吴裕雄--天生自然python Google深度学习框架:Tensorflow实现迁移学习
Posted 天生自然
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了吴裕雄--天生自然python Google深度学习框架:Tensorflow实现迁移学习相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。


import glob import os.path import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.python.platform import gfile import tensorflow.contrib.slim as slim # 加载通过TensorFlow-Slim定义好的inception_v3模型。 import tensorflow.contrib.slim.python.slim.nets.inception_v3 as inception_v3 # 处理好之后的数据文件。 INPUT_DATA = \'../../datasets/flower_processed_data.npy\' # 保存训练好的模型的路径。 TRAIN_FILE = \'train_dir/model\' # 谷歌提供的训练好的模型文件地址。因为GitHub无法保存大于100M的文件,所以 # 在运行时需要先自行从Google下载inception_v3.ckpt文件。 CKPT_FILE = \'../../datasets/inception_v3.ckpt\' # 定义训练中使用的参数。 LEARNING_RATE = 0.0001 STEPS = 300 BATCH = 32 N_CLASSES = 5 # 不需要从谷歌训练好的模型中加载的参数。 CHECKPOINT_EXCLUDE_SCOPES = \'InceptionV3/Logits,InceptionV3/AuxLogits\' # 需要训练的网络层参数明层,在fine-tuning的过程中就是最后的全联接层。 TRAINABLE_SCOPES=\'InceptionV3/Logits,InceptionV3/AuxLogit\'
def get_tuned_variables(): exclusions = [scope.strip() for scope in CHECKPOINT_EXCLUDE_SCOPES.split(\',\')] variables_to_restore = [] # 枚举inception-v3模型中所有的参数,然后判断是否需要从加载列表中移除。 for var in slim.get_model_variables(): excluded = False for exclusion in exclusions: if var.op.name.startswith(exclusion): excluded = True break if not excluded: variables_to_restore.append(var) return variables_to_restore
def get_trainable_variables(): scopes = [scope.strip() for scope in TRAINABLE_SCOPES.split(\',\')] variables_to_train = [] # 枚举所有需要训练的参数前缀,并通过这些前缀找到所有需要训练的参数。 for scope in scopes: variables = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, scope) variables_to_train.extend(variables) return variables_to_train
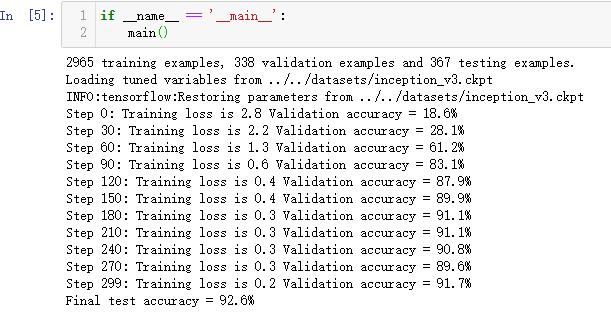
def main(): # 加载预处理好的数据。 processed_data = np.load(INPUT_DATA) training_images = processed_data[0] n_training_example = len(training_images) training_labels = processed_data[1] validation_images = processed_data[2] validation_labels = processed_data[3] testing_images = processed_data[4] testing_labels = processed_data[5] print("%d training examples, %d validation examples and %d testing examples." % ( n_training_example, len(validation_labels), len(testing_labels))) # 定义inception-v3的输入,images为输入图片,labels为每一张图片对应的标签。 images = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 299, 299, 3], name=\'input_images\') labels = tf.placeholder(tf.int64, [None], name=\'labels\') # 定义inception-v3模型。因为谷歌给出的只有模型参数取值,所以这里 # 需要在这个代码中定义inception-v3的模型结构。虽然理论上需要区分训练和 # 测试中使用到的模型,也就是说在测试时应该使用is_training=False,但是 # 因为预先训练好的inception-v3模型中使用的batch normalization参数与 # 新的数据会有出入,所以这里直接使用同一个模型来做测试。 with slim.arg_scope(inception_v3.inception_v3_arg_scope()): logits, _ = inception_v3.inception_v3( images, num_classes=N_CLASSES, is_training=True) trainable_variables = get_trainable_variables() # 定义损失函数和训练过程。 tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy( tf.one_hot(labels, N_CLASSES), logits, weights=1.0) total_loss = tf.losses.get_total_loss() train_step = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(LEARNING_RATE).minimize(total_loss) # 计算正确率。 with tf.name_scope(\'evaluation\'): correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits, 1), labels) evaluation_step = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) # 定义加载Google训练好的Inception-v3模型的Saver。 load_fn = slim.assign_from_checkpoint_fn( CKPT_FILE, get_tuned_variables(), ignore_missing_vars=True) # 定义保存新模型的Saver。 saver = tf.train.Saver() with tf.Session() as sess: # 初始化没有加载进来的变量。 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) # 加载谷歌已经训练好的模型。 print(\'Loading tuned variables from %s\' % CKPT_FILE) load_fn(sess) start = 0 end = BATCH for i in range(STEPS): _, loss = sess.run([train_step, total_loss], feed_dict={ images: training_images[start:end], labels: training_labels[start:end]}) if i % 30 == 0 or i + 1 == STEPS: saver.save(sess, TRAIN_FILE, global_step=i) validation_accuracy = sess.run(evaluation_step, feed_dict={ images: validation_images, labels: validation_labels}) print(\'Step %d: Training loss is %.1f Validation accuracy = %.1f%%\' % ( i, loss, validation_accuracy * 100.0)) start = end if start == n_training_example: start = 0 end = start + BATCH if end > n_training_example: end = n_training_example # 在最后的测试数据上测试正确率。 test_accuracy = sess.run(evaluation_step, feed_dict={ images: testing_images, labels: testing_labels}) print(\'Final test accuracy = %.1f%%\' % (test_accuracy * 100))
以上是关于吴裕雄--天生自然python Google深度学习框架:Tensorflow实现迁移学习的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章