springboot启动过程解析
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了springboot启动过程解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 虽然golang开始在后台开发横行,但是springboot还是目前大多数企业使用的技术栈。由于其成熟性,丰富的组件以及生态环境,是很多公司的首选。学习springboot需要了解其启动过程,对原理的理解可以避免停留在CRUD层面,对底层有很多深入的理解可以助力我们成长,解决深层次问题。2.SpringApplication构造函数
3.run函数
4.prepareContext 资源加载,并且初始化。
5.refresh ioc的最后一步,对bean进行后续处理。
spring boot 2.1.7启动过程源码解析
约定
本文基于spring boot 2.1.7.RELEASE进行剖析,使用的spring cloud为Greenwich.SR6版本,github仓库为:spring boot演示。该仓库有多个子模块,下文使用的是consumer子模块。
术语约定:
- spring boot容器,main方法启动的spring boot ApplicationContext,也就是用户接触到的容器。
- spring cloud容器,spring cloud ApplicationContext,也称为父容器,因为spring cloud ApplicationContext最后会作为spring boot ApplicationContext的父容器。
- 代码埋点,为了方便对某个代码进行讲述,这里标记了一些数字,如果找不到,可以全局搜索下。
1. SpringApplication入口
执行入口如下。
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConsumerApplication
public static void main(String[] args)
SpringApplication.run(ConsumerApplication.class, args);
最后会运行new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args),所以核心方法是SpringApplication的run方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args)
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources)
this(null, primarySources);
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources)
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 根据类路径中的类是否存在,进而确定ApplicationContext类型,例如存在DispatcherSerlver,则是servlet。
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 从META-INF/spring.factories中,获取对应的ApplicationContextInitializer配置
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 从META-INF/spring.factories中,获取对应的ApplicationListener配置
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args)
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 埋点(1) 加载EventListener,并转发starting事件
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 埋点(2) 创建environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 埋点(3) 打印banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] ConfigurableApplicationContext.class , context);
// 埋点(4) 初始化ApplicationContext,并设置environment,运行initializer,并注册primarySource类为BeanDefinitionRegistry
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 埋点(5) 调用ApplicationContext.refresh
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo)
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
catch (Throwable ex)
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
try
listeners.running(context);
catch (Throwable ex)
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
return context;
2. 获取SpringApplicationRunListener
在上面埋点(1)中,SpringApplicationRunListeners会从所有依赖的jar的META-INF/spring.factories文件中获取SpringApplicationRunListener的所有实现类,这里是spring boot的SPI机制。
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args)
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] SpringApplication.class, String[].class ;
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,
getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
spring boot这里添加了一个默认的SpringApplicationRunListener实现类是:EventPublishingRunListener

SpringApplicationRunListeners是SpringApplicationRunListener的复数形式,会将所有事件,直接调用SpringApplicationRunListener方法。
class SpringApplicationRunListeners
private final Log log;
private final List<SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners;
SpringApplicationRunListeners(Log log, Collection<? extends SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners)
this.log = log;
this.listeners = new ArrayList<>(listeners);
public void starting()
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners)
listener.starting();
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment)
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners)
listener.environmentPrepared(environment);
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners)
listener.contextPrepared(context);
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners)
listener.contextLoaded(context);
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners)
listener.started(context);
public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners)
listener.running(context);
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception)
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners)
callFailedListener(listener, context, exception);
private void callFailedListener(SpringApplicationRunListener listener, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
Throwable exception)
try
listener.failed(context, exception);
catch (Throwable ex)
if (exception == null)
ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(ex);
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled())
this.log.error("Error handling failed", ex);
else
String message = ex.getMessage();
message = (message != null) ? message : "no error message";
this.log.warn("Error handling failed (" + message + ")");
在SpringApplicationRunListeners中,共定义了7种spring boot应用的事件,并全部转发给SpringApplicationRunListener运行,这7种事件是spring boot的扩展点,基于这些扩展点,spring boot内部实现了日志自动化配置、加载application.yaml等功能。spring cloud实现了设置父ApplicationContext,设置远程配置。
| spring boot启动扩展点 | 执行时机 | EventPublishingRunListener对应发出的事件类型 |
|---|---|---|
| starting事件 | SpringApplication启动后,立即执行 | ApplicationStartingEvent |
| environmentPrepared事件 | 最重要的事件。在environment创建后触发,可以用来启动spring cloud容器,加载bootstrap.yaml;加载application.yaml;初始化日志系统和日志级别等日志配置 | ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent |
| contextPrepared事件 | 在ApplicationContext创建后,调用ApplicationContextInitializer初始化ApplicationContext后触发。目前spring-cloud-context内部没有用到 | ApplicationContextInitializedEvent |
| contextLoaded事件 | 在注册完main方法所在配置类为BeanDefinition后触发 | ApplicationPreparedEvent |
| started事件 | 刷新ApplicationContext加载非懒加载单例后触发 | ApplicationStartedEvent |
| running事件 | 调用完ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner后触发,表示spring boot应用启动成功,在这个阶段可以注册到consul上 | ApplicationReadyEvent |
| failed事件 | spring boot启动过程中抛出异常,触发这个事件 | ApplicationFailedEvent |
2.1 EventPublishingRunListener的实现
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered
private final SpringApplication application;
private final String[] args;
private final SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster initialMulticaster;
public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args)
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
// (1) 将SpringApplication中的listener加入到事件分发器中。
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners())
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
@Override
public int getOrder()
return 0;
// 前三种事件,ConfigurableApplicationContext还没构建,这时只对SpringApplication.listener生效
@Override
public void starting()
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment)
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment));
@Override
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationContextInitializedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
// 从ApplicationPreparedEvent开始,将对SpringApplication.listener添加到ConfigurableApplicationContext中,这时不仅仅SpringApplication.listener生效,ConfigurableApplicationContext中的listener也生效
@Override
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : this.application.getListeners())
if (listener instanceof ApplicationContextAware)
((ApplicationContextAware) listener).setApplicationContext(context);
context.addApplicationListener(listener);
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
@Override
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
context.publishEvent(new ApplicationStartedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
@Override
public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
context.publishEvent(new ApplicationReadyEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
@Override
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception)
ApplicationFailedEvent event = new ApplicationFailedEvent(this.application, this.args, context, exception);
if (context != null && context.isActive())
// Listeners have been registered to the application context so we should
// use it at this point if we can
context.publishEvent(event);
else
// An inactive context may not have a multicaster so we use our multicaster to
// call all of the context's listeners instead
if (context instanceof AbstractApplicationContext)
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : ((AbstractApplicationContext) context)
.getApplicationListeners())
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
this.initialMulticaster.setErrorHandler(new LoggingErrorHandler());
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(event);
private static class LoggingErrorHandler implements ErrorHandler
private static Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(EventPublishingRunListener.class);
@Override
public void handleError(Throwable throwable)
logger.warn("Error calling ApplicationEventListener", throwable);
下面给出完整的EventPublishingRunListener事件的生效情况。从代码可以看出,在ConfigurableApplicationContext构建之前,事件只有SpringApplication.getListeners()能接收。到了contextLoaded,会把SpringApplication.getListeners()添加到ConfigurableApplicationContext中,之后从started事件开始,使用ConfigurableApplicationContext的publishEvent,这个时候ConfigurableApplicationContext中的listener也生效
| spring boot启动扩展点 | 执行时机 | EventPublishingRunListener对应发出的事件类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| starting事件 | SpringApplication启动后,立即执行 | ApplicationStartingEvent | 只对SpringApplication.getListeners()生效 |
| environmentPrepared事件 | 最重要的事件。在environment创建后触发,可以用来启动spring cloud容器,加载bootstrap.yaml;加载application.yaml;初始化日志系统和日志级别等日志配置 | ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent | 只对SpringApplication.getListeners()生效 |
| contextPrepared事件 | 在ApplicationContext创建后,调用ApplicationContextInitializer初始化ApplicationContext后触发。目前spring-cloud-context内部没有用到 | ApplicationContextInitializedEvent | 只对SpringApplication.getListeners()生效 |
| contextLoaded事件 | 在注册完main方法所在配置类为BeanDefinition后触发 | ApplicationPreparedEvent | 只对SpringApplication.getListeners()生效 |
| started事件 | 刷新ApplicationContext加载非懒加载单例后触发 | ApplicationStartedEvent | 不仅仅SpringApplication.getListeners()生效,ConfigurableApplicationContext中的listener也生效 |
| running事件 | 调用完ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner后触发,表示spring boot应用启动成功,在这个阶段可以注册到consul上 | ApplicationReadyEvent | 不仅仅SpringApplication.getListeners()生效,ConfigurableApplicationContext中的listener也生效 |
| failed事件 | spring boot启动过程中抛出异常,触发这个事件 | ApplicationFailedEvent | 不仅仅SpringApplication.getListeners()生效,ConfigurableApplicationContext中的listener也生效 |
那么,这里SpringApplication.getListeners()都有哪些呢,相信你也有这样的疑问,其实在SpringApplication构造时,就已经通过SPI机制初始化了listeners,之后也可以通过addListeners()手动添加listener
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources)
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 从META-INF/spring.factories中,获取对应的ApplicationContextInitializer配置
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 从META-INF/spring.factories中,获取对应的ApplicationListener配置
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
public void setListeners(Collection<? extends ApplicationListener<?>> listeners)
this.listeners = new ArrayList<>();
this.listeners.addAll(listeners);
/**
* Add @link ApplicationListeners to be applied to the SpringApplication and
* registered with the @link ApplicationContext.
* @param listeners the listeners to add
*/
public void addListeners(ApplicationListener<?>... listeners)
this.listeners.addAll(Arrays.asList(listeners));
通过debug,可以发现有这么些listeners,注意这个顺序,这个顺序是他们的接收顺序,每个listener都可以设置自己的order,spring boot会按照order从小到大排序。

0 = BootstrapApplicationListener@1696
1 = LoggingSystemShutdownListener@1697
2 = ConfigFileApplicationListener@1698
3 = AnsiOutputApplicationListener@1699
4 = LoggingApplicationListener@1700
5 = ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener@1701
6 = BackgroundPreinitializer@1702
7 = DelegatingApplicationListener@1703
8 = RestartListener@1704
9 = ParentContextCloserApplicationListener@1705
10 = ClearCachesApplicationListener@1706
11 = FileEncodingApplicationListener@1707
12 = LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener@1708
最后,用一张图总结下listener的调用逻辑

2.2 starting事件的处理
这里再回到埋点(1)的地方,这里加载完SpringApplicationRunListener,会调用staring(),从上面的分析,可以知道,最终转化为ApplicationStartingEvent,交给上面13个ApplicationListener进行监听处理。
实际上,这个阶段是非常早的,只有LoggingApplicationListener会进行处理。主要作用是选定日志系统,根据类路径下相关的类,根据classpath的jar确定了要使用的日系统,例如logback、log4j
public class LoggingApplicationListener implements GenericApplicationListener
private static final ConfigurationPropertyName LOGGING_LEVEL = ConfigurationPropertyName.of("logging.level");
private static final ConfigurationPropertyName LOGGING_GROUP = ConfigurationPropertyName.of("logging.group");
private static final Bindable<Map<String, String>> STRING_STRING_MAP = Bindable.mapOf(String.class, String.class);
private static final Bindable<Map<String, String[]>> STRING_STRINGS_MAP = Bindable.mapOf(String.class,
String[].class);
/**
* The default order for the LoggingApplicationListener.
*/
public static final int DEFAULT_ORDER = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 20;
/**
* The name of the Spring property that contains a reference to the logging
* configuration to load.
*/
public static final String CONFIG_PROPERTY = "logging.config";
/**
* The name of the Spring property that controls the registration of a shutdown hook
* to shut down the logging system when the JVM exits.
* @see LoggingSystem#getShutdownHandler
*/
public static final String REGISTER_SHUTDOWN_HOOK_PROPERTY = "logging.register-shutdown-hook";
/**
* The name of the @link LoggingSystem bean.
*/
public static final String LOGGING_SYSTEM_BEAN_NAME = "springBootLoggingSystem";
/**
* The name of the @link LogFile bean.
*/
public static final String LOGFILE_BEAN_NAME = "springBootLogFile";
private static final Map<String, List<String>> DEFAULT_GROUP_LOGGERS;
static
MultiValueMap<String, String> loggers = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
loggers.add("web", "org.springframework.core.codec");
loggers.add("web", "org.springframework.http");
loggers.add("web", "org.springframework.web");
loggers.add("web", "org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.web");
loggers.add("web", "org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializerBeans");
loggers.add("sql", "org.springframework.jdbc.core");
loggers.add("sql", "org.hibernate.SQL");
DEFAULT_GROUP_LOGGERS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(loggers);
private static final Map<LogLevel, List<String>> LOG_LEVEL_LOGGERS;
static
MultiValueMap<LogLevel, String> loggers = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
loggers.add(LogLevel.DEBUG, "sql");
loggers.add(LogLevel.DEBUG, "web");
loggers.add(LogLevel.DEBUG, "org.springframework.boot");
loggers.add(LogLevel.TRACE, "org.springframework");
loggers.add(LogLevel.TRACE, "org.apache.tomcat");
loggers.add(LogLevel.TRACE, "org.apache.catalina");
loggers.add(LogLevel.TRACE, "org.eclipse.jetty");
loggers.add(LogLevel.TRACE, "org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl");
LOG_LEVEL_LOGGERS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(loggers);
private static final Class<?>[] EVENT_TYPES = ApplicationStartingEvent.class,
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent.class, ApplicationPreparedEvent.class, ContextClosedEvent.class,
ApplicationFailedEvent.class ;
private static final Class<?>[] SOURCE_TYPES = SpringApplication.class, ApplicationContext.class ;
private static final AtomicBoolean shutdownHookRegistered = new AtomicBoolean(false);
private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private LoggingSystem loggingSystem;
private LogFile logFile;
private int order = DEFAULT_ORDER;
private boolean parseArgs = true;
private LogLevel springBootLogging = null;
@Override
public boolean supportsEventType(ResolvableType resolvableType)
return isAssignableFrom(resolvableType.getRawClass(), EVENT_TYPES);
@Override
public boolean supportsSourceType(Class<?> sourceType)
return isAssignableFrom(sourceType, SOURCE_TYPES);
private boolean isAssignableFrom(Class<?> type, Class<?>... supportedTypes)
if (type != null)
for (Class<?> supportedType : supportedTypes)
if (supportedType.isAssignableFrom(type))
return true;
return false;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event)
if (event instanceof ApplicationStartingEvent)
onApplicationStartingEvent((ApplicationStartingEvent) event);
else if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent)
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
else if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent)
onApplicationPreparedEvent((ApplicationPreparedEvent) event);
else if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent
&& ((ContextClosedEvent) event).getApplicationContext().getParent() == null)
onContextClosedEvent();
else if (event instanceof ApplicationFailedEvent)
onApplicationFailedEvent();
// 选定日志系统,根据classpath的jar确定用logback还是log4j
private void onApplicationStartingEvent(ApplicationStartingEvent event)
this.loggingSystem = LoggingSystem.get(event.getSpringApplication().getClassLoader());
this.loggingSystem.beforeInitialize();
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event)
if (this.loggingSystem == null)
this.loggingSystem = LoggingSystem.get(event.getSpringApplication().getClassLoader());
initialize(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication().getClassLoader());
private void onApplicationPreparedEvent(ApplicationPreparedEvent event)
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = event.getApplicationContext().getBeanFactory();
if (!beanFactory.containsBean(LOGGING_SYSTEM_BEAN_NAME))
beanFactory.registerSingleton(LOGGING_SYSTEM_BEAN_NAME, this.loggingSystem);
if (this.logFile != null && !beanFactory.containsBean(LOGFILE_BEAN_NAME))
beanFactory.registerSingleton(LOGFILE_BEAN_NAME, this.logFile);
3. 创建spring boot environment
根据web应用类型,创建environment,这时已经有了properties/env等source,然后会把命令行参数添加到第一位,SimpleCommandLinePropertySource。
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments)
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 添加命令行参数
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment)
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
之后触发environmentPrepared事件,也就是ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent。根据order来,处理这个事件的有BootstrapApplicationListener,之后LoggingSystemShutdownListener,再调用ConfigFileApplicationListener,最后LoggingApplicationListener初始化日志系统。最后使用ConfigurationPropertySources.attach,保证支持spring boot宽松绑定配置。
3.1 环境预初始化阶段之BootstrapApplicationListener
3.1.1 初始化spring cloud容器
spring-cloud-context中的BootstrapApplicationListener,只处理ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent,创建spring cloud容器。见:org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener#bootstrapServiceContext
public class BootstrapApplicationListener
implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent>, Ordered
/**
* Property source name for bootstrap.
*/
public static final String BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "bootstrap";
/**
* The default order for this listener.
*/
public static final int DEFAULT_ORDER = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 5;
/**
* The name of the default properties.
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_PROPERTIES = "defaultProperties";
private int order = DEFAULT_ORDER;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event)
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
if (!environment.getProperty("spring.cloud.bootstrap.enabled", Boolean.class,
true))
return;
// don't listen to events in a bootstrap context
// boostrap容器初始化的过程中也会调用BootstrapApplicationListener,不处理boostrap容器的事件,防止重入,这里通过是否包含source name来判断,而不通过ApplicationContext,因为ApplicationContext这个时候还没构建
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME))
return;
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
/// 通过spring.cloud.bootstrap.name设置配置文件名,默认是bootstrap,可以通过命令行/环境变量等设置,此时application.yaml还会加载
String configName = environment
.resolvePlaceholders("$spring.cloud.bootstrap.name:bootstrap");
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer : event.getSpringApplication()
.getInitializers())
if (initializer instanceof ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer)
context = findBootstrapContext(
(ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer) initializer,
configName);
if (context == null)
// 构建bootstrap容器,这里默认设置了配置文件名为bootstrap,因而配置文件名为bootstrap.yaml/bootstrap.properties
context = bootstrapServiceContext(environment, event.getSpringApplication(),
configName);
event.getSpringApplication()
.addListeners(new CloseContextOnFailureApplicationListener(context));
//埋点(6)将spring cloud 所有的ApplicationContextInitializer类型的bean,添加到spring boot application中
apply(context, event.getSpringApplication(), environment);
这里详细看下如何构建spring cloud容器。
//
private ConfigurableApplicationContext bootstrapServiceContext(
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, final SpringApplication application,
String configName)
StandardEnvironment bootstrapEnvironment = new StandardEnvironment();
MutablePropertySources bootstrapProperties = bootstrapEnvironment
.getPropertySources();
for (PropertySource<?> source : bootstrapProperties)
bootstrapProperties.remove(source.getName());
// 设置spring cloud配置文件目录
String configLocation = environment
.resolvePlaceholders("$spring.cloud.bootstrap.location:");
String configAdditionalLocation = environment
.resolvePlaceholders("$spring.cloud.bootstrap.additional-location:");
Map<String, Object> bootstrapMap = new HashMap<>();
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.name", configName);
// if an app (or test) uses spring.main.web-application-type=reactive, bootstrap
// will fail
// force the environment to use none, because if though it is set below in the
// builder
// the environment overrides it
bootstrapMap.put("spring.main.web-application-type", "none");
if (StringUtils.hasText(configLocation))
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.location", configLocation);
if (StringUtils.hasText(configAdditionalLocation))
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.additional-location",
configAdditionalLocation);
// 添加BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME作为source
bootstrapProperties.addFirst(
new MapPropertySource(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, bootstrapMap));
for (PropertySource<?> source : environment.getPropertySources())
if (source instanceof StubPropertySource)
continue;
bootstrapProperties.addLast(source);
// TODO: is it possible or sensible to share a ResourceLoader?
// 通过SpringApplication构建spring cloud容器,不打印banner
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder()
.profiles(environment.getActiveProfiles()).bannerMode(Mode.OFF)
.environment(bootstrapEnvironment)
// Don't use the default properties in this builder
.registerShutdownHook(false).logStartupInfo(false)
.web(WebApplicationType.NONE);
final SpringApplication builderApplication = builder.application();
if (builderApplication.getMainApplicationClass() == null)
// gh_425:
// SpringApplication cannot deduce the MainApplicationClass here
// if it is booted from SpringBootServletInitializer due to the
// absense of the "main" method in stackTraces.
// But luckily this method's second parameter "application" here
// carries the real MainApplicationClass which has been explicitly
// set by SpringBootServletInitializer itself already.
builder.main(application.getMainApplicationClass());
// 对于refreshEndpoint等事件触发的ApplicationContext重新构建,environment会包含refreshArgs source,这里把日志相关的listener过滤掉,防止重新设置日志系统
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains("refreshArgs"))
// If we are doing a context refresh, really we only want to refresh the
// Environment, and there are some toxic listeners (like the
// LoggingApplicationListener) that affect global static state, so we need a
// way to switch those off.
builderApplication
.setListeners(filterListeners(builderApplication.getListeners()));
// 埋点(7) 设置spring cloud的config类
builder.sources(BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration.class);
final ConfigurableApplicationContext context = builder.run();
// gh-214 using spring.application.name=bootstrap to set the context id via
// `ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer` prevents apps from getting the actual
// spring.application.name
// during the bootstrap phase.
context.setId("bootstrap");
// Make the bootstrap context a parent of the app context
// 埋点(8) 添加AncestorInitializer初始化器到外部SpringApplication,从而将spring cloud容器设置为外部SpringApplication对应的容器的父容器
addAncestorInitializer(application, context);
// It only has properties in it now that we don't want in the parent so remove
// it (and it will be added back later)
bootstrapProperties.remove(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
// 埋点(9),将spring cloud application构建后得到的bootstrap.properties,添加到子容器的环境中
mergeDefaultProperties(environment.getPropertySources(), bootstrapProperties);
return context;
从埋点(7),我们可以看到spring cloud application对应的容器使用的配置类是BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration,该类会导入BootstrapImportSelector。BootstrapImportSelector通过spring boot SPI,导入BootstrapConfiguration作为key的所有扩展点作为spring cloud容器的bean。且默认使用的配置文件为bootstrap.yaml/bootstrap.properties
@Configuration
@Import(BootstrapImportSelector.class)
public class BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration
public class BootstrapImportSelector implements EnvironmentAware, DeferredImportSelector
private Environment environment;
private MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory();
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment)
this.environment = environment;
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata)
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>(SpringFactoriesLoader
.loadFactoryNames(BootstrapConfiguration.class, classLoader));
names.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
this.environment.getProperty("spring.cloud.bootstrap.sources", ""))));
List<OrderedAnnotatedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : names)
try
elements.add(
new OrderedAnnotatedElement(this.metadataReaderFactory, name));
catch (IOException e)
continue;
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(elements);
String[] classNames = elements.stream().map(e -> e.name).toArray(String[]::new);
return classNames;
spring-cloud-context中的所有BootstrapConfiguration自动化配置类如下:
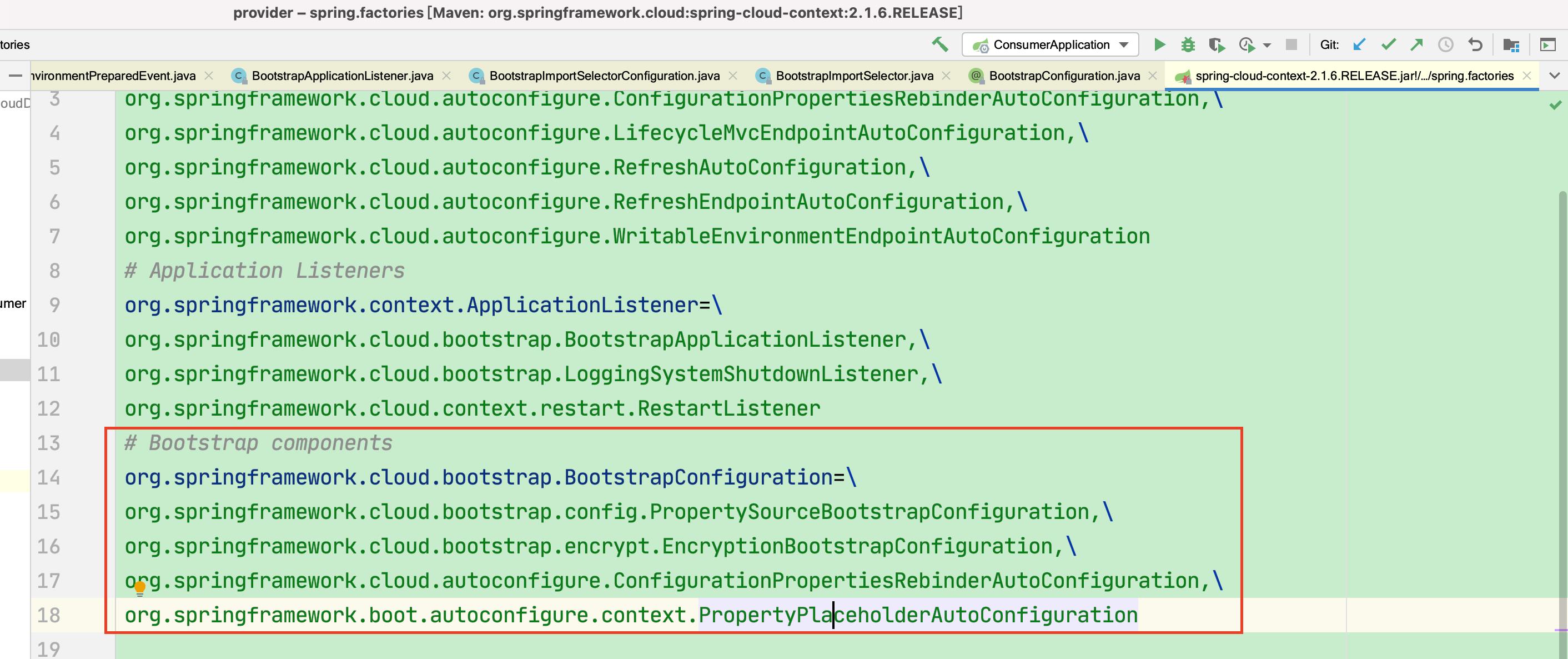
BootstrapConfiguration这里注入了很多spring cloud的基础设施,例如远程配置consul/nacos。相关基础设置通过BootstrapConfiguration设置到spring cloud容器中,最后外部spring boot容器也能拿到相关bean。注意这里读取的配置文件是bootstrap.yaml,设置到application.yaml不生效,此时application.yaml还没加载!!! 通过spring.cloud.bootstrap.name可以设置spring cloud配置文件名,默认是bootstrap,这里只能通过命令行/环境变量等设置啦。
(1) consul

(2) nacos

3.1.2 添加AncestorInitializer初始化器到spring boot SpringApplication
在上面的埋点(8) ,默认会添加AncestorInitializer初始化器到外部SpringApplication,当外部SpringApplication运行ApplicationContextInitializer时,会将spring cloud容器设置为外部SpringApplication对应的容器的父容器
// BootstrapApplicationListener
private void addAncestorInitializer(SpringApplication application,
ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
boolean installed = false;
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer : application
.getInitializers())
if (initializer instanceof AncestorInitializer)
installed = true;
// New parent
// 如果父类中有AncestorInitializer的初始化器,修改父context
((AncestorInitializer) initializer).setParent(context);
if (!installed)
// 如果父类中没有AncestorInitializer的初始化器,则添加AncestorInitializer
application.addInitializers(new AncestorInitializer(context));
private static class AncestorInitializer implements
ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered
private ConfigurableApplicationContext parent;
AncestorInitializer(ConfigurableApplicationContext parent)
this.parent = parent;
public void setParent(ConfigurableApplicationContext parent)
this.parent = parent;
@Override
public int getOrder()
// Need to run not too late (so not unordered), so that, for instance, the
// ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer runs later and picks up the merged
// Environment. Also needs to be quite early so that other initializers can
// pick up the parent (especially the Environment).
return Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 5;
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
while (context.getParent() != null && context.getParent() != context)
context = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) context.getParent();
// 将spring cloud defaultProperties调整到最后,同时将defaultProperties包含的bootstrap.yaml添加到defaultProperties前面,也就是倒数第二
reorderSources(context.getEnvironment());
// 将spring cloud context设置为当前容器的父容器
new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(this.parent)
.initialize(context);
private void reorderSources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment)
PropertySource<?> removed = environment.getPropertySources()
.remove(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES);
if (removed instanceof ExtendedDefaultPropertySource)
ExtendedDefaultPropertySource defaultProperties = (ExtendedDefaultPropertySource) removed;
environment.getPropertySources().addLast(new MapPropertySource(
DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, defaultProperties.getSource()));
for (PropertySource<?> source : defaultProperties.getPropertySources()
.getPropertySources())
if (!environment.getPropertySources().contains(source.getName()))
environment.getPropertySources().addBefore(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES,
source);
3.1.3 将spring cloud application构建后得到的bootstrap.properties,添加到spring boot子容器的environment
上面埋点(9),将spring cloud application构建后得到的properties,添加到子容器的环境中,name为defaultProperties,主要是bootstrap.yaml等追加到spring boot environment中。
// BootstrapApplicationListener
private void mergeAdditionalPropertySources(MutablePropertySources environment,
MutablePropertySources bootstrap)
PropertySource<?> defaultProperties = environment.get(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES);
ExtendedDefaultPropertySource result = defaultProperties instanceof ExtendedDefaultPropertySource
? (ExtendedDefaultPropertySource) defaultProperties
: new ExtendedDefaultPropertySource(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES,
defaultProperties);
// 过滤出bootstrap有,而spring boot environment没有的source,作为default
for (PropertySource<?> source : bootstrap)
if (!environment.contains(source.getName()))
result.add(source);
for (String name : result.getPropertySourceNames())
// spring cloud environment移除了bootstrap.yaml
bootstrap.remove(name);
// bootstrap中特有的bootstrap.yaml,追加到spring boot environment中
addOrReplace(environment, result);
// spring cloud environment重新添加bootstrap.yaml。。。
addOrReplace(bootstrap, result);
3.1.4 将spring cloud 所有的ApplicationContextInitializer类型的bean,添加到spring boot application中执行
埋点(6)将spring cloud 所有的ApplicationContextInitializer类型的bean,添加到spring boot application中。
// BootstrapApplicationListener
private void apply(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
SpringApplication application, ConfigurableEnvironment environment)
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
List<ApplicationContextInitializer> initializers = getOrderedBeansOfType(context,
ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
application.addInitializers(initializers
.toArray(new ApplicationContextInitializer[initializers.size()]));
addBootstrapDecryptInitializer(application);
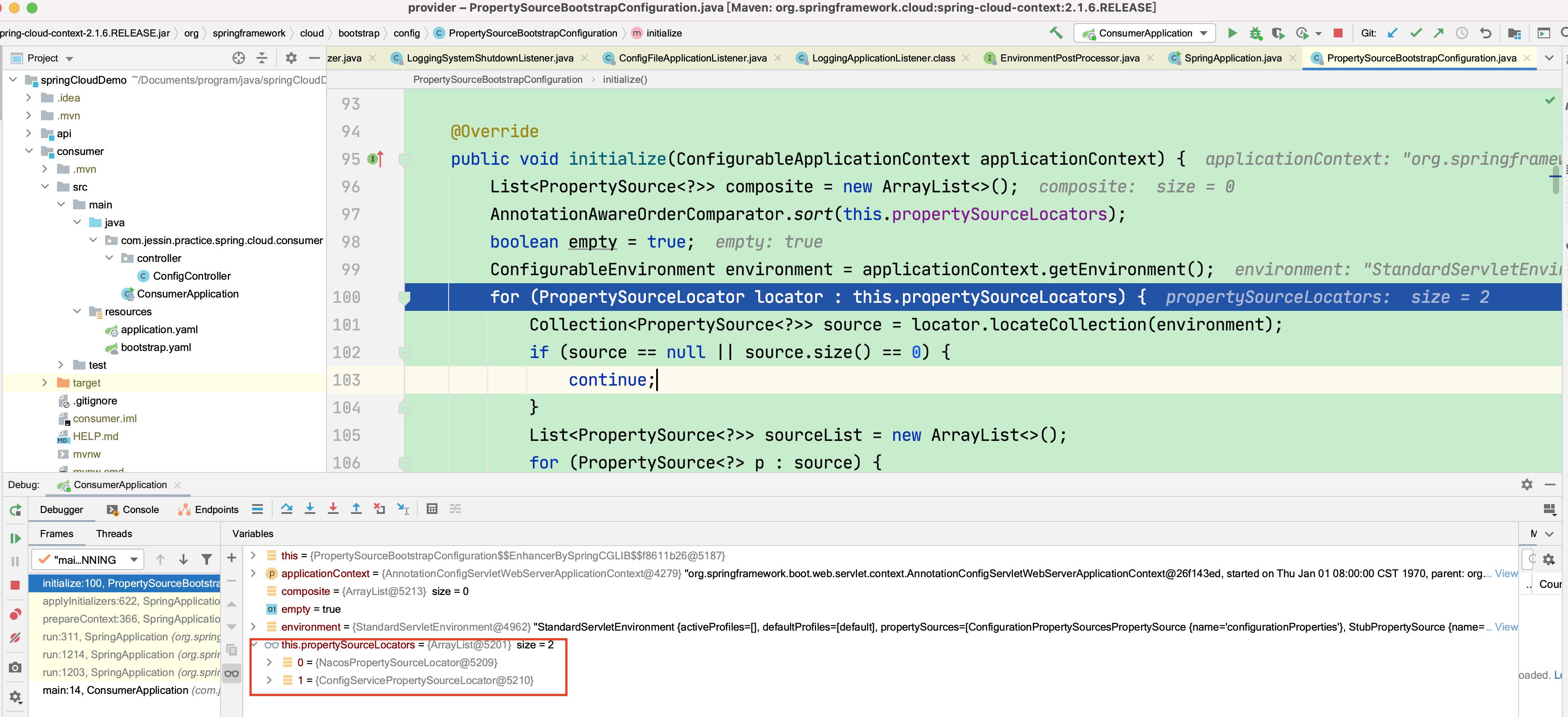
其中spring-cloud-context自带的配置类为PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration,这个类实现了ApplicationContextInitializer,其initialize会从spring cloud容器中找到所有的PropertySourceLocator bean,利用PropertySourceLocator对spring boot容器的environment进行初始化。注意,这里autowired=false,允许不存在PropertySourceLocator对应的bean。
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(PropertySourceBootstrapProperties.class)
public class PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration implements
ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered
/**
* Bootstrap property source name.
*/
public static final String BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = BootstrapApplicationListener.BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME
+ "Properties";
private static Log logger = LogFactory
.getLog(PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration.class);
private int order = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10;
// 从spring cloud容器中找到所有的PropertySourceLocator bean,并注入
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<PropertySourceLocator> propertySourceLocators = new ArrayList<>();
public void setPropertySourceLocators(
Collection<PropertySourceLocator> propertySourceLocators)
this.propertySourceLocators = new ArrayList<>(propertySourceLocators);
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext)
List<PropertySource<?>> composite = new ArrayList<>();
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.propertySourceLocators);
boolean empty = true;
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
for (PropertySourceLocator locator : this.propertySourceLocators)
Collection<PropertySource<?>> source = locator.locateCollection(environment);
if (source == null || source.size() == 0)
continue;
List<PropertySource<?>> sourceList = new ArrayList<>();
for (PropertySource<?> p : source)
sourceList.add(new BootstrapPropertySource<>(p));
logger.info("Located property source: " + sourceList);
composite.addAll(sourceList);
empty = false;
if (!empty)
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
String logConfig = environment.resolvePlaceholders("$logging.config:");
LogFile logFile = LogFile.get(environment);
for (PropertySource<?> p : environment.getPropertySources())
if (p.getName().startsWith(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME))
propertySources.remove(p.getName());
// 埋点(10) 将PropertySourceLocator加载的所有的外部配置,添加到spring cloud容器的enviroment中
insertPropertySources(propertySources, composite);
// 重新初始化日志系统和日志级别
reinitializeLoggingSystem(environment, logConfig, logFile);
setLogLevels(applicationContext, environment);
handleIncludedProfiles(environment);
对于spring cloud容器而言,PropertySourceLocator是一个扩展点,可以加载远程配置,consul/nacos等均基于这个扩展点加载远程配置。埋点(10) 将spring cloud PropertySourceLocator加载的所有的外部配置,添加到spring boot容器的environment中(注意这些ApplicationContextInitializer在spring boot容器执行!!),默认加在最前面,最后根据远程配置,重新初始化日志系统和日志级别。远程配置在命令行参数之前。
如果要修改远程优先,有两种方法,一种是修改远程配置;另一种是修改bootstrap.yaml中consul/nacos中的配置,使得读取远程失败。
// PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration
private void insertPropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources,
List<PropertySource<?>> composite)
MutablePropertySources incoming = new MutablePropertySources();
List<PropertySource<?>> reversedComposite = new ArrayList<>(composite);
// Reverse the list so that when we call addFirst below we are maintaining the
// same order of PropertySources
// Wherever we call addLast we can use the order in the List since the first item
// will end up before the rest
// 倒序,因为下面addFirst是头插法,保证最后是正序的,
Collections.reverse(reversedComposite);
for (PropertySource<?> p : reversedComposite)
incoming.addFirst(p);
PropertySourceBootstrapProperties remoteProperties = new PropertySourceBootstrapProperties();
Binder.get(environment(incoming)).bind("spring.cloud.config",
Bindable.ofInstance(remoteProperties));
// 默认情况下外部配置加到最前面
if (!remoteProperties.isAllowOverride() || (!remoteProperties.isOverrideNone()
&& remoteProperties.isOverrideSystemProperties()))
for (PropertySource<?> p : reversedComposite)
propertySources.addFirst(p);
return;
consul注入ConsulPropertySourceLocator
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnConsulEnabled
public class ConsulConfigBootstrapConfiguration
public ConsulConfigBootstrapConfiguration()
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties
@Import(ConsulAutoConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = "spring.cloud.consul.config.enabled",
matchIfMissing = true
)
protected static class ConsulPropertySourceConfiguration
@Autowired
private ConsulClient consul;
protected ConsulPropertySourceConfiguration()
@Bean
public ConsulConfigProperties consulConfigProperties()
return new ConsulConfigProperties();
@Bean
public ConsulConfigCacheProperties consulConfigCacheProperties()
return new ConsulConfigCacheProperties();
@Bean
public ConsulConfigCacheClient consulConfigCacheClient(ConsulConfigCacheProperties consulConfigCacheProperties)
return new ConsulConfigCacheClient(consulConfigCacheProperties);
@Bean
public ConsulPropertySourceLocator consulPropertySourceLocator(ConsulConfigProperties consulConfigProperties, ConsulConfigCacheClient consulConfigCacheClient)
return new ConsulPropertySourceLocator(this.consul, consulConfigProperties, consulConfigCacheClient);
nacos注入ConsulPropertySourceLocator
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = "spring.cloud.nacos.config.enabled",
matchIfMissing = true
)
public class NacosConfigBootstrapConfiguration
public NacosConfigBootstrapConfiguration()
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public NacosConfigProperties nacosConfigProperties()
return new NacosConfigProperties();
@Bean
public NacosPropertySourceLocator nacosPropertySourceLocator(NacosConfigProperties nacosConfigProperties)
return new NacosPropertySourceLocator(nacosConfigProperties);
3.2 环境预初始化阶段之LoggingSystemShutdownListener
这个listener是spring-cloud-context引进来的,主要是为了重新确定使用的日志系统。。。
public class LoggingSystemShutdownListener
implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent>, Ordered
/**
* Default order for the listener.
*/
public static final int DEFAULT_ORDER = BootstrapApplicationListener.DEFAULT_ORDER
+ 1;
private int order = DEFAULT_ORDER;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event)
shutdownLogging();
private void shutdownLogging()
// 清理并重新初始化日志系统
LoggingSystem loggingSystem = LoggingSystem
.get(ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
loggingSystem.cleanUp();
loggingSystem.beforeInitialize();
@Override
public int getOrder()
return this.order;
public void setOrder(int order)
this.order = order;
3.3 环境预初始化阶段之ConfigFileApplicationListener
spring boot使用ConfigFileApplicationListener来加载application.yaml,application.yaml位于defaultProperties(bootstrap.yaml)之前。ConfigFileApplicationListener实现了EnvironmentPostProcessor,在postProcessEnvironment方法中对environment进下增强。todo 命令行参数丢了???
public class ConfigFileApplicationListener implements EnvironmentPostProcessor, SmartApplicationListener, Ordered
private static final String DEFAULT_PROPERTIES = "defaultProperties";
// Note the order is from least to most specific (last one wins)
private static final String DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS = "classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/";
private static final String DEFAULT_NAMES = "application";
private static final Set<String> NO_SEARCH_NAMES = Collections.singleton(null);
private static final Bindable<String[]> STRING_ARRAY = Bindable.of(String[].class);
/**
* The "active profiles" property name.
*/
public static final String ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY = "spring.profiles.active";
/**
* The "includes profiles" property name.
*/
public static final String INCLUDE_PROFILES_PROPERTY = "spring.profiles.include";
/**
* The "config name" property name.
*/
public static final String CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY = "spring.config.name";
/**
* The "config location" property name.
*/
public static final String CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY = "spring.config.location";
/**
* The "config additional location" property name.
*/
public static final String CONFIG_ADDITIONAL_LOCATION_PROPERTY = "spring.config.additional-location";
/**
* The default order for the processor.
*/
public static final int DEFAULT_ORDER = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10;
private final DeferredLog logger = new DeferredLog();
private String searchLocations;
private String names;
private int order = DEFAULT_ORDER;
@Override
public boolean supportsEventType(Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventType)
return ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType)
|| ApplicationPreparedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType);
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event)
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent)
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent)
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event)
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
// 这里把自己放到第一位
postProcessors.add(this);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors)
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> loadPostProcessors()
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(EnvironmentPostProcessor.class, getClass().getClassLoader());
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application)
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
3.4 环境预初始化阶段之LoggingApplicationListener
在application.yaml加载之后,这里设置日志级别和日志文件
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event)
if (this.loggingSystem == null)
this.loggingSystem = LoggingSystem.get(event.getSpringApplication().getClassLoader());
this.initialize(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication().getClassLoader());
protected void initialize(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ClassLoader classLoader)
(new LoggingSystemProperties(environment)).apply();
this.logFile = LogFile.get(environment);
if (this.logFile != null)
this.logFile.applyToSystemProperties();
this.initializeEarlyLoggingLevel(environment);
this.initializeSystem(environment, this.loggingSystem, this.logFile);
this.initializeFinalLoggingLevels(environment, this.loggingSystem);
this.registerShutdownHookIfNecessary(environment, this.loggingSystem);
4. 初始化spring boot ApplicationContext,并设置environment,运行ApplicationContextInitializer
在之前会打印spring boot banner欢迎条,比较简单,这里直接跳过。默认情况下,如果路径下有DispatcherServlet,则webApplicationType为SERVLET,使用的ApplicationContext为AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。在埋点(4)中,会把environment设置到ApplicationContext中,然后使用所有添加到SpringApplication的ApplicationContextInitializer,对ApplicationContext进行初始化
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner)
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// 使用所有添加到SpringApplication的ApplicationContextInitializer,对ApplicationContext进行初始化
applyInitializers(context);
// 触发contextPrepared
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo)
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null)
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory)
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
// Load the sources
// 加载所有的配置类,注册为beandefinition,通过main方法传递过来的
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
// 触发contextLoaded
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
本实例中,有如下ApplicationContextInitializer,这里重点讲解两个
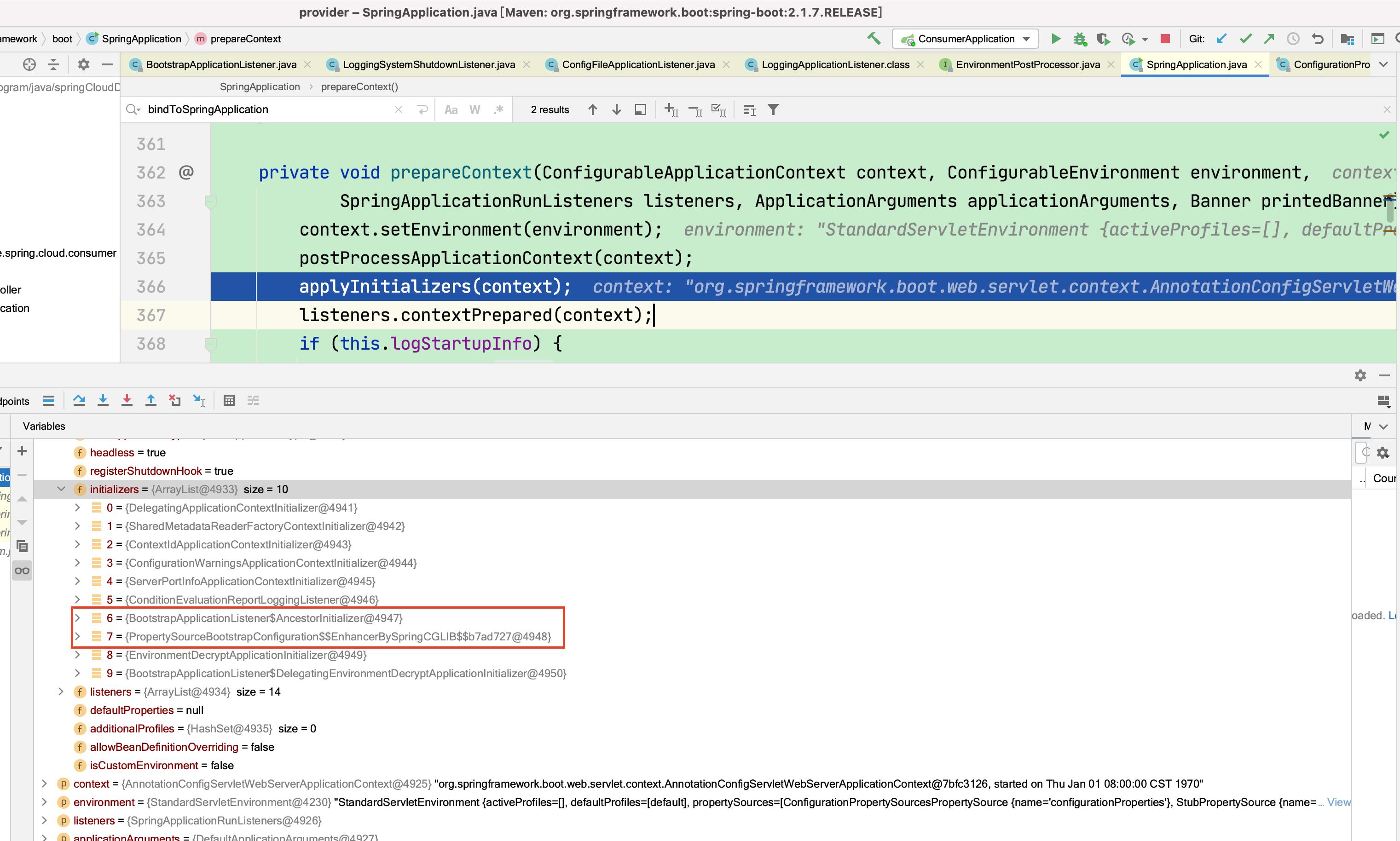
一个是AncestorInitializer,在3.1.2中已经讲到了,主要是将spring cloud defaultProperties调整到spring boot environment最后,同时将defaultProperties包含的bootstrap.yaml添加到defaultProperties前面,也就是倒数第二,将spring cloud context设置为spring boot context的parent。自此,spring boot容器有办法访问到spring cloud基础设施相关bean
一个是PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration,在3.1.4已经讲到了,将spring cloud PropertySourceLocator加载的所有的外部配置,添加到spring boot容器的environment中,默认加在最前面,最后根据远程配置,重新初始化日志系统和日志级别。

4.1 触发contextPrepared
ApplicationContextInitializedEvent
这个事件目前没看到spring cloud context内部有用到
4.2 load bean definition
加载所有的配置类,注册为bean definition,通过main方法传递过来的,则加载main所在配置类。
4.3 触发contextLoaded
ApplicationPreparedEvent,在LoggingApplicationListener会注册日志系统作为单例bean。
private void onApplicationPreparedEvent(ApplicationPreparedEvent event)
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = event.getApplicationContext().getBeanFactory();
if (!beanFactory.containsBean(LOGGING_SYSTEM_BEAN_NAME))
beanFactory.registerSingleton(LOGGING_SYSTEM_BEAN_NAME, this.loggingSystem);
if (this.logFile != null && !beanFactory.containsBean(LOGFILE_BEAN_NAME))
beanFactory.registerSingleton(LOGFILE_BEAN_NAME, this.logFile);
ApplicationPreparedEvent,在ConfigFileApplicationListener会添加PropertySourceOrderingPostProcessor
private void onApplicationPreparedEvent(ApplicationEvent event)
this.logger.switchTo(ConfigFileApplicationListener.class);
addPostProcessors(((ApplicationPreparedEvent) event).getApplicationContext());
/**
* Add appropriate post-processors to post-configure the property-sources.
* @param context the context to configure
*/
protected void addPostProcessors(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new PropertySourceOrderingPostProcessor(context));
5. 刷新ApplicationContext,加载单例bean
这里refresh前,所有的配置文件均已加载完毕,包括bootstrap.yaml/application.yaml,远程配置已经放到第一位,加载完所有单例后,发送started(ApplicationStartedEvent)事件
之后找到当前ApplicationContext的所有的ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner类型的bean,并把main参数传递给它,运行这些runner。
最后发送running(ApplicationReadyEvent)事件,spring boot启动完成。在RefreshEventListener会监听这个事件,设置状态为ready,防止spring boot未启动完全就处理environment refresh。这里可以做很多事情,例如将服务实例注册到consul上。
public class RefreshEventListener implements SmartApplicationListener
private static Log log = LogFactory.getLog(RefreshEventListener.class);
private ContextRefresher refresh;
private AtomicBoolean ready = new AtomicBoolean(false);
public RefreshEventListener(ContextRefresher refresh)
this.refresh = refresh;
@Override
public boolean supportsEventType(Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventType)
return ApplicationReadyEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType)
|| RefreshEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType);
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event)
if (event instanceof ApplicationReadyEvent)
handle((ApplicationReadyEvent) event);
else if (event instanceof RefreshEvent)
handle((RefreshEvent) event);
public void handle(ApplicationReadyEvent event)
// spring boot启动后,才设置ready
this.ready.compareAndSet(false, true);
public void handle(RefreshEvent event)
以上是关于springboot启动过程解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章