python实现线性回归之弹性网回归
Posted 西西嘛呦
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python实现线性回归之弹性网回归相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
弹性网回归是lasso回归和岭回归的结合,其代价函数为:
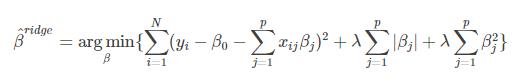
若令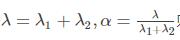 ,则
,则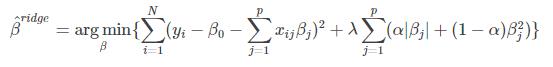
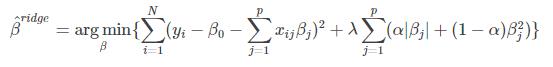
由此可知,弹性网的惩罚系数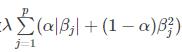 恰好为岭回归罚函数和Lasso罚函数的一个凸线性组合.当α=0时,弹性网回归即为岭回归;当 α=1时,弹性网回归即为Lasso回归.因此,弹性网回归兼有Lasso回归和岭回归的优点,既能达到变量选择的目的,又具有很好的群组效应。
恰好为岭回归罚函数和Lasso罚函数的一个凸线性组合.当α=0时,弹性网回归即为岭回归;当 α=1时,弹性网回归即为Lasso回归.因此,弹性网回归兼有Lasso回归和岭回归的优点,既能达到变量选择的目的,又具有很好的群组效应。
上述解释摘自:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41500849/article/details/80447501
接下来是实现代码,代码来源: https://github.com/eriklindernoren/ML-From-Scratch
首先还是定义一个基类,各种线性回归都需要继承该基类:
class Regression(object): """ Base regression model. Models the relationship between a scalar dependent variable y and the independent variables X. Parameters: ----------- n_iterations: float The number of training iterations the algorithm will tune the weights for. learning_rate: float The step length that will be used when updating the weights. """ def __init__(self, n_iterations, learning_rate): self.n_iterations = n_iterations self.learning_rate = learning_rate def initialize_weights(self, n_features): """ Initialize weights randomly [-1/N, 1/N] """ limit = 1 / math.sqrt(n_features) self.w = np.random.uniform(-limit, limit, (n_features, )) def fit(self, X, y): # Insert constant ones for bias weights X = np.insert(X, 0, 1, axis=1) self.training_errors = [] self.initialize_weights(n_features=X.shape[1]) # Do gradient descent for n_iterations for i in range(self.n_iterations): y_pred = X.dot(self.w) # Calculate l2 loss mse = np.mean(0.5 * (y - y_pred)**2 + self.regularization(self.w)) self.training_errors.append(mse) # Gradient of l2 loss w.r.t w grad_w = -(y - y_pred).dot(X) + self.regularization.grad(self.w) # Update the weights self.w -= self.learning_rate * grad_w def predict(self, X): # Insert constant ones for bias weights X = np.insert(X, 0, 1, axis=1) y_pred = X.dot(self.w) return y_pred
然后是弹性网回归的核心:
class l1_l2_regularization(): """ Regularization for Elastic Net Regression """ def __init__(self, alpha, l1_ratio=0.5): self.alpha = alpha self.l1_ratio = l1_ratio def __call__(self, w): l1_contr = self.l1_ratio * np.linalg.norm(w) l2_contr = (1 - self.l1_ratio) * 0.5 * w.T.dot(w) return self.alpha * (l1_contr + l2_contr) def grad(self, w): l1_contr = self.l1_ratio * np.sign(w) l2_contr = (1 - self.l1_ratio) * w return self.alpha * (l1_contr + l2_contr)
接着是弹性网回归的代码:
class ElasticNet(Regression): """ Regression where a combination of l1 and l2 regularization are used. The ratio of their contributions are set with the \'l1_ratio\' parameter. Parameters: ----------- degree: int The degree of the polynomial that the independent variable X will be transformed to. reg_factor: float The factor that will determine the amount of regularization and feature shrinkage. l1_ration: float Weighs the contribution of l1 and l2 regularization. n_iterations: float The number of training iterations the algorithm will tune the weights for. learning_rate: float The step length that will be used when updating the weights. """ def __init__(self, degree=1, reg_factor=0.05, l1_ratio=0.5, n_iterations=3000, learning_rate=0.01): self.degree = degree self.regularization = l1_l2_regularization(alpha=reg_factor, l1_ratio=l1_ratio) super(ElasticNet, self).__init__(n_iterations, learning_rate) def fit(self, X, y): X = normalize(polynomial_features(X, degree=self.degree)) super(ElasticNet, self).fit(X, y) def predict(self, X): X = normalize(polynomial_features(X, degree=self.degree)) return super(ElasticNet, self).predict(X)
其中涉及到的一些函数可参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiximayou/p/12802868.html
最后是运行主函数:
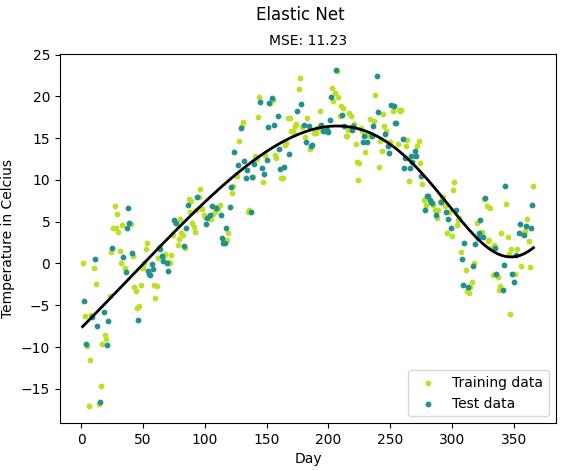
from __future__ import print_function import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import sys sys.path.append("/content/drive/My Drive/learn/ML-From-Scratch/") import numpy as np import pandas as pd # Import helper functions from mlfromscratch.supervised_learning import ElasticNet from mlfromscratch.utils import k_fold_cross_validation_sets, normalize, mean_squared_error from mlfromscratch.utils import train_test_split, polynomial_features, Plot def main(): # Load temperature data data = pd.read_csv(\'mlfromscratch/data/TempLinkoping2016.txt\', sep="\\t") time = np.atleast_2d(data["time"].values).T temp = data["temp"].values X = time # fraction of the year [0, 1] y = temp X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.4) poly_degree = 13 model = ElasticNet(degree=15, reg_factor=0.01, l1_ratio=0.7, learning_rate=0.001, n_iterations=4000) model.fit(X_train, y_train) # Training error plot n = len(model.training_errors) training, = plt.plot(range(n), model.training_errors, label="Training Error") plt.legend(handles=[training]) plt.title("Error Plot") plt.ylabel(\'Mean Squared Error\') plt.xlabel(\'Iterations\') plt.savefig("test1.png") plt.show() y_pred = model.predict(X_test) mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred) print ("Mean squared error: %s (given by reg. factor: %s)" % (mse, 0.05)) y_pred_line = model.predict(X) # Color map cmap = plt.get_cmap(\'viridis\') # Plot the results m1 = plt.scatter(366 * X_train, y_train, color=cmap(0.9), s=10) m2 = plt.scatter(366 * X_test, y_test, color=cmap(0.5), s=10) plt.plot(366 * X, y_pred_line, color=\'black\', linewidth=2, label="Prediction") plt.suptitle("Elastic Net") plt.title("MSE: %.2f" % mse, fontsize=10) plt.xlabel(\'Day\') plt.ylabel(\'Temperature in Celcius\') plt.legend((m1, m2), ("Training data", "Test data"), loc=\'lower right\') plt.savefig("test2.png") plt.show() if __name__ == "__main__": main()
结果:
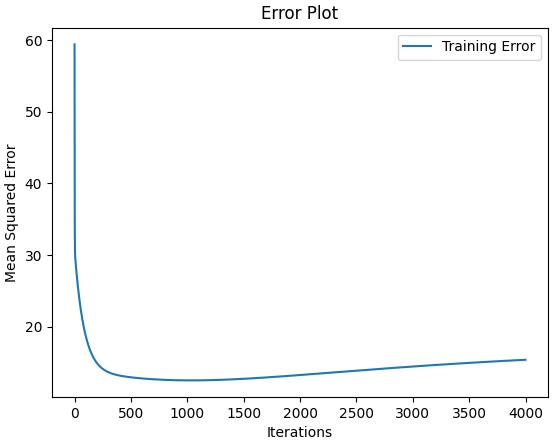
Mean squared error: 11.232800207362782 (given by reg. factor: 0.05)
以上是关于python实现线性回归之弹性网回归的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章