python_tensorflow_Django实现逻辑回归
Posted C~K
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python_tensorflow_Django实现逻辑回归相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.工程概要
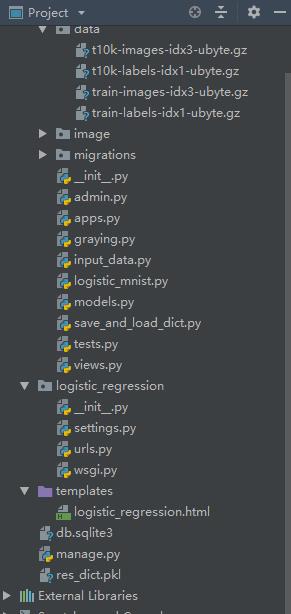
2.data文件以及input_data文件准备
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1EBNyNurBXWeJVyhNeVnmnA
提取码:4nnl
3.logisstic_mnist.py
def logistic_regression():
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from app01 import input_data
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
print(\'Download and Extract MNIST dataset\')
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(\'app01/data/\', one_hot=True)
print("type of \'mnist\' is %s" % (type(mnist)))
print("number of train data is %d" % (mnist.train.num_examples))
print("number of test data is %d" % (mnist.test.num_examples))
trainimg = mnist.train.images
for img in trainimg:
for i in range(0, 748):
if img[i] < 0.6:
img[i] = 0
else:
img[i] = 1
trainlabel = mnist.train.labels
testimg = mnist.test.images
for img in testimg:
for i in range(0, 748):
if img[i] < 0.6:
img[i] = 0
else:
img[i] = 1
testlabel = mnist.test.labels
print("type of the \'trainimg\' is %s" % (type(trainimg)))
print("type of the \'trainlabel\' is %s" % (type(trainlabel)))
print("type of the \'testimg\' is %s" % (type(testimg)))
print("type of the \'testlabel\' is %s" % (type(testlabel)))
print("shape of the \'trainimg\' is %s" % (trainimg.shape,))
print("shape of the \'trainlabel\' is %s" % (trainlabel.shape,))
print("shape of the \'testimg\' is %s" % (testimg.shape,))
print("shape of the \'testlabel\' is %s" % (testlabel.shape,))
print(\'how dose the training data look like?\')
nsample = 5
randidx = np.random.randint(trainimg.shape[0], size=nsample)
for i in randidx:
curr_img = np.reshape(trainimg[i, :], (28, 28))
curr_label = np.argmax(trainlabel[i, :])
plt.matshow(curr_img, cmap=plt.get_cmap(\'gray\'))
plt.title(""+str(i)+"th Training Data"+"Label is"+str(curr_label))
print(""+str(i)+"th Training Data"+"Label is"+str(curr_label))
plt.show()
print(\'Batch Learning?\')
batch_size = 100
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
print("type of \'batch_xs\' is %s" % (type(batch_xs)))
print("type of \'batch_ys\' is %s" % (type(batch_ys)))
print("shape of \'batch_xs\' is %s" % (batch_xs.shape, ))
print("shape of \'batch_ys\' is %s" % (batch_ys.shape, ))
# print(trainlabel[0])
x = tf.placeholder(\'float\', [None, 784])
y = tf.placeholder(\'float\', [None, 10])
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
actv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W) + b)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y*tf.log(actv), reduction_indices=1))
learning_rate = 0.01
optm = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(actv, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
accr = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(pred, \'float\'))
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
training_epochs = 50
batch_size = 100
display_step = 5
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0.
num_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
for i in range(num_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
feeds = {x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys}
sess.run(optm, feed_dict=feeds)
avg_cost += sess.run(cost, feed_dict=feeds)/num_batch
if epoch % display_step == 0:
feeds_train = {x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys}
feeds_test = {x: mnist.test.images, y: mnist.test.labels}
train_acc = sess.run(accr, feed_dict=feeds_train)
test_acc = sess.run(accr, feed_dict=feeds_test)
print("Epoch: %03d/%03d cost: %.9f train_acc: %.3f test_acc: %.3f" % (epoch, training_epochs, avg_cost, train_acc, test_acc))
W_out = W.eval(session=sess)
b_out = b.eval(session=sess)
res_dict = {\'W\': W_out, \'b\': b_out}
print(\'DONE\')
return res_dict
4.views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from app01 import logistic_mnist as lomni
from app01 import save_and_load_dict as save_load
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
if request.method == \'GET\':
return render(request, \'logistic_regression.html\', {\'range\': range(0, 28)})
if request.method == \'POST\':
choice = request.GET.get(\'n\')
print(\'choice:\', choice)
if choice == \'1\':
res_dict = lomni.logistic_regression()
save_load.save_obj(res_dict, \'res_dict\')
return render(request, \'logistic_regression.html\', {\'resdict\': res_dict})
if choice == \'2\':
import numpy as np
my_test = []
for row in range(0, 28):
for line in range(0, 28):
if request.POST.get(\'(\'+str(row)+\',\'+str(line)+\')\') == None:
my_test.append(0)
else:
my_test.append(1)
my_test = np.array(my_test)
print(\'my_test:\', my_test)
res_dict = save_load.load_obj(\'res_dict\')
W = np.array(res_dict[\'W\'])
b = np.array(res_dict[\'b\'])
# print(W, b)
pred = np.argmax(np.matmul(my_test, W)+b)
return render(request, \'logistic_regression.html\', {\'resdict\': res_dict, \'pred\':pred})
if choice == \'3\':
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
img = Image.open(\'app01/image/sharped5.png\')
img_array = np.array(img)
img_array = np.zeros(784).reshape(28, 28)
print(img_array + 0)
return render(request, \'logistic_regression.html\', {\'img_array\': img_array+0, \'range\': range(0, 28)})
5.urls.py
"""logistic_regression URL Configuration
The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see:
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/topics/http/urls/
Examples:
Function views
1. Add an import: from my_app import views
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path(\'\', views.home, name=\'home\')
Class-based views
1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path(\'\', Home.as_view(), name=\'home\')
Including another URLconf
1. Import the include() function: from django.urls import include, path
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path(\'blog/\', include(\'blog.urls\'))
"""
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
path(\'admin/\', admin.site.urls),
path(\'index/\', views.index),
]
6.logistic_regression.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/index/?n=1" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<input type="submit" value="逻辑回归训练">
</form>
{% if resdict != none %}
<div>
<p>训练结果:</p>
<p>W:{{ resdict.W }}</p>
<p>b:{{ resdict.b }}</p>
</div>
{% endif %}
<form action="/index/?n=2" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<table border="1">
<thead></thead>
<tbody >
{% for row in range %}
<tr>
{% for line in range %}
<td>
<input type="checkbox" name="({{ row }},{{ line }})" class="paint">
</td>
{% endfor %}
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
<input type="submit" value="进行手写识别">
</form>
{% if pred != none %}
<div>
<p>
检测结果是{{ pred }}
</p>
</div>
{% endif %}
<form action="/index/?n=3" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<input type="submit" value="开始检测目标文件夹中的手写字体!">
<p>{{ img }}</p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
7.save_and_load_dict.py
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/index/?n=1" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<input type="submit" value="逻辑回归训练">
</form>
{% if resdict != none %}
<div>
<p>训练结果:</p>
<p>W:{{ resdict.W }}</p>
<p>b:{{ resdict.b }}</p>
</div>
{% endif %}
<form action="/index/?n=2" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<table border="1">
<thead></thead>
<tbody >
{% for row in range %}
<tr>
{% for line in range %}
<td>
<input type="checkbox" name="({{ row }},{{ line }})" class="paint">
</td>
{% endfor %}
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
<input type="submit" value="进行手写识别">
</form>
{% if pred != none %}
<div>
<p>
检测结果是{{ pred }}
</p>
</div>
{% endif %}
<form action="/index/?n=3" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<input type="submit" value="开始检测目标文件夹中的手写字体!">
<p>{{ img }}</p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
8.graying.py
import sys
print(sys.argv[0])
import os
path_curr = os.path.abspath(\'.\')
path_up = os.path.abspath(\'..\')
print(path_up)
threshold = 140
table = []
for a in range(256):
if a > threshold:
table.append(1)
else:
table.append(0)
from PIL import Image
for i in range(0, 10):
img = Image.open(\'image/\'+str(i)+\'.png\')
Img = img.convert(\'L\')
Img.save(\'image/grey\'+str(i)+\'.png\')
photo = Img.point(table, \'1\')
photo.save(\'image/sharped\'+str(i)+\'.png\')
以上是关于python_tensorflow_Django实现逻辑回归的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章