python 数据可视化 -- 真实数据的噪声平滑处理
Posted 0820LL
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python 数据可视化 -- 真实数据的噪声平滑处理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
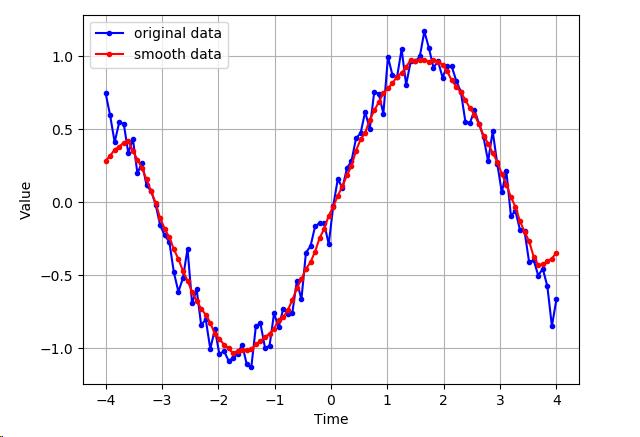
平滑数据噪声的一个简单朴素的做法是,对窗口(样本)求平均,然后仅仅绘制出给定窗口的平均值,而不是所有的数据点。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def moving_average(interval, window_size): window = np.ones(int(window_size)) / float(window_size) return np.convolve(interval, window, \'same\') # numpy的卷积函数 t = np.linspace(start = -4, stop = 4, num = 100) y = np.sin(t) + np.random.randn(len(t)) * 0.1 y_av = moving_average(interval = y, window_size = 10) plt.plot(t, y, "b.-", t, y_av, "r.-") plt.xlabel(\'Time\') plt.ylabel(\'Value\') plt.legend([\'original data\', \'smooth data\']) plt.grid(True) plt.show()
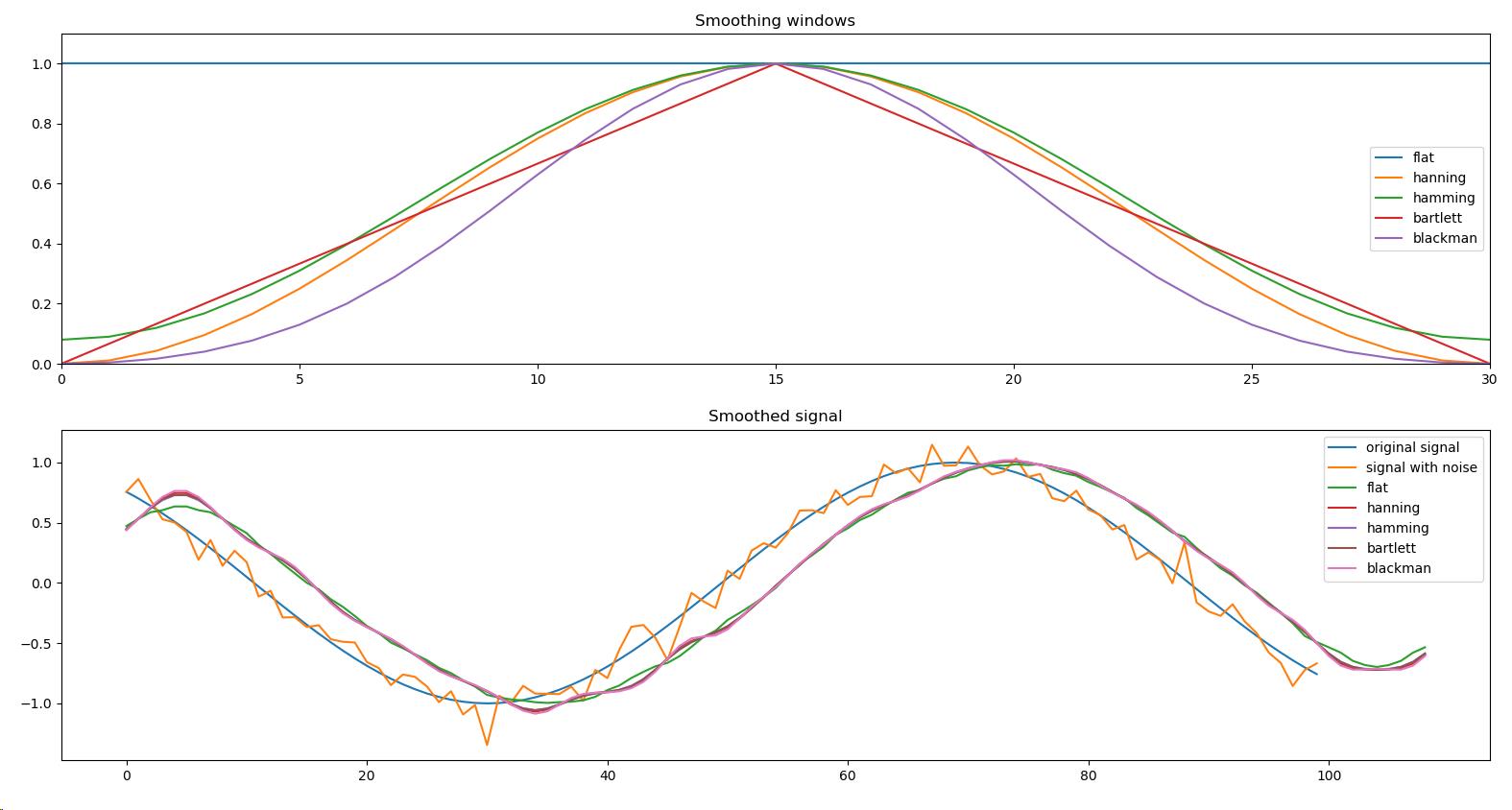
以下方法是基于信号(数据点)窗口的卷积(函数的总和)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np WINDOWS = [\'flat\', \'hanning\', \'hamming\', \'bartlett\', \'blackman\'] def smooth(x, window_len = 11, window = \'hanning\'): if x.ndim != 1: raise ValueError(\'smooth only accepts 1 dimension arrays.\') if x.size < window_len: raise ValueError(\'Input vector needs to be bigger than window size.\') if window_len < 3: return x if not window in WINDOWS: raise ValueError(\'Window is one of "flat", "hanning", "hamming", "bartlett", "blackman"\') s = np.r_[x[window_len-1:0:-1], x, x[-1:-window_len:-1]] if window == \'flat\': w = np.ones(window_len, \'d\') else: w = eval(\'np.\' + window + \'(window_len)\') y = np.convolve(w/w.sum(), s, mode=\'valid\') return y t = np.linspace(-4, 4, 100) x = np.sin(t) xn = x + np.random.randn(len(t))*0.1 y = smooth(x) ws = 31 plt.figure() plt.subplot(211) plt.plot(np.ones(ws)) for w in WINDOWS[1:]: eval(\'plt.plot(np.\' + w + \'(ws))\') plt.axis([0, 30, 0, 1.1]) plt.legend(WINDOWS) plt.title(\'Smoothing windows\') plt.subplot(212) plt.plot(x) plt.plot(xn) for w in WINDOWS: plt.plot(smooth(xn, 10, w)) l = [\'original signal\', \'signal with noise\'] l.extend(WINDOWS) plt.legend(l) plt.title(\'Smoothed signal\') plt.show()
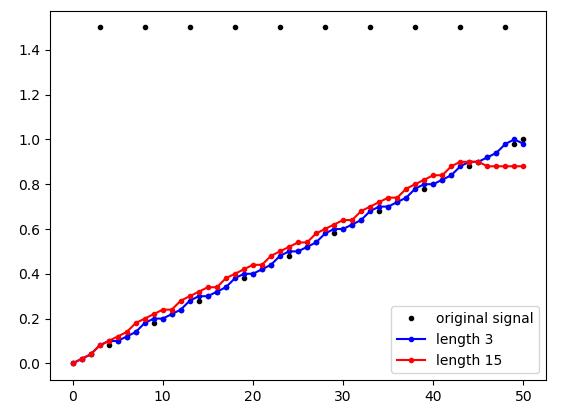
中值过滤,即逐项的遍历信号,并用相邻信号项中的中值替代当前项
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import scipy.signal as signal x = np.linspace(start=0, stop=1, num=51) x[3::5] = 1.5 # 从第4个 数开始,每个5个数,将其值改为 1.5 plt.plot(x, \'k.\') plt.plot(signal.medfilt(volume=x, kernel_size=3), \'b.-\') # 在给定大小的邻域内取中值替代数据值,在邻域中没有元素的位置补0 plt.plot(signal.medfilt(volume=x, kernel_size=15), \'r.-\') plt.legend([\'original signal\', \'length 3\', \'length 15\']) plt.show()
以上是关于python 数据可视化 -- 真实数据的噪声平滑处理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章