Python 解析库BeautifulSoup
Posted Crown-V
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python 解析库BeautifulSoup相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一.简介
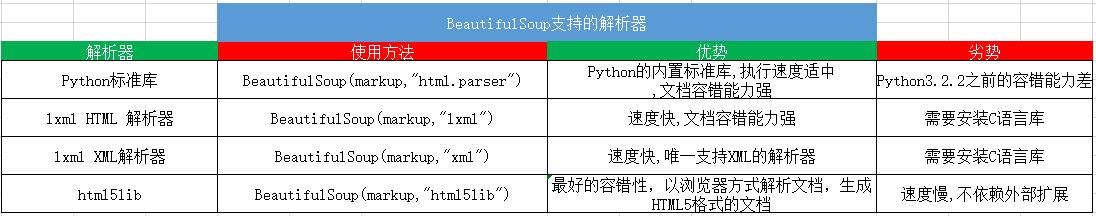
二.安装命令
pip install beautifulsoup4
三.基本使用
1.基本使用

html =\'\'\' <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>故事</title> </head> <body> <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>这个是dromouse</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sister; and their names were <a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="sister" id="link1"><!--GH--></a> <a href="http://www.baidu.com/oracle" class="sister" id="link2">Local</a>and <a href="http://www.baidu.com/title" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> </body> </html> \'\'\' from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,\'lxml\') #将网页以标准格式输出 soup.prettify() #输出title节点的内容 title = soup.title.string print(title)
2.节点选择器
直接调用节点的名称就可以选择节点元素,再调用string属性就可以得到节点内的文本了,这种选择方式速度就非常快了
选择元素直接soup.<标签名> ,获取名称soup.<标签名>.name,获取属性soup.<标签名>.attrs,获取内容soup.<标签名>.string

html =\'\'\' <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>故事</title> </head> <body> <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>这个是dromouse</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sister; and their names were <a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="sister" id="link1"><!--GH--></a> <a href="http://www.baidu.com/oracle" class="sister" id="link2">Local</a>and <a href="http://www.baidu.com/title" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> </body> </html> \'\'\' from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,\'lxml\') #将网页以标准格式输出 soup.prettify() #输出title节点的内容 title = soup.title.string #输出节点的名称 name = soup.title.name head = soup.head #获取节点的属性 attrs = soup.p.attrs attr = soup.p.attrs[\'name\'] print(attrs)
3.关联选择
在做选择的时候,有时候不能左到一步就选到想要的节点元素,需要先选中某一个节点元素,然后以它为基准再选择它的子节点、父节点、兄弟节点等。
(1)子节点和子孙节点
选择节点元素后,如果想要获取它的直接子节点,可以调用contents属性
html =\'\'\' <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>故事</title> </head> <body> <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>这个是dromouse</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sister; and their names were <a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="sister" id="link1"><!--GH--></a> <a href="http://www.baidu.com/oracle" class="sister" id="link2">Local</a>and <a href="http://www.baidu.com/title" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> </body> </html> \'\'\' from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,\'lxml\') print(soup.p.contents)
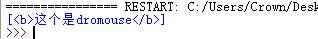
还可以用children属性,直接子孙
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,\'lxml\') #列表形式 children = soup.p.children #键值对 for i,child in enumerate(children): print(i,child)
如果想要得到所有的子孙节点的话,可以调用descendants属性
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,\'lxml\') #列表形式 children = soup.p.descendants #键值对 for i,child in enumerate(children): print(i,child)
(2)父节点和祖先节点
使用parent访问父节点
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,\'lxml\') #父节点 parent = soup.a.parent print(parent)
如果再往上访问祖父节点,使用parents
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,\'lxml\') #父节点 parent = soup.a.parents #枚举输出列表类型 list = list(enumerate(parent)) print(list)
(3)兄弟节点
如果要获取同级节点,也就是兄弟节点,下一个兄弟节点[next_siblings],上一个兄弟节点[previous_siblings]
4.方法选择器
前面所讲的方法都是通过属性来选择的,这种方法非常快,但是如果进行比较复杂的选择的话,它就比较繁琐

(1)find_all()和find()
查询所有符合条件的元素,find_all(name,attrs,recursive,text,**kwargs),find与find_all类似,只不过是返回单个元素
1.节点名

html =\'\'\' <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>故事</title> </head> <body> <ul> <li>1</li> <li>2</li> <li>3</li> <li>4</li> </ul> <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>这个是dromouse</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sister; and their names were <a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="sister" id="link1"><!--GH--></a> <a href="http://www.baidu.com/oracle" class="sister" id="link2">Local</a>and <a href="http://www.baidu.com/title" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> </body> </html> \'\'\' from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,\'lxml\') ul = soup.find_all(name=\'ul\') print(ul[0])
2.属性值

from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,\'lxml\') ul = soup.find_all(attrs={\'class\':\'title\'}) print(ul[0])
id = \'\',或者class变为class_ = \'\'
3.文本
text参数可用来匹配节点的文本,传入的形式可以是字符串,可以是正则表达式对象

import re from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,\'lxml\') ul = soup.find_all(text=re.compile(\'dr\')) print(ul[0])

5.CSS选择器
Beautiful Soup还提供了另外一种选择器,那就是CSS选择器。
使用CSS选择器时,只需要调用select()方法,传入相应的CSS选择器即可
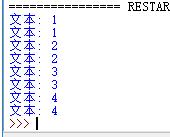
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,\'lxml\') li = soup.select("li") for i in li: print("文本:",i.get_text()) #使用get_text() print("文本:",i.string) #使用string
以上是关于Python 解析库BeautifulSoup的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
