用 python 来操作word文件(使用 docx 库)
Posted 德辰
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了用 python 来操作word文件(使用 docx 库)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
实例一:
from docx import Document
from docx.enum.text import WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH
from docx.oxml.ns import qn # 中文格式
from docx.shared import Pt # 磅数
from docx.shared import Inches # 图片尺寸
import time
today = time.strftime("%Y{y}%m{m}%d{d}", time.localtime()).format(y="年", m="月", d="日")
price = input("请输入今日价格:")
company_list = ["客户1", "客户2", "客户3", "客户4", "客户5", "客户6", "客户7", "客户8", "客户9", "客户10"]
for i in company_list:
document = Document()
document.styles["Normal"].font.name = u"微软雅黑"
document.styles["Normal"].font.size = Pt(14)
# 设置文档的基础字体
document.styles[\'Normal\']._element.rPr.rFonts.set(qn(\'w:eastAsia\'), u\'微软雅黑\')
# 设置文档的基础样式
document.add_picture("d:/无标题.png", width=Inches(6))
# 在文件最上头插入图片作为文件红头,宽度为6英寸
p1 = document.add_paragraph()
# 初始化建立第一个自然段
p1.alignment = WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.CENTER
# 对齐方式为居中,没有这句默认左对齐
run1 = p1.add_run("关于下达%s产品价格的通知" % (today))
# 这里是第一段的内容
run1.font.name = "微软雅黑"
# 设置西文字体
run1._element.rPr.rFonts.set(qn(\'w:eastAsia\'), u\'微软雅黑\')
# 设置中文字体
run1.font.size = Pt(21)
# 设置字体大小为21磅
run1.font.bold = True
# 设置加粗
p1.space_after = Pt(5)
# 设置段后距离5磅
p1.space_before = Pt(5)
# 设置段后距离5磅
p2 = document.add_paragraph()
run2 = p2.add_run(i + ": ")
# 这里是对客户的称呼
run2.font.name = "仿宋_GB2312"
run2._element.rPr.rFonts.set(qn(\'w:eastAsia\'), u\'仿宋_GB2312\')
run2.font.size = Pt(16)
run2.font.bold = True
p3 = document.add_paragraph()
run3 = p3.add_run(" 根据公司安排,为提供优质客户服务,我单位现将价格通知如下。 ")
run3.font.name = "仿宋_GB2312"
run3._element.rPr.rFonts.set(qn(\'w:eastAsia\'), u\'仿宋_GB2312\')
run3.font.size = Pt(16)
run3.font.bold = True
table = document.add_table(rows=3, cols=3, style="Table Grid")
table.cell(0, 0).merge(table.cell(0,2))
table_run1 = table.cell(0,0).paragraphs[0].add_run("XXX产品报价表")
table_run1.font.name = u"隶书"
table_run1.font.bold = True
table_run1._element.rPr.rFonts.set(qn(\'w:eastAsia\'), u\'隶书\')
table.cell(0, 0).paragraphs[0].alignment = WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.CENTER
table.cell(1, 0).text = "日期"
table.cell(1, 1).text = "价格"
table.cell(1, 2).text = "备注"
table.cell(2, 0).text = today
table.cell(2, 1).text = str(price)
table.cell(2, 2).text = ""
p4 = document.add_paragraph()
p4.alignment = WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.CENTER
run4 = p4.add_run(" (联系人: 小杨 电话:18888888888) ")
run4.font.name = "仿宋_GB2312"
run4._element.rPr.rFonts.set(qn(\'w:eastAsia\'), u\'仿宋_GB2312\')
run4.font.size = Pt(16)
run4.font.bold = True
document.add_page_break()
p5 = document.add_paragraph()
run4 = p5.add_run("此处是广告")
document.save("%s-价格通知.docx" % i)
效果图:
docx 库 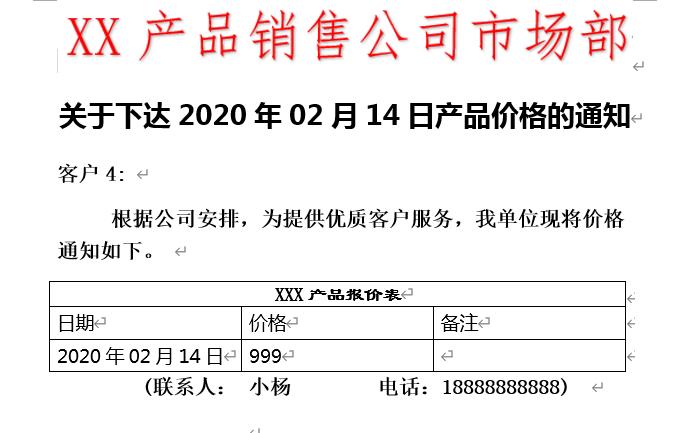
文章结构:
一、docx 基本用,创建 docx 文件并添加数据
二、深入理解文本格式(format),并设置所格式属性(attribute)
三、深入理解样式(styles),以及如何运用样式
四、常用样式(style)示例
一、docx基本用法,创建docx 文件并添加数据
官方文档:https://python-docx.readthedocs.org/en/latest/
docx 可以操作 doxc 格式文件
linux 安装 sudo pip install python_docx (不要安装错了,python_docx 是新版本,如果只是安装 docx 有些 API 会不匹配)
windows 安装 pip install python_docx
基本用法:
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding: utf-8 from docx import Document from docx.shared import Inches #创建 Document 对象,相当于打开一个 word 文档 document = Document() #向文档中添加一个标题,标题级别设置为0级 document.add_heading(\'This is title\', level=0) #向文档中添加一个段落,并将段落引用赋给变量 p #使用 add_run 方法追加字段,并设置格式 p = document.add_paragraph(\'This is paragraph\') p.add_run(\'bold\').bold = True p.add_run(\' and some \') p.add_run(\'italic.\').italic = True #添加标题和段落,采用不同的形式 document.add_heading(\'This is Heading, level 1\', level=1) document.add_paragraph(\'Intese quote\',style="Intense Quote") document.add_paragraph(\'first item in unordered list\', style=\'List Bullet\') document.add_paragraph(\'first item in ordered list\', style=\'List Number\') #添加图片,设置图片大小 document.add_picture(r"D:\\picture\\a.jpg", width=Inches(2.25)) #添加表格,填入表格内容 table = document.add_table(rows=2, cols=2) table.cell(0,0).text = "cell_00" table.cell(0,1).text = "cell_01" table.cell(1,0).text = "cell_10" table.cell(1,1).text = "cell_11" #保存文本 document.save(\'demo.docx\')
效果展示:
<-------------------- start -------------------->

<-------------------- end -------------------->
二、深入理解文本格式(format),并设置所格式属性(attribute)
根据官方文档所述,word 中主要有两种用文本格式等级:块等级(block-level)和内联等级(inline-level)
word 中大部分内容都是由这两种等级的对象组成的
块等级(block-level):
段落是 word 文件中的主要块对象(block-level object)
块等级项(block-level item)主要任务是将文本格式从左边界向右边界展示(flows);\\
对于段落而言,边界就是分段标识,或者是文本的列边界
列表(table)也是块对象(block-level object)
内联等级(inline-level):
内联对象(inline-level object)是块对象(block-level object)的组成部分
块对象的所有内容都包含在内联对象中,一个块对象由一个或多个内联对象组成
run 是常用的内联对象,例如:
p = document.add_paragraph(\'This is paragraph\') p.add_run(\'bold\').bold = True p.add_run(\' and some \') p.add_run(\'italic.\').italic = True
这个例子中一个段落(块对象)包含三个 run(内联对象),每一个 run 都设置有不同属性
块等级,及其属性
块对象一般包括:段落(paragraph)、图片(inline picture)、表(table)、标题(heading)、有序列表(numbered lists)、无序列表(bullets lists)
块对象的属性指定了块对象所在的位置,例如缩进、段间距离
常用属性:alignment
from docx.enum.text import WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH paragraph = document.add_paragraph("hello") paragraph_format = paragraph.paragraph_format #设置段落水平居中对齐 paragraph_format.alignment = WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.CENTER #WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH 存储了多种对齐格式,例如: #WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.LEFT,左对齐;默认左对齐 #WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.RIGHT,右对齐
indent,缩进
from docx.shared import Inches from docx.shared import Pt #设置段落从左开始缩进,使用Inches来衡量 paragraph_format.left_indent = Inches(0.5) #设置段落从右开始缩进,使用Pt来衡量 paragraph_format.right_indent = Pt(20) #设置段落第一行缩进,可以与上两个缩进叠加 paragraph_format.first_line_indent = Inches(0.5)
space,行间距
from docx.shared import Pt #设置与上一段间隔 Pt(5) paragraph.space_after = Pt(5) #设置与下一段间隔 Pt(10) paragraph.space_before = Pt(10)
内联等级,及其属性
内联对象一般包括:文字、句子、段落
内联对象的属性指定了字体,例如粗体(bold)、斜体(italic)、大小(size)等等
常用属性:name and size
document = Document() paragraph = document.add_paragraph() run = paragraph.add_run("hellohellohello") font = run.font #设置字体样式 font.name = \'Calibri\' #设置字体大小 font.size = Pt(55)
bold 、underline and underline
#设置为斜体 font.italic = True #不设置下划线 font.underline = False #设置粗体为继承上一个字体的格式 font.bold = None #这一类属性,每个有三种状态 #True 为使用属性;False 为不使用属性;None 默认属性继承自上一个字体 #此外,underline 属性还可以设置值,例如 font.underline = WD_UNDERLINE.DOT_DASH
color
#以RGB方式设置颜色 from docx.shared import RGBColor font.color.rgb = RGBColor(0x42, 0x24, 0xE9) #使用内建主题设置颜色 from docx.enum.dml import MSO_THEME_COLOR font.color.theme_color = MSO_THEME_COLOR.ACCENT_1
三、深入理解样式(styles),以及如何运用样式
在 word 中,样式包括:段落样式(paragraph styles)、字符样式(character styles)、表样式(table styles)、列表样式(numbering styles)
样式类似于前端开发的 CSS,一处定义,处处使用
docx 库内的 styles 样式不包含 word 中全部的样式,有一些还在开发中,但是基本够用
Document 的属性 styles,包含了所有 docx 提供的可用样式
选取段落可用样式
#显示所有段落样式 from docx.enum.style import WD_STYLE_TYPE styles = document.styles paragraph_styles = [ s for s in styles if s.type == WD_STYLE_TYPE.PARAGRAPH ] for style in paragraph_styles: print(style.name) #styles 为 Document 的属性,style 为段落的属性 #除了段落(paragraph),还有 run,表(table)有 style 属性
段落设置样式
document = Document() #从styles中选取样式 paragraph = document.add_paragraph() paragraph.style = document.styles[\'Heading 1\'] #用样式名称直接赋值 paragraph2 = document.add_paragraph() paragraph2.style = \'List Bullet\' #在创建段落时赋值 paragraph = document.add_paragraph(style=\'Body Text\')
定义样式(style)中的字符格式(character format)
定义样式中的字符格式后,所有运用此样式的段落都有相应的字符格式
document = Document() #从样式库中选取 \'Normal\' 样式,并提取 \'Normal\' 样式的字符属性 style = document.styles[\'Normal\'] font = style.font #设置样式中的字符属性 ,操作方法和上面改变内联对象属性方法一致 font.name = "Microsoft YaHei UI" font.size = Pt(50) #将设置好字符属性的样式运用到段落中 p = document.add_paragraph("change font attribution", style = \'Normal\')
定义样式(style)中的段落格式(paragraph format)
定义样式中的段落格式后,所有运用此样式的段落都有相应的段落格式
document = Document() styles = document.styles #选取 style,并设置 style 中的段落格式 style = styles[\'Heading 2\'] para_format = style.paragraph_format para_format.left_indent = Pt(20) para_format.widow_control = True #将设置好段落格式的 style 运用到段落中 p = document.add_paragraph(\'This is Heading, level 1\', style = style)
简单总结
文章第二部分直接设置段落的格式(paragraph.format),字符的格式(run.font)
在这一部分,运用了 style 对象,统一设置了段落格式、字符格式
一旦 style 对象设置好了以后,可以多次反复利用
style 对象是从文件对象中提取(document.styles)的,docx 提供的 Style 类对象
四、常用样式(style)示例
段落样式
from docx.enum.style import WD_STYLE_TYPE from docx import * document = Document() styles = document.styles #生成所有段落样式 for s in styles: if s.type == WD_STYLE_TYPE.PARAGRAPH: document.add_paragraph(\'Paragraph style is : \'+ s.name, style = s) document.save(\'para_style.docx\')
字符样式
from docx.enum.style import WD_STYLE_TYPE from docx import * document = Document() styles = document.styles para = document.add_paragraph() #生成所有字符样式 for s in styles: if s.type == WD_STYLE_TYPE.CHARACTER: run = para.add_run("Character style is: "+s.name+"\\n") run.style = s document.save(\'character_style.docx\')
表格样式
from docx.enum.style import WD_STYLE_TYPE from docx import * document = Document() styles = document.styles #生成所有表样式 for s in styles: if s.type == WD_STYLE_TYPE.TABLE: document.add_paragraph("Table style is : "+ s.name) document.add_table(3,3, style = s) document.add_paragraph("\\n") document.save(\'demo2.docx\')
以上是关于用 python 来操作word文件(使用 docx 库)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
如何在 Linux 上使用 Python 读取 word 文件信息
Python:读取 .doc.docx 两种 Word 文件简述及“Word 未能引发事件”错误