Python网络爬虫入门篇
Posted z寒江雪
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python网络爬虫入门篇相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 预备知识
学习者需要预先掌握Python的数字类型、字符串类型、分支、循环、函数、列表类型、字典类型、文件和第三方库使用等概念和编程方法。
Python入门篇:https://www.cnblogs.com/wenwei-blog/p/10592541.html
2. Python爬虫基本流程

a. 发送请求
使用http库向目标站点发起请求,即发送一个Request,Request包含:请求头、请求体等。
Request模块缺陷:不能执行JS 和CSS 代码。
b. 获取响应内容
如果requests的内容存在于目标服务器上,那么服务器会返回请求内容。
Response包含:html、Json字符串、图片,视频等。
c. 解析内容
对用户而言,就是寻找自己需要的信息。对于Python爬虫而言,就是利用正则表达式或者其他库提取目标信息。
解析html数据:正则表达式(RE模块),第三方解析库如Beautifulsoup,pyquery等
解析json数据:json模块
解析二进制数据:以wb的方式写入文件
d. 保存数据
解析得到的数据可以多种形式,如文本,音频,视频保存在本地。
数据库(MySQL,Mongdb、Redis)
文件
3. Requests库入门
Requests是用python语言基于urllib编写的,采用的是Apache2 Licensed开源协议的HTTP库。
3.1 Requests库安装和测试
安装:
Win平台:以“管理员身份运行cmd”,执行 pip install requests

测试:

3.2 Requests库的7个主要方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
| requests.request() | 构造一个请求,支撑一下个方法的基础方法。 |
| requests.get() | 获取HTML网页的主要方法,对应HTTP的GET |
| requests.head() | 获取HTML网页投信息的方法,对应HTTP的HEAD |
| requests.post() | 向HTML网页提交POST请求的方法,对应HTTP的POST |
| requests.put() | 向HTML网页提交PUT请求的方法,对应HTTP的PUT |
| requests.patch() | 向HTML网页提交局部修改请求,对应HTTP的PATCH |
| requests.delete() | 向HTML网页提交删除请求,对应HTTP的DELETE |
带可选参数的请求方式:
requests.request(method,url,**kwargs)
method:请求方式,对应get/put/post等7种
url:获取页面的url链接
**kwargs:控制访问的参数,均为可选项,共以下13个
params:字典或字节系列,作为参数增加到url中
>>> kv = {\'key1\':\'value1\',\'key2\':\'value2\'}
>>> r = requests.request(\'GET\',\'http://python123.io/ws\',params=kv)
>>> print(r.url)
https://python123.io/ws?key1=value1&key2=value2
data:字典、字节系列或文件对象,作为requests的内容
>>> kv = {\'key1\':\'value1\',\'key2\':\'value2\'}
>>> r = requests.request(\'POST\',\'http://python123.io/ws\',data=kv)
>>> body = \'主题内容\'
>>> r = requests.request(\'POST\',\'http:///python123.io/ws\',data=body)
json:JSON格式的数据,作为equests的内容
>>> kv = {\'key1\':\'value1\',\'key2\':\'value2\'}
>>> r = requests.request(\'POST\',\'http://python123.io/ws\',json=kv)
headers:字典,HTTP定制头
>>> hd = {\'user-agent\':\'Chrome/10\'}
>>> r = requests.request(\'POST\',\'http://www.baidu.com\',headers=hd)
cookies:字典或cookieJar,Request中的cookie
files:字典类型,传输文件
>>> f = {\'file\':open(\'/root/po.sh\',\'rb\')}
>>> r = requests.request(\'POST\',\'http://python123.io/ws\',file=f)
timeout:设置超时时间,秒为单位。
>>> r = requests.request(\'GET\',\'http://python123.io/ws\',timeout=30)
proxies:字典类型,设置访问代理服务器,可以增加登录验证。
>>> pxs = {\'http\':\'http://user:pass@10.10.10.2:1234\',
... \'https\':\'https://10.10.10.3:1234\'}
>>> r = requests.request(\'GET\',\'http://www.baidu.com\',proxies=pxs)
allow_redirects:True/False,默认为True,重定向开关
stream:True/False,默认为True,获取内容立即下载开关
verify:rue/False,默认为True,认证SSL证书开关
Cert:本地SSL证书路径
auth:元组类型,支持HTTP认证功能
3.3 Requests库的get()方法


3.4 Requests的Response对象
Response对象包含服务器返回的所有信息,也包含请求的Request信息

Response对象的属性
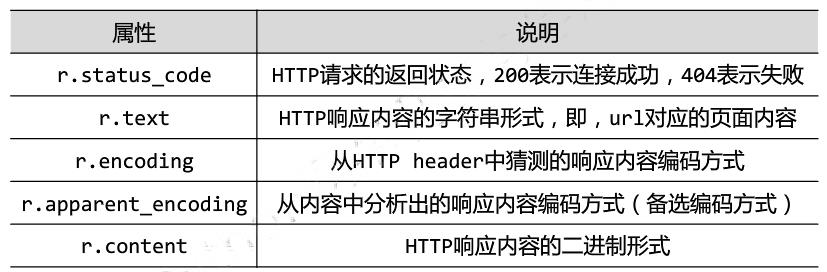

3.5 理解Response的编码

注意:编码为ISO-8859-1不支持编译中文,需要设置 r = encoding="utf-8"
3.6 理解Requests库的异常
Requests库支持常见的6种连接异常

注意:网络连接有风险。异常处理很重要。raise_for_status()如果不等于200则产生异常requests.HTTPError。
3.7 爬取网页的通用代码框架
import requests def getHTMLText(url): try: r = requests.get(url,timeout=30) r.raise_for_status() r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding return r.text except: return "产生异常" if __name__ == "__main__": url = "http://www.baidu.com" print(getHTMLText(url))
4. 网络爬虫的“盗亦有道”:Robots协议
robots是网站跟爬虫间的协议,robots.txt(统一小写)是一种存放于网站根目录下的ASCII编码的文本文件,它通常告诉网络搜索引擎的漫游器(又称网络蜘蛛),此网站中的哪些内容是不应被搜索引擎的漫游器获取的,哪些是可以被漫游器获取的。因为一些系统中的URL是大小写敏感的,所以robots.txt的文件名应统一为小写。robots.txt应放置于网站的根目录下。
网络爬虫的尺寸:

4.1 网络爬虫引发的问题
a. 网络爬虫的“性能”骚扰
web默认接受人类访问,由于网络爬虫的频繁访问会给服务器带来巨大的额资源开销。
b. 网络爬虫的法律风险
服务器上的数据有产权归属,网络爬虫获取数据牟利将带来法律风险
c. 网络爬虫的隐私泄露
网络爬虫可能具备突破简单控制访问的能力,获取被保护的数据从而泄露个人隐私。
4.2 网络爬虫限制
a. 来源审查:判断User-Agent进行限制
检查来访HTTP协议头的user-agent域,只响应浏览器或友好爬虫的访问
b. 发布公告:Robots协议
告知所有爬虫网站的爬取策略,要求遵守Robots协议
4.3 真实的Robots协议案例
京东的Robots协议:
https://www.jd.com/robots.txt

#注释,*代表所有,/代表根目录
4.4 robots协议的遵守方式
对robots协议的理解

自动或人工识别roboes.txt,z再进行内容爬取。
robots协议是建议但非约束性,网络爬虫可以补遵守,但存在法律风险。
原则:人类行为可以补参考robots协议,比如正常阅览网站,或者较少爬取网站频率。
5. Requests库网络爬虫实战
5.1 京东商品页面爬取
目标页面地址:https://item.jd.com/5089267.html

实例代码:
import requests url = \'https://item.jd.com/5089267.html\' try: r = requests.get(url) r.raise_for_status() r.encoding =r.apparent_encoding print(r.text[:1000]) except: print("爬取失败")
结果:

5.2 当当网商品页面爬取
目标页面地址:http://product.dangdang.com/26487763.html

代码:
import requests url = \'http://product.dangdang.com/26487763.html\' try: r = requests.get(url) r.raise_for_status() r.encoding =r.apparent_encoding print(r.text[:1000]) except IOError as e: print(str(e))
出现报错:
HTTPConnectionPool(host=\'127.0.0.1\', port=80): Max retries exceeded with url: /26487763.html (Caused by NewConnectionError(\'<urllib3.connection.HTTPConnection object at 0x10fc390>: Failed to establish a new connection: [Errno 111] Connection refused\',))
报错原因:当当网拒绝不合理的浏览器访问。
查看初识的http请求头:
print(r.request.headers)

代码改进:构造合理的HTTP请求头
import requests url = \'http://product.dangdang.com/26487763.html\' try: kv = {\'user-agent\':\'Mozilla/5.0\'} r = requests.get(url,headers=kv) r.raise_for_status() r.encoding =r.apparent_encoding print(r.text[:1000]) except IOError as e: print(str(e))
结果正常爬取:
5.3 百度360搜索引擎关键词提交
百度关键词接口:http://www.baidu.com/s?wd=keyword
代码实现:
import requests keyword = "python" try: kv = {\'wd\':keyword} r = requests.get("http://www.baidu.com/s",params=kv) print(r.request.url) r.raise_for_status() print(len(r.text)) except IOError as e: print(str(e))
执行结果:

360关键词接口:
http://www.so.com/s?q=keyword
代码实现:
import requests keyword = "Linux" try: kv = {\'q\':keyword} r = requests.get("http://www.so.com/s",params=kv) print(r.request.url) r.raise_for_status() print(len(r.text)) except IOError as e: print(str(e))
执行结果:

5.4 网络图片爬取和存储
网络图片链接的格式:
http://FQDN/picture.jpg
校花网:http://www.xiaohuar.com
选择一个图片地址:http://www.xiaohuar.com/d/file/20141116030511162.jpg
实现代码:
import requests import os url = "http://www.xiaohuar.com/d/file/20141116030511162.jpg" dir = "D://pics//" path = dir + url.split(\'/\')[-1] #设置图片保存路径并以原图名名字命名 try: if not os.path.exists(dir): os.mkdir(dir) if not os.path.exists(path): r = requests.get(url) with open(path,\'wb\') as f: f.write(r.content) f.close() print("文件保存成功") else: print("文件已存在") except IOError as e: print(str(e))
查看图片已经存在:

5.5 ip地址归属地查询
ip地址归属地查询网站接口:http://www.ip138.com/ips138.asp?ip=
实现代码:
import requests url = "http://www.ip38.com/ip.php?ip=" try: r = requests.get(url+\'104.193.88.77\') r.raise_for_status() r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding print(r.text) except IOError as e: print(str(e))
5.5 有道翻译翻译表单提交
打开有道翻译,在开发者模式依次单击“Network”按钮和“XHR”按钮,找到翻译数据:

import requests import json def get_translate_date(word=None): url = "http://fanyi.youdao.com/translate?smartresult=dict&smartresult=rule" #post参数需要放在请求实体里,构建一个新字典 form_data = {\'i\': word, \'from\': \'AUTO\', \'to\': \'AUTO\', \'smartresult\': \'dict\', \'client\': \'fanyideskweb\', \'salt\': \'15569272902260\', \'sign\': \'b2781ea3e179798436b2afb674ebd223\', \'ts\': \'1556927290226\', \'bv\': \'94d71a52069585850d26a662e1bcef22\', \'doctype\': \'json\', \'version\': \'2.1\', \'keyfrom\': \'fanyi.web\', \'action\': \'FY_BY_REALTlME\' } #请求表单数据 response = requests.post(url,data=form_data) #将JSON格式字符串转字典 content = json.loads(response.text) #打印翻译后的数据 print(content[\'translateResult\'][0][0][\'tgt\']) if __name__ == \'__main__\': word = input("请输入你要翻译的文字:") get_translate_date(word)
执行结果:

6 Beautiful Soup库入门
6.1 简介
6.2 Beautiful Soup安装
6.3 BeautifulSoup库解析器
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(\'<p>Hello</p>\',\'lxml\') print(soup.p.string)
6.4 BeautifulSoup的基本用法
>>> from bs4 import BeautifulSoup >>> import requests >>> r = requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html") >>> demo = r.text >>> demo \'<html><head><title>This is a python demo page</title></head>\\r\\n<body>\\r\\n<p class="title"><b>The demo python introduces several python courses.</b></p>\\r\\n<p class="course">Python is a wonderful general-purpose programming language. You can learn Python from novice to professional by tracking the following courses:\\r\\n<a href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" class="py1" id="link1">Basic Python</a> and <a href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-1001870001" class="py2" id="link2">Advanced Python</a>.</p>\\r\\n</body></html>\' >>> soup = BeautifulSoup(demo,"html.parser") >>> soup.title #获取标题 <title>This is a python demo page</title> >>> soup.a #获取a标签 <a class="py1" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" id="link1">Basic Python</a> >>> soup.title.string \'This is a python demo page\' >>> soup.prettify() #输出html标准格式内容 \'<html>\\n <head>\\n <title>\\n This is a python demo page\\n </title>\\n </head>\\n <body>\\n <p class="title">\\n <b>\\n The demo python introduces several python courses.\\n </b>\\n </p>\\n <p class="course">\\n Python is a wonderful general-purpose programming language. You can learn Python from novice to professional by tracking the following courses:\\n <a class="py1" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" id="link1">\\n Basic Python\\n </a>\\n and\\n <a class="py2" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-1001870001" id="link2">\\n Advanced Python\\n </a>\\n .\\n </p>\\n </body>\\n</html>\' >>> soup.a.name #每个<tag>都有自己的名字,通过<tag>.name获取 \'a\' >>> soup.p.name \'p\' >>> tag = soup.a >>> tag.attrs {\'href\': \'http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001\', \'class\': [\'py1\'], \'id\': \'link1\'} >>> tag.attrs[\'class\'] [\'py1\'] >>> tag.attrs[\'href\'] \'http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001\' >>> type(tag.attrs) <class \'dict\'> >>> type(tag) <class \'bs4.element.Tag\'> >>>
6.5 标签树的遍历
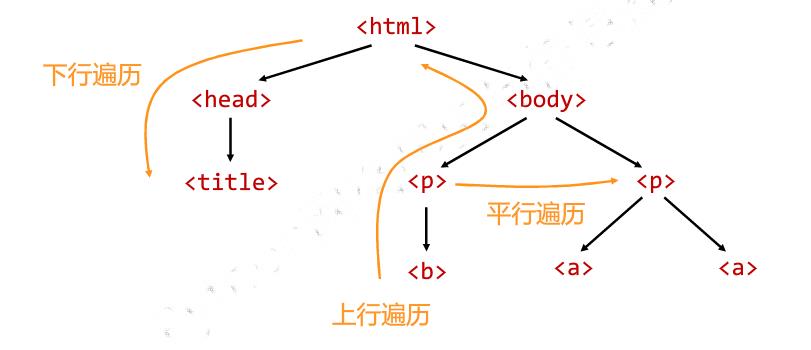
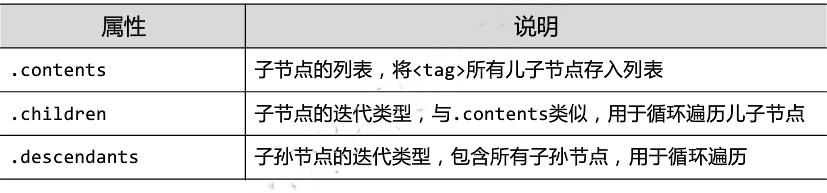

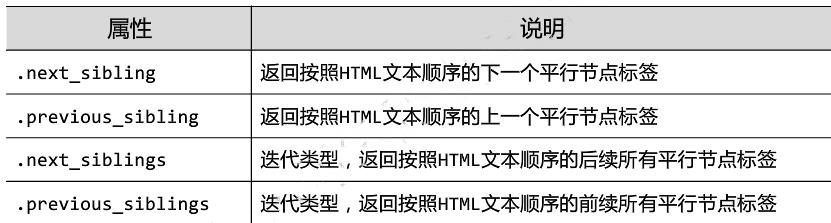
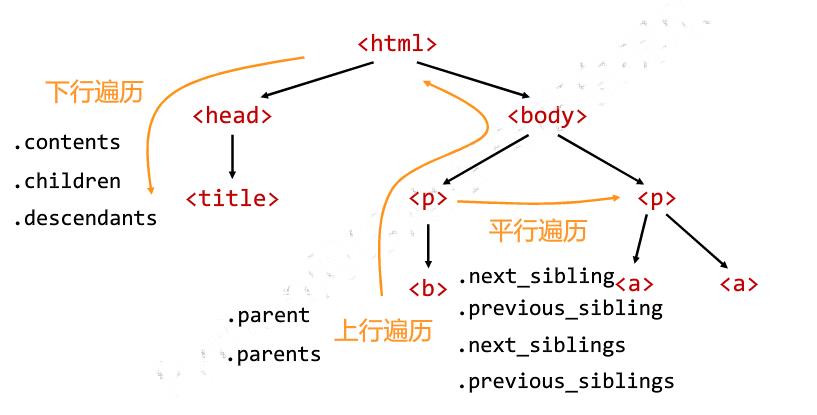
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import requests demo = requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html").text soup = BeautifulSoup(demo,"html.parser") #标签树的上行遍历 print("遍历儿子节点:\\n") for child in soup.body.children: print(child) print("遍历子孙节点:\\n") for child1 in soup.body.descendants: print(child1) print(soup.title.parent) print(soup.html.parent) for parent in soup.a.parents: if parent is None: print(parent) else: print(parent.name) #标签树的平行遍历 print(soup.a.next_sibling) print(soup.a.next_sibling.next_sibling) print(soup.a.previous_sibling)
7 正则表达式
正则表达式是处理字符串的强大工具,它有自己特定的语法结构,实现字符串的检索、替换、匹配验证都可以。对于爬虫来说,
从HTML里提取想要的信息非常方便。python的re库提供了整个正则表达式的实现
7.1 案例引入
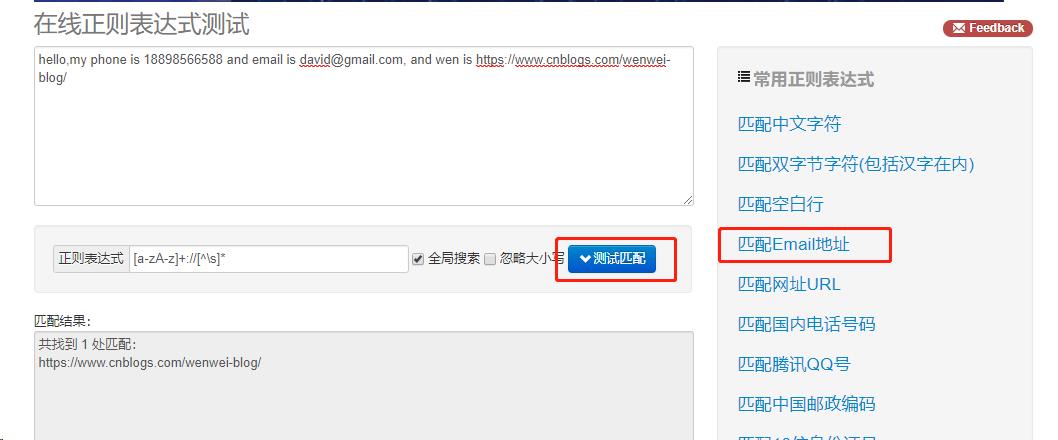
这里介绍一个正则表达式测试工具http://tool.oschina.net/regex,输入待匹配的文本,然选择常用的正则表达式,得到相应的匹配结果,
适合新手入门。这里输入:
hello,my phone is 18898566588 and email is david@gmail.com, and wen is https://www.cnblogs.com/wenwei-blog/
点击“匹配Email地址”,即可匹配出网址。
7.2 常用正则表达式匹配规则
以上是关于Python网络爬虫入门篇的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章