<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<link rel="icon" type="image/svg+xml" href="/vite.svg" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Vite + TS</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script type="module" src="/src/main.ts"></script>
</body>
</html>
"name": "webgpu_learn_typescript",
"private": true,
"version": "0.0.0",
"type": "module",
"scripts":
"dev": "vite",
"build": "tsc && vite build",
"preview": "vite preview"
,
"devDependencies":
"typescript": "^5.0.2",
"vite": "^4.3.2"
,
"dependencies":
"@types/node": "^20.1.7",
"@webgpu/types": "^0.1.32",
"ts-shader-loader": "^2.0.2"
"compilerOptions":
"target": "ES2020",
"useDefineForClassFields": true,
"module": "ESNext",
"lib": ["ES2020", "DOM", "DOM.Iterable"],
"skipLibCheck": true,
/* Bundler mode */
"moduleResolution": "bundler",
"allowImportingTsExtensions": true,
"resolveJsonModule": true,
"isolatedModules": true,
"noEmit": true,
/* Linting */
"strict": true,
"noUnusedLocals": true,
"noUnusedParameters": true,
"noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": true,
// type
"types": ["@webgpu/types"],
// js
"allowJs": true
,
"include": ["src"]
/Users/song/Code/webgpu_learn/webgpu-for-beginners/webgpu_learn_typescript/src_04_渐变颜色的矩形/main.ts
async function main()
const adapter = await navigator.gpu?.requestAdapter();
const device = await adapter?.requestDevice()!;
if (!device)
console.log("need a browser that supports WebGPU");
return;
// Get a WebGPU context from the canvas and configure it
const canvas = document.createElement("canvas");
canvas.style.width = "500px";
canvas.style.height = "300px";
canvas.style.border = "1px solid red";
const context = canvas.getContext("webgpu")!;
const presentationFormat = navigator.gpu.getPreferredCanvasFormat();
context.configure(
device,
format: presentationFormat,
);
//
const module = device.createShaderModule(
label: "our hardcoded rgb triangle shaders",
code: `
struct OurVertexShaderOutput
@builtin(position) position: vec4f,
@location(0) color: vec4f,
;
@vertex fn vs(
@builtin(vertex_index) vertexIndex : u32
) -> OurVertexShaderOutput
// 位置
var pos = array<vec2f, 6>(
// 第一个三角形的坐标
vec2f(0.0, 0.0), // 0
vec2f(1.0, 0.0), // 1
vec2f(1.0, 1.0), // 2
vec2f(1.0, 1.0), // 3
vec2f(0.0, 1.0), // 4
vec2f(0.0, 0.0), // 5
);
// 颜色
var color = array<vec4f, 6>(
vec4f(1, 0, 0, 1),
vec4f(1, 0, 0, 1),
vec4f(0, 1, 0, 1),
vec4f(0, 1, 0, 1),
vec4f(0, 1, 0, 1),
vec4f(1, 0, 0, 1),
);
var vsOutput: OurVertexShaderOutput;
vsOutput.position = vec4f(pos[vertexIndex], 0.0, 1.0);
// 渐变颜色的矩形
vsOutput.color = color[vertexIndex];
return vsOutput;
@fragment fn fs(fsInput: OurVertexShaderOutput) -> @location(0) vec4f
return fsInput.color;
`,
);
const pipeline = device.createRenderPipeline(
label: "hardcoded rgb triangle pipeline",
layout: "auto",
vertex:
module,
entryPoint: "vs",
,
fragment:
module,
entryPoint: "fs",
targets: [ format: presentationFormat ],
,
);
const renderPassDescriptor =
label: "our basic canvas renderPass",
colorAttachments: [
// view: <- to be filled out when we render
clearValue: [1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1],
loadOp: "clear",
storeOp: "store",
,
],
;
function render()
// Get the current texture from the canvas context and
// set it as the texture to render to.
renderPassDescriptor.colorAttachments[0].view = context
.getCurrentTexture()
.createView();
const encoder = device.createCommandEncoder(
label: "render triangle encoder",
);
const pass = encoder.beginRenderPass(
renderPassDescriptor as GPURenderPassDescriptor
);
pass.setPipeline(pipeline);
pass.draw(6); // call our vertex shader 3 times
pass.end();
const commandBuffer = encoder.finish();
device.queue.submit([commandBuffer]);
render();
document.body.appendChild(canvas);
main();
/Users/song/Code/webgpu_learn/webgpu-for-beginners/webgpu_learn_typescript/src_02_三角形/main.ts
async function main()
const adapter = await navigator.gpu?.requestAdapter();
const device = await adapter?.requestDevice()!;
if (!device)
fail("need a browser that supports WebGPU");
return;
// Get a WebGPU context from the canvas and configure it
const canvas = document.createElement("canvas");
canvas.style.width = "500px";
canvas.style.height = "300px";
// const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const context = canvas.getContext("webgpu")!;
const presentationFormat = navigator.gpu.getPreferredCanvasFormat();
context.configure(
device,
format: presentationFormat,
);
//
const module = device.createShaderModule(
label: "our hardcoded rgb triangle shaders",
code: `
struct OurVertexShaderOutput
@builtin(position) position: vec4f,
@location(0) color: vec4f,
;
@vertex fn vs(
@builtin(vertex_index) vertexIndex : u32
) -> OurVertexShaderOutput
// 位置
var pos = array<vec2f, 3>(
vec2f(0.0, 0.0), // top center
vec2f(1.0, 0.0), // bottom left
vec2f(0.5, 1.0) // bottom right
);
// 颜色
var color = array<vec4f, 3>(
vec4f(1, 0, 0, 1), // red
vec4f(0, 1, 0, 1), // green
vec4f(0, 0, 1, 1), // blue
);
var vsOutput: OurVertexShaderOutput;
vsOutput.position = vec4f(pos[vertexIndex], 0.0, 1.0);
vsOutput.color = color[vertexIndex];
return vsOutput;
@fragment fn fs(fsInput: OurVertexShaderOutput) -> @location(0) vec4f
return fsInput.color;
`,
);
const pipeline = device.createRenderPipeline(
label: "hardcoded rgb triangle pipeline",
layout: "auto",
vertex:
module,
entryPoint: "vs",
,
fragment:
module,
entryPoint: "fs",
targets: [ format: presentationFormat ],
,
);
const renderPassDescriptor =
label: "our basic canvas renderPass",
colorAttachments: [
// view: <- to be filled out when we render
clearValue: [0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 1],
loadOp: "clear",
storeOp: "store",
,
],
;
function render()
// Get the current texture from the canvas context and
// set it as the texture to render to.
renderPassDescriptor.colorAttachments[0].view = context
.getCurrentTexture()
.createView();
const encoder = device.createCommandEncoder(
label: "render triangle encoder",
);
const pass = encoder.beginRenderPass(
renderPassDescriptor as GPURenderPassDescriptor
);
pass.setPipeline(pipeline);
pass.draw(3); // call our vertex shader 3 times
pass.end();
const commandBuffer = encoder.finish();
device.queue.submit([commandBuffer]);
const observer = new ResizeObserver((entries) =>
for (const entry of entries)
const canvas = entry.target;
const width = entry.contentBoxSize[0].inlineSize;
const height = entry.contentBoxSize[0].blockSize;
(canvas as HTMLCanvasElement).width = Math.min(
width,
device.limits.maxTextureDimension2D
);
(canvas as HTMLCanvasElement).height = Math.min(
height,
device.limits.maxTextureDimension2D
);
// re-render
render();
);
observer.observe(canvas);
document.body.appendChild(canvas);
function fail(msg: string)
// eslint-disable-next-line no-alert
alert(msg);
main();
/Users/song/Code/webgpu_learn/webgpu-for-beginners/webgpu_learn_typescript/src_06_红色三角形_郭隆帮老师/main.ts
import vertexShader, fragmentShader from "./shader";
async function main()
// 获取适配器
const adapter = await navigator.gpu?.requestAdapter();
// 获取gpu设备对象
const device = await adapter?.requestDevice()!;
if (!device)
fail("need a browser that supports WebGPU");
return;
// Get a WebGPU context from the canvas and configure it
// 创建canvas画布,配置gpu上下文,将该元素作为webgpu的画布
const canvas = document.createElement("canvas");
canvas.style.width = "500px";
canvas.style.height = "300px";
const context = canvas.getContext("webgpu")!;
const presentationFormat = navigator.gpu.getPreferredCanvasFormat();
context.configure(
device, // gpu设备对象
format: presentationFormat, //gpu渲染器使用的颜色格式,比如说rgba bgra,这里默认就好
);
const vertexArray = new Float32Array([
// 三角形三个顶点坐标的x、y、z值
0.0,
0.0,
0.0, //顶点1坐标
1.0,
0.0,
0.0, //顶点2坐标
0.0,
1.0,
0.0, //顶点3坐标
]);
// 定点缓冲区
const vertexBuffer = device.createBuffer(
size: vertexArray.byteLength, //顶点数据的字节长度
//usage设置该缓冲区的用途(作为顶点缓冲区|可以写入顶点数据)
usage: GPUBufferUsage.VERTEX | GPUBufferUsage.COPY_DST,
);
// 将顶点信息写入缓冲器
device.queue.writeBuffer(vertexBuffer, 0, vertexArray);
const pipeline = device.createRenderPipeline(
layout: "auto",
vertex:
//顶点相关配置
buffers: [
// 顶点所有的缓冲区模块设置
//其中一个顶点缓冲区设置
arrayStride: 3 * 4, //一个顶点数据占用的字节长度,该缓冲区一个顶点包含xyz三个分量,每个数字是4字节浮点数,3*4字节长度
attributes: [
// 顶点缓冲区属性
shaderLocation: 0, //GPU显存上顶点缓冲区标记存储位置
format: "float32x3", //格式:loat32x3表示一个顶点数据包含3个32位浮点数
offset: 0, //arrayStride表示每组顶点数据间隔字节数,offset表示读取改组的偏差字节数,没特殊需要一般设置0
,
],
,
],
module: device.createShaderModule(
label: "triangle vertex",
code: vertexShader,
),
entryPoint: "main",
,
fragment:
module: device.createShaderModule(
label: "fragment vertex",
code: fragmentShader,
),
entryPoint: "main", //指定入口函数
targets: [
format: presentationFormat, //和WebGPU上下文配置的颜色格式保持一致
,
],
,
primitive:
topology: "triangle-list", //绘制三角形
// topology: "point-list", //绘制三角形
// topology: "line-list", //绘制三角形
,
);
// 创建GPU命令编码器对象
const commandEncoder = device.createCommandEncoder();
const renderPass = commandEncoder.beginRenderPass(
label: "our basic canvas renderPass",
// 给渲染通道指定颜色缓冲区,配置指定的缓冲区
colorAttachments: [
// 指向用于Canvas画布的纹理视图对象(Canvas对应的颜色缓冲区)
// 该渲染通道renderPass输出的像素数据会存储到Canvas画布对应的颜色缓冲区(纹理视图对象)
view: context.getCurrentTexture().createView(),
storeOp: "store", //像素数据写入颜色缓冲区
loadOp: "clear",
clearValue: r: 0.5, g: 0.5, b: 0.5, a: 1.0 , //背景颜色
,
],
);
// 关联顶点缓冲区数据和渲染管线
renderPass.setVertexBuffer(0, vertexBuffer);
renderPass.setPipeline(pipeline);
renderPass.draw(3); // call our vertex shader 3 times
renderPass.end();
// 命令缓冲器
const commandBuffer = commandEncoder.finish();
device.queue.submit([commandBuffer]);
document.body.appendChild(canvas);
function fail(msg: string)
// eslint-disable-next-line no-alert
alert(msg);
main();
// 顶点着色器代码
const vertexShader = /* wgsl */ `
@vertex
fn main(@location(0) pos: vec3<f32>) -> @builtin(position) vec4<f32>
return vec4<f32>(pos,1.0);
`;
// 片元着色器代码
const fragmentShader = /* wgsl */ `
@fragment
fn main() -> @location(0) vec4<f32>
return vec4<f32>(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);//片元设置为红色
`;
export vertexShader, fragmentShader ;
/Users/song/Code/webgpu_learn/webgpu-for-beginners/webgpu_learn_typescript/src_01_测试是否支持webgpu/main.ts
const oApp = document.getElementById("app")!;
if (navigator.gpu)
oApp.innerHTML = "web gpu ok";
else
oApp.innerHTML = "web gpu not ok";
/Users/song/Code/webgpu_learn/webgpu-for-beginners/webgpu_learn_typescript/src_05_两倍数组/main.ts
async function main()
const adapter = await navigator.gpu?.requestAdapter();
const device = await adapter?.requestDevice();
if (!device)
console.log("need a browser that supports WebGPU");
return;
const module = device.createShaderModule(
label: "doubling compute module",
code: `
@group(0) @binding(0) var<storage, read_write> data: array<f32>;
@compute @workgroup_size(1) fn computeSomething(
@builtin(global_invocation_id) id: vec3<u32>
)
let i = id.x;
data[i] = data[i] * 2.0;
`,
);
const pipeline = device.createComputePipeline(
label: "doubling compute pipeline",
layout: "auto",
compute:
module,
entryPoint: "computeSomething",
,
);
const input = new Float32Array([1, 3, 5]);
// create a buffer on the GPU to hold our computation
// input and output
const workBuffer = device.createBuffer(
label: "work buffer",
size: input.byteLength,
usage:
GPUBufferUsage.STORAGE |
GPUBufferUsage.COPY_SRC |
GPUBufferUsage.COPY_DST,
);
// Copy our input data to that buffer
device.queue.writeBuffer(workBuffer, 0, input);
// create a buffer on the GPU to get a copy of the results
const resultBuffer = device.createBuffer(
label: "result buffer",
size: input.byteLength,
usage: GPUBufferUsage.MAP_READ | GPUBufferUsage.COPY_DST,
);
// Setup a bindGroup to tell the shader which
// buffer to use for the computation
const bindGroup = device.createBindGroup(
label: "bindGroup for work buffer",
layout: pipeline.getBindGroupLayout(0),
entries: [ binding: 0, resource: buffer: workBuffer ],
);
// Encode commands to do the computation
const encoder = device.createCommandEncoder(
label: "doubling encoder",
);
const pass = encoder.beginComputePass(
label: "doubling compute pass",
);
pass.setPipeline(pipeline);
pass.setBindGroup(0, bindGroup);
pass.dispatchWorkgroups(input.length);
pass.end();
// Encode a command to copy the results to a mappable buffer.
encoder.copyBufferToBuffer(workBuffer, 0, resultBuffer, 0, resultBuffer.size);
// Finish encoding and submit the commands
const commandBuffer = encoder.finish();
device.queue.submit([commandBuffer]);
// Read the results
await resultBuffer.mapAsync(GPUMapMode.READ);
// const result = new Float32Array(
// (resultBuffer.getMappedRange() as any).slice()
// );
const result = new Float32Array(resultBuffer.getMappedRange().slice(0));
resultBuffer.unmap();
console.log("input", input);
console.log("result", result);
main();
/Users/song/Code/webgpu_learn/webgpu-for-beginners/webgpu_learn_typescript/src_03_纯红色三角形/main.ts
async function main()
const adapter = await navigator.gpu?.requestAdapter();
const device = await adapter?.requestDevice()!;
if (!device)
fail("need a browser that supports WebGPU");
return;
// Get a WebGPU context from the canvas and configure it
const canvas = document.createElement("canvas");
canvas.style.width = "500px";
canvas.style.height = "300px";
canvas.style.border = "1px solid red";
// const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const context = canvas.getContext("webgpu")!;
const presentationFormat = navigator.gpu.getPreferredCanvasFormat();
context.configure(
device,
format: presentationFormat,
);
//
const module = device.createShaderModule(
label: "our hardcoded rgb triangle shaders",
code: `
struct OurVertexShaderOutput
@builtin(position) position: vec4f,
@location(0) color: vec4f,
;
@vertex fn vs(
@builtin(vertex_index) vertexIndex : u32
) -> OurVertexShaderOutput
// 位置
var pos = array<vec2f, 3>(
vec2f(0.0, 0.0), // top center
vec2f(1.0, 0.0), // bottom left
vec2f(0.0, 1.0) // bottom right
);
// 颜色
var color = array<vec4f, 3>(
vec4f(1, 0, 0, 1), // red
vec4f(0, 1, 0, 1), // green
vec4f(0, 0, 1, 1), // blue
);
var vsOutput: OurVertexShaderOutput;
vsOutput.position = vec4f(pos[vertexIndex], 0.0, 1.0);
// 纯红色的三角形
// vsOutput.color = color[vertexIndex];
vsOutput.color = vec4f(1, 0, 0, 0.5);
return vsOutput;
@fragment fn fs(fsInput: OurVertexShaderOutput) -> @location(0) vec4f
return fsInput.color;
`,
);
const pipeline = device.createRenderPipeline(
label: "hardcoded rgb triangle pipeline",
layout: "auto",
vertex:
module,
entryPoint: "vs",
,
fragment:
module,
entryPoint: "fs",
targets: [ format: presentationFormat ],
,
);
const renderPassDescriptor =
label: "our basic canvas renderPass",
colorAttachments: [
// view: <- to be filled out when we render
clearValue: [1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1],
loadOp: "clear",
storeOp: "store",
,
],
;
function render()
// Get the current texture from the canvas context and
// set it as the texture to render to.
renderPassDescriptor.colorAttachments[0].view = context
.getCurrentTexture()
.createView();
const encoder = device.createCommandEncoder(
label: "render triangle encoder",
);
const pass = encoder.beginRenderPass(
renderPassDescriptor as GPURenderPassDescriptor
);
pass.setPipeline(pipeline);
pass.draw(3); // call our vertex shader 3 times
pass.end();
const commandBuffer = encoder.finish();
device.queue.submit([commandBuffer]);
const observer = new ResizeObserver((entries) =>
for (const entry of entries)
const canvas = entry.target;
const width = entry.contentBoxSize[0].inlineSize;
const height = entry.contentBoxSize[0].blockSize;
(canvas as HTMLCanvasElement).width = Math.min(
width,
device.limits.maxTextureDimension2D
);
(canvas as HTMLCanvasElement).height = Math.min(
height,
device.limits.maxTextureDimension2D
);
// re-render
render();
);
observer.observe(canvas);
document.body.appendChild(canvas);
function fail(msg: string)
// eslint-disable-next-line no-alert
alert(msg);
main();
/Users/song/Code/webgpu_learn/webgpu-for-beginners/webgpu_learn_typescript/src/main.ts
import vertexShader, fragmentShader from "./shader";
async function main()
// 获取适配器
const adapter = await navigator.gpu?.requestAdapter();
// 获取gpu设备对象
const device = await adapter?.requestDevice()!;
if (!device)
fail("need a browser that supports WebGPU");
return;
// Get a WebGPU context from the canvas and configure it
// 创建canvas画布,配置gpu上下文,将该元素作为webgpu的画布
const canvas = document.createElement("canvas");
canvas.style.width = "500px";
canvas.style.height = "300px";
const context = canvas.getContext("webgpu")!;
const presentationFormat = navigator.gpu.getPreferredCanvasFormat();
context.configure(
device, // gpu设备对象
format: presentationFormat, //gpu渲染器使用的颜色格式,比如说rgba bgra,这里默认就好
);
const vertexArray = new Float32Array([
// 三角形三个顶点坐标的x、y、z值
0.0,
0.0,
0.0, //顶点1坐标
1.0,
0.0,
0.0, //顶点2坐标
0.0,
1.0,
0.0, //顶点3坐标
]);
// 定点缓冲区
const vertexBuffer = device.createBuffer(
size: vertexArray.byteLength, //顶点数据的字节长度
//usage设置该缓冲区的用途(作为顶点缓冲区|可以写入顶点数据)
usage: GPUBufferUsage.VERTEX | GPUBufferUsage.COPY_DST,
);
// 将顶点信息写入缓冲器
device.queue.writeBuffer(vertexBuffer, 0, vertexArray);
const pipeline = device.createRenderPipeline(
layout: "auto",
vertex:
//顶点相关配置
buffers: [
// 顶点所有的缓冲区模块设置
//其中一个顶点缓冲区设置
arrayStride: 3 * 4, //一个顶点数据占用的字节长度,该缓冲区一个顶点包含xyz三个分量,每个数字是4字节浮点数,3*4字节长度
attributes: [
// 顶点缓冲区属性
shaderLocation: 0, //GPU显存上顶点缓冲区标记存储位置
format: "float32x3", //格式:loat32x3表示一个顶点数据包含3个32位浮点数
offset: 0, //arrayStride表示每组顶点数据间隔字节数,offset表示读取改组的偏差字节数,没特殊需要一般设置0
,
],
,
],
module: device.createShaderModule(
label: "triangle vertex",
code: vertexShader,
),
entryPoint: "main",
,
fragment:
module: device.createShaderModule(
label: "fragment vertex",
code: fragmentShader,
),
entryPoint: "main", //指定入口函数
targets: [
format: presentationFormat, //和WebGPU上下文配置的颜色格式保持一致
,
],
,
primitive:
topology: "triangle-list", //绘制三角形
// topology: "point-list", //绘制三角形
// topology: "line-list", //绘制三角形
,
);
// 创建GPU命令编码器对象
const commandEncoder = device.createCommandEncoder();
const renderPass = commandEncoder.beginRenderPass(
label: "our basic canvas renderPass",
// 给渲染通道指定颜色缓冲区,配置指定的缓冲区
colorAttachments: [
// 指向用于Canvas画布的纹理视图对象(Canvas对应的颜色缓冲区)
// 该渲染通道renderPass输出的像素数据会存储到Canvas画布对应的颜色缓冲区(纹理视图对象)
view: context.getCurrentTexture().createView(),
storeOp: "store", //像素数据写入颜色缓冲区
loadOp: "clear",
clearValue: r: 0.5, g: 0.5, b: 0.5, a: 1.0 , //背景颜色
,
],
);
// 关联顶点缓冲区数据和渲染管线
renderPass.setVertexBuffer(0, vertexBuffer);
renderPass.setPipeline(pipeline);
renderPass.draw(3); // call our vertex shader 3 times
renderPass.end();
// 命令缓冲器
const commandBuffer = commandEncoder.finish();
device.queue.submit([commandBuffer]);
document.body.appendChild(canvas);
function fail(msg: string)
// eslint-disable-next-line no-alert
alert(msg);
main();
// 顶点着色器代码
const vertexShader = /* wgsl */ `
@vertex
fn main(@location(0) pos: vec3<f32>) -> @builtin(position) vec4<f32>
return vec4<f32>(pos,1.0);
`;
// 片元着色器代码
const fragmentShader = /* wgsl */ `
@fragment
fn main() -> @location(0) vec4<f32>
return vec4<f32>(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);//片元设置为红色
`;
export vertexShader, fragmentShader ;
大家好,本文学习MSAA以及在WebGPU中的实现。
上一篇博文
WebGPU学习(二): 学习“绘制一个三角形”示例
下一篇博文
WebGPU学习(四):Alpha To Coverage
学习MSAA
介绍
MSAA(多重采样抗锯齿),是硬件实现的抗锯齿技术
动机
参考深入剖析MSAA :
具体到实时渲染领域中,走样有以下三种:
1.几何体走样(几何物体的边缘有锯齿),几何走样由于对几何边缘采样不足导致。
2.着色走样,由于对着色器中着色公式(渲染方程)采样不足导致。比较明显的现象就是高光闪烁。
3.时间走样,主要是对高速运动的物体采样不足导致。比如游戏中播放的动画发生跳变等。
这里讨论几何体走样。
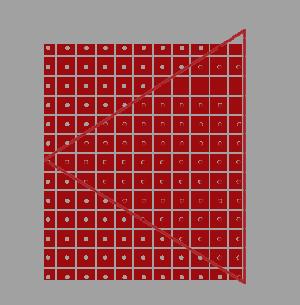
如上图所示,我们要绘制一个三角形。它由三个顶点组成,红线范围内的三角形是片元primitive覆盖的区域。
primitive会被光栅化为fragment,而一个fragment最终对应屏幕上的一个像素,如图中的小方块所示。
gpu会根据像素中心的采样点是否被pritimive覆盖来判断是否生成该fragment和执行对应的fragment shader。
图中红色的点是被覆盖的采样点,它所在的像素会被渲染。
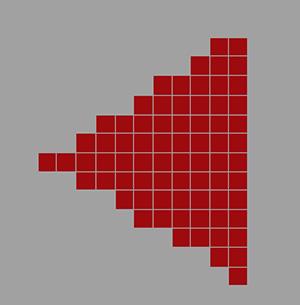
下图是最终渲染的结果,我们看到三角形边缘产生了锯齿:
原理
MSAA通过增加采样点来减轻几何体走样。
它包括4个步骤:
1.针对采样点进行覆盖检测
2.每个被覆盖的fragment执行一次fragment shader
3.针对采样点进行深度检测和模版检测
4.解析(resolve)
下面以4X MSAA为例(每个像素有4个采样点),说明每个步骤:
1.针对采样点进行覆盖检测
gpu会计算每个fragment的coverage(覆盖率),从而得知对应像素的每个采样点是否被覆盖的信息。
coverage相关知识可以参考WebGPU学习(四):Alpha To Coverage -> 学习Alpha To Coverage -> 原理
这里为了简化,我们只考虑通过“检测每个像素有哪些采样点被primitive覆盖”来计算coverager:
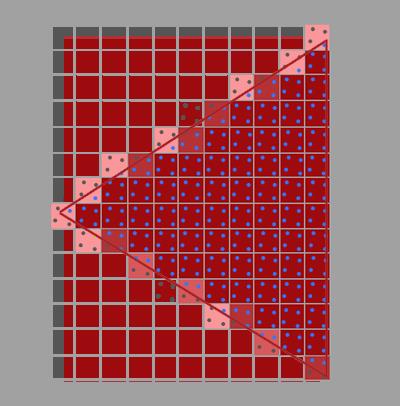
如上图所示,蓝色的采样点是在三角形中,是被覆盖的采样点。
2.每个被覆盖的fragment执行一次fragment shader
如果一个像素至少有一个采样点被覆盖,那么会执行一次它对应的fragment(注意,只执行一次哈,不是执行4次)(它所有的输入varying变量都是针对其像素中心点而言的,所以计算的输出的颜色始终是针对该栅格化出的像素中心点而言的),输出的颜色保存在color buffer中(覆盖的采样点都要保存同一个输出的颜色)
3.针对采样点进行深度检测和模版检测
所有采样点的深度值和模版值都要存到depth buffer和stencil buffer中(无论是否被覆盖)。
被覆盖的采样点会进行深度检测和模版检测,通过了的采样点会进入“解析”步骤。
那为什么要保存所有采样点的深度和模版值了(包括没有被覆盖的)?因为它们在深度检测和模版检测阶段决定所在的fragment是否被丢弃:
那是因为之后需要每个sample(采样点)都执行一下depth-test,以确定整个fragment是否要流向(通往缓冲区输出的)流水线下一阶段——只有当全部fragment-sample的Depth-Test都Fail掉的时候,才决定抛弃掉这个fragment(蒙版值stencil也是这样的,每个sample都得进行Stencil-Test)。
4.解析
什么是解析?
根据深入剖析MSAA 的说法:
像超采样一样,过采样的信号必须重新采样到指定的分辨率,这样我们才可以显示它。
这个过程叫解析(resolving)。
根据乱弹纪录II:Alpha To Coverage 的说法:
在把所有像素输出到渲染缓冲区前执行Resolve以生成单一像素值。
。。。。。。
也该是时候谈到一直说的“计算输出的颜色”是怎么一回事了。MultiSample的Resolve阶段,如果是屏幕输出的话这个阶段会发生在设备的屏幕输出直前;如果是FBO输出,则是发生在把这个Multisample-FBO映射到非multisample的FBO(或屏幕)的时候(见[多重采样(MultiSample)下的FBO反锯齿] )。Resolve,说白了就是把MultiSample的存储区域的数据,根据一定法则映射到可以用于显示的Buffer上了(这里的输出缓冲区包括了Color、Depth或还有Stencil这几个)。Depth和Stencil前面已经提及了法则了,Color方面其实也简单,一般的显卡的默认处理就是把sample的color取平均了。注意,因为depth-test等Test以及Coverage mask的影响下,有些sample是不参与计算的(被摒弃),例如4XMSAA下上面的0101,就只有两个sample,又已知各sample都对应的只是同一个颜色值,所以输出的颜色 = 2 * fragment color / 4 = 0.5 * fragment color。也就是是说该fragemnt最终显示到屏幕(或Non-MS-FBO)上是fragment shader计算出的color值的一半——这不仅是颜色亮度减半还包括真·透明度值的减半。
我的理解:
“解析”是把每个像素经过上述步骤得到的采样点的颜色值,取平均值,得到这个像素的颜色值。
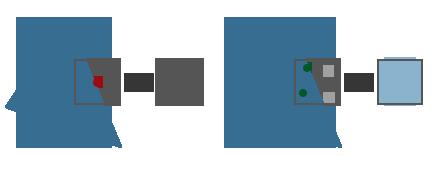
如上图右边所示,像素的2个采样点进入了“解析”,最终该像素的颜色值为 0.5(2/4) * 原始颜色值
经过上述所有步骤后,最终的渲染结果如下:
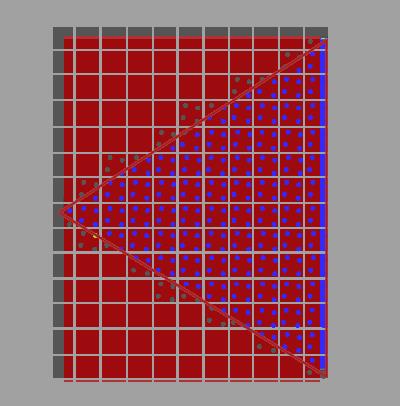
总结
MSAA能减轻几何体走样,但会增加color buffer、depth buffer、stencil buffer开销。
参考资料
深入剖析MSAA
乱弹纪录II:Alpha To Coverage
Anti Aliasing
WebGPU实现MSAA
有下面几个要点:
目前我没找到查询的方法,但至少支持4个采样点
参考 Investigation: Multisampled Render Targets and Resolve Operations:
We can say that 4xMSAA is guaranteed on all WebGPU implementations, and we need to provide APIs for queries on whether we can create a multisampled texture with given format and sample count.
dictionary GPURenderPipelineDescriptor : GPUPipelineDescriptorBase {
...
unsigned long sampleCount = 1;
...
};
dictionary GPUTextureDescriptor : GPUObjectDescriptorBase {
...
unsigned long sampleCount = 1;
...
};
我们在WebGPU 规范中看到render pipeline descriptor和texture descriptor可以设置sampleCount。
在“解析”步骤中,需要重新采样到指定的分辨率:
过采样的信号必须重新采样到指定的分辨率,这样我们才可以显示它
所以我们应该设置color的resolveTarget(depth、stencil不支持resolveTarget),它包含“分辨率”的信息。
我们来看下WebGPU 规范:
dictionary GPURenderPassColorAttachmentDescriptor {
required GPUTextureView attachment;
GPUTextureView resolveTarget;
required (GPULoadOp or GPUColor) loadValue;
GPUStoreOp storeOp = "store";
};
resolveTarget在render pass colorAttachment descriptor中设置,它的类型是GPUTextureView。
而GPUTextureView是从GPUTexture得来的,我们来看下GPUTexture的descriptor的定义:
dictionary GPUExtent3DDict {
required unsigned long width;
required unsigned long height;
required unsigned long depth;
};
typedef (sequence<unsigned long> or GPUExtent3DDict) GPUExtent3D;
dictionary GPUTextureDescriptor : GPUObjectDescriptorBase {
...
required GPUExtent3D size;
...
};
GPUTextureDescriptor的size属性有width和height属性,只要texture对应了屏幕大小,我们就能获得屏幕“分辨率”的信息(depth设为1,因为分辨率只有宽、高,没有深度)。
实现sample
我们对应到sample来看下。
打开webgpu-samplers->helloTriangleMSAA.ts文件。
代码基本上与我们上篇文章学习的webgpu-samplers->helloTriangle.ts差不多,
我们看下创建render pipeline代码
const sampleCount = 4;
const pipeline = device.createRenderPipeline({
...
sampleCount,
});
这里设置了sample count为4
我们看下frame函数->render pass descrptor代码
const renderPassDescriptor: GPURenderPassDescriptor = {
colorAttachments: [{
attachment: attachment,
resolveTarget: swapChain.getCurrentTexture().createView(),
...
}],
};
- 设置attachment为多重采样的texture的view
该texture的创建代码为:
const texture = device.createTexture({
size: {
width: canvas.width,
height: canvas.height,
depth: 1,
},
sampleCount,
format: swapChainFormat,
usage: GPUTextureUsage.OUTPUT_ATTACHMENT,
});
const attachment = texture.createView();
注意:texture的sampleCount应该与render pipeline的sampleCount一样,都是4
- 设置resolveTarget为swapChain对应的view
swapChain.getCurrentTexture()获得的texture的大小是与屏幕相同,所以它包含了屏幕分辨率的信息。
参考资料
helloTriangleMSAA.ts
Investigation: Multisampled Render Targets and Resolve Operations




