Python操作MySql --Python
Posted Thanlon
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python操作MySql --Python相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Python版本:v3.7
模块:pymysql
1、连接数据库
connectDB.py:
# coding:utf-8
import pymysql
host = \'localhost\' # 主机
username = \'root\' # 用户名
pwd = \'nxl123\' # 密码
dbName = \'testdb\' # 数据库名
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect(host, username, pwd, dbName)
# 通过cursor方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
# sql语句
sql = \'SELECT VERSION()\'
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 使用fetchone方法获取一个查询结果集
data = cursor.fetchone()
# 输出结果集
print(\'db version:%s\' % data)
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
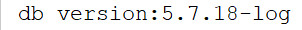
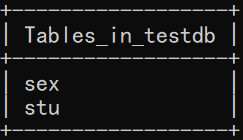
2、创建表
createTables.py:
# coding:utf-8
import pymysql
host = \'localhost\' # 主机
username = \'root\' # 用户名
pwd = \'nxl123\' # 密码
dbName = \'testdb\' # 数据库名
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect(host, username, pwd, dbName)
# 通过cursor方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
# 执行sql语句,如果存在stu和sex表,就将其删除
cursor.execute(\'DROP TABLE IF EXISTS stu\')
cursor.execute(\'DROP TABLE IF EXISTS sex\')
# sql语句,创建stu表
sql = \'\'\'CREATE TABLE stu(
stuId SMALLINT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
stuNo VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL UNIQUE KEY,
stuName VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
age SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
sexId SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL)\'\'\'
sql2 = \'\'\'CREATE TABLE sex(
id SMALLINT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY,
sex ENUM(\'男\',\'女\') NOT NULL)\'\'\'
# 执行sql、sql2语句
cursor.execute(sql)
cursor.execute(sql2)
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
3、插入数据
insertData.py:
# coding:utf-8
import pymysql
host = \'localhost\' # 主机
username = \'root\' # 用户名
pwd = \'nxl123\' # 密码
dbName = \'testdb\' # 数据库名
db = pymysql.connect(host, username, pwd, dbName)
# 通过cursor方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
# sql语句
# sql = \'\'\'INSERT stu(stuNo,stuName,age,sexId) VALUES(\'2015011070\',\'Thanlon\',22,1) \'\'\'
# sql = \'\'\'INSERT stu(stuNo,stuName,age,sexId) VALUES(\'2015011071\',\'Maria\',20,2) \'\'\'
# sql = \'\'\'INSERT sex(id,sex) VALUES(1,\'男\')\'\'\'
sql = \'\'\'INSERT sex(id,sex) VALUES(2,\'女\')\'\'\'
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交到数据库执行
db.commit()
except:
# 发生错误时回滚
db.rollback()
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
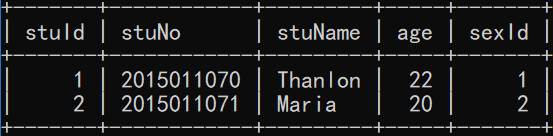
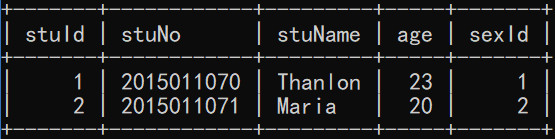
stu 表:
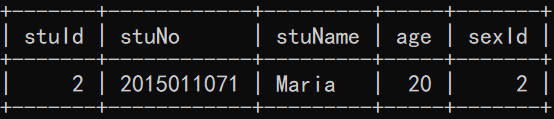
sex 表:

4、删除数据
deleteData.py:
# coding:utf-8
import pymysql
host = \'localhost\' # 主机
username = \'root\' # 用户名
pwd = \'nxl123\' # 密码
dbName = \'testdb\' # 数据库名
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect(\'localhost\', username, pwd, dbName)
# 通过cursor方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "DELETE FROM stu WHERE age>\'%d\'" % (20)
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交到数据库执行
db.commit()
except:
# 语句产生异常时打印提示信息
print(\'更新数据时出现异常!\')
finally:
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
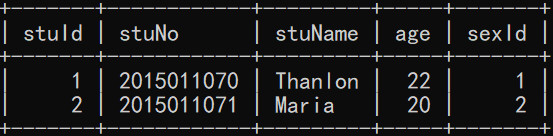
stu表:(删除数据后的stu表)
5、查询数据
selectData.py:
# coding:utf-8
import pymysql
host = \'localhost\' # 主机
username = \'root\' # 用户名
pwd = \'nxl123\' # 密码
dbName = \'testdb\' # 数据库名
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect(host, username, pwd, dbName)
# 通过cursor方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
# sql = \'\'\'SELECT *FROM stu\'\'\'
sql = \'\'\'SELECT stuID,stuNo,stuName,age,x.sex FROM sex AS x INNER JOIN stu AS s ON s.sexId = x.id\'\'\'
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# results接收全部的返回结果行
results = cursor.fetchall()
# print(results)
# 返回执行execute方法后影响的行数
results_count = cursor.rowcount
# 打印输出影响的行数
print(\'execute()方法执行后影响的行数:%d行\' % results_count)
# 遍历结果集
for row in results:
stuID = row[0]
stuNo = row[1]
stuName = row[2]
age = row[3]
sex = row[4]
# 打印查询结果
print(stuID, stuNo, stuName, age, sex)
except:
print(\'获取数据出现异常!\')
finally:
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()

6、修改数据
updateData.py:
# coding:utf-8
import pymysql
host = \'localhost\' # 主机
username = \'root\' # 用户名
pwd = \'nxl123\' # 密码
dbName = \'testdb\' # 数据库名
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect(host, username, pwd, dbName)
# 通过cursor方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
# 将性别为男的学生年龄加1
sql = \'\'\'UPDATE stu SET age=age+1 WHERE sexId=1\'\'\'
try:
# 执行语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交到数据库执行
db.commit()
except:
print(\'更新数据时出现异常!\')
finally:
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
执行语句前stu表信息:
执行语句后stu表信息:
以上是关于Python操作MySql --Python的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章