python copy模块
Posted -零
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python copy模块相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
python copy模块
copy模块用于对象的拷贝操作
该模块只提供了两个主要的方法:
copy.copy:浅复制
copy.deepcopy:深复制
直接赋值,深拷贝和浅拷贝的区别
直接赋值:简单地拷贝对象的引用,两个对象的id相同。就是对象的引用(别名),就是给当前内存中的对象增加一个“标签”而已。通过使用内置函数 id() ,可以看出指向内存中同一个对象。
浅拷贝(copy):拷贝父对象,不会拷贝对象的内部的子对象。即浅复制只复制对象本身,没有复制该对象所引用的对象。A shallow copy constructs a new compound object and then (to the extentpossible) inserts references into it to the objects found in the original.
深拷贝(deepcopy): copy 模块的 deepcopy 方法,完全拷贝了父对象及其子对象。即创建一个新的组合对象,同时递归地拷贝所有子对象,新的组合对象与原对象没有任何关联。虽然实际上会共享不可变的子对象,但不影响它们的相互独立性。A deep copy constructs a new compound object and then, recursively, insertscopies into it of the objects found in the original. 浅拷贝和深拷贝的不同仅仅是对组合对象来说,所谓的组合对象就是包含了其它对象的对象,如列表,类实例。而对于数字、字符串以及其它“原子”类型,没有拷贝一说,产生的都是原对象的引用,所以两者就是一样的结果了。
直接赋值
a={1:{1,2,3}}
b=a
print(a is b)
print(a ==b )
运行结果:
True
True
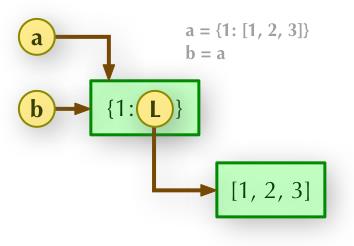
b = a: 赋值引用,a 和 b 都指向同一个对象。
浅拷贝
import copy import functools @functools.total_ordering class MyClass: def __init__(self, name): self.name = name def __eq__(self, other): return self.name == other.name def __gt__(self, other): return self.name > other.name a = MyClass(\'a\') my_list = [a] dup = copy.copy(my_list) print(\' my_list:\', my_list) print(\' dup:\', dup) print(\' dup is my_list:\', (dup is my_list)) print(\' dup == my_list:\', (dup == my_list)) print(\'dup[0] is my_list[0]:\', (dup[0] is my_list[0])) print(\'dup[0] == my_list[0]:\', (dup[0] == my_list[0]))
运行结果:
my_list: [<__main__.MyClass object at 0x101f9c160>] dup: [<__main__.MyClass object at 0x101f9c160>] dup is my_list: False dup == my_list: True dup[0] is my_list[0]: True dup[0] == my_list[0]: True
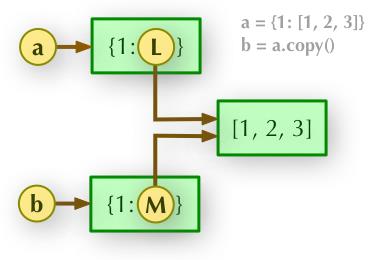
b = a.copy(): 浅拷贝, a 和 b 是一个独立的对象,但他们的子对象还是指向统一对象(是引用)。
深度拷贝
import copy import functools @functools.total_ordering class MyClass: def __init__(self, name): self.name = name def __eq__(self, other): return self.name == other.name def __gt__(self, other): return self.name > other.name a = MyClass(\'a\') my_list = [a] dup = copy.deepcopy(my_list) print(\' my_list:\', my_list) print(\' dup:\', dup) print(\' dup is my_list:\', (dup is my_list)) print(\' dup == my_list:\', (dup == my_list)) print(\'dup[0] is my_list[0]:\', (dup[0] is my_list[0])) print(\'dup[0] == my_list[0]:\', (dup[0] == my_list[0]))
运行结果:
my_list: [<__main__.MyClass object at 0x101e9c160>] dup: [<__main__.MyClass object at 0x1044e1f98>] dup is my_list: False dup == my_list: True dup[0] is my_list[0]: False dup[0] == my_list[0]: True Customizing Copy Behavior
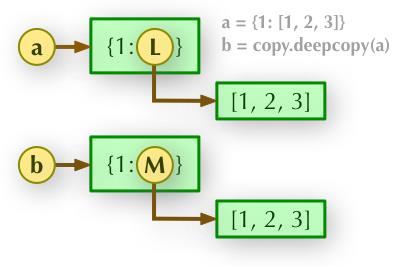
b = copy.deepcopy(a): 深度拷贝, a 和 b 完全拷贝了父对象及其子对象,两者是完全独立的。
定制复制行为
可以使用* copy__()和* deepcopy__()特殊方法控制复制的方式。
import copy import functools @functools.total_ordering class MyClass: def __init__(self, name): self.name = name def __eq__(self, other): return self.name == other.name def __gt__(self, other): return self.name > other.name def __copy__(self): print(\'__copy__()\') return MyClass(self.name) def __deepcopy__(self, memo): print(\'__deepcopy__({})\'.format(memo)) return MyClass(copy.deepcopy(self.name, memo)) a = MyClass(\'a\') sc = copy.copy(a) dc = copy.deepcopy(a)
__copy__() __deepcopy__({})
以上是关于python copy模块的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章