model.cuda()
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
criterion = criterion.cuda()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
# 节约时间,三次够了
iter_step = 3
loss1 = []
loss2 = []
for step in range(iter_step):
loss1_count = 0
loss2_count = 0
for images, labels in train_loader:
images = images.cuda()
labels = labels.cuda()
images = images.reshape(-1, 1, 28, 28)
output = model(images)
pred = output.squeeze()
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = criterion(pred, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
_, pred = torch.max(pred, 1)
loss1_count += int(torch.sum(pred == labels)) / 100
# 测试
else:
test_loss = 0
accuracy = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for images, labels in test_loader:
images = images.cuda()
labels = labels.cuda()
pred = model(images.reshape(-1, 1, 28, 28))
_, pred = torch.max(pred, 1)
loss2_count += int(torch.sum(pred == labels)) / 100
loss1.append(loss1_count / len(train_loader))
loss2.append(loss2_count / len(test_loader))
print(f\'第{step}次训练:训练准确率:{loss1[len(loss1)-1]},测试准确率:{loss2[len(loss2)-1]}\')
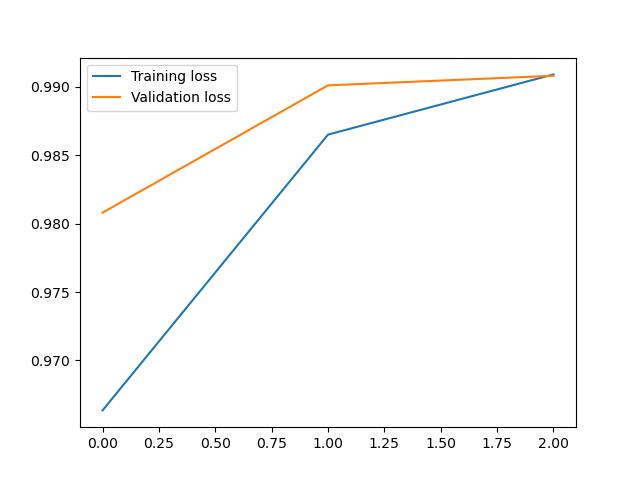
plt.plot(loss1, label=\'Training loss\')
plt.plot(loss2, label=\'Validation loss\')
plt.legend()
输出:
第0次训练:训练准确率:0.9646166666666718,测试准确率:0.9868999999999996
第1次训练:训练准确率:0.9865833333333389,测试准确率:0.9908999999999998
第2次训练:训练准确率:0.9917000000000039,测试准确率:0.9879999999999994
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x21f03092fd0>
以上是关于卷积神经网络中nn.Conv2d()和nn.MaxPool2d()以及卷积神经网络实现minist数据集分类的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章